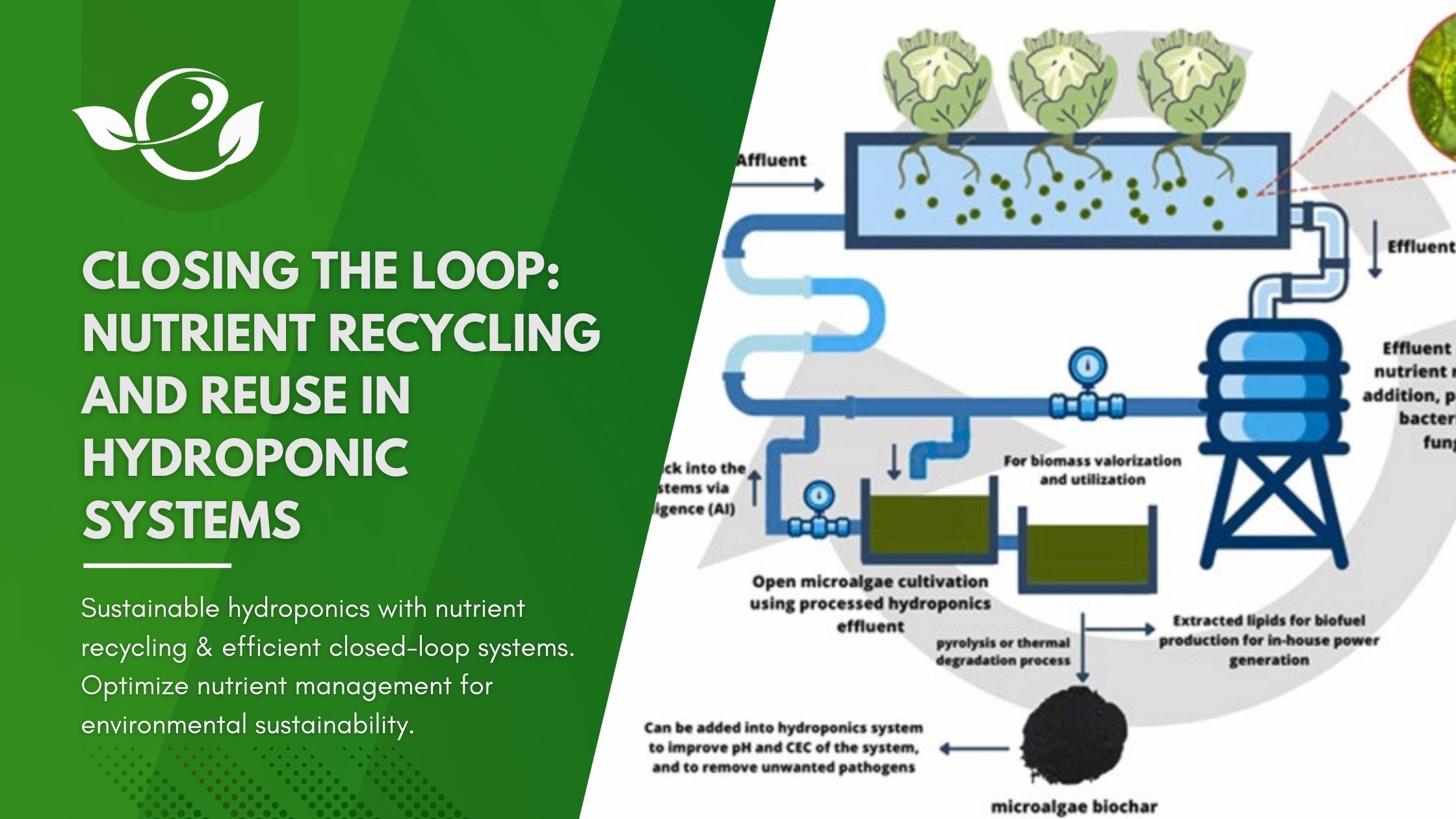
Hydroponic systems have revolutionized agriculture by providing an efficient and sustainable method for plant cultivation without soil. Instead, plants receive their essential nutrients directly from water solutions. However, this innovative approach brings with it the challenge of managing nutrients effectively. This article explores the critical practice of nutrient recycling and reuse in hydroponic systems, delving into its benefits, strategies, and future implications.
Understanding Nutrient Cycling in Hydroponic Systems
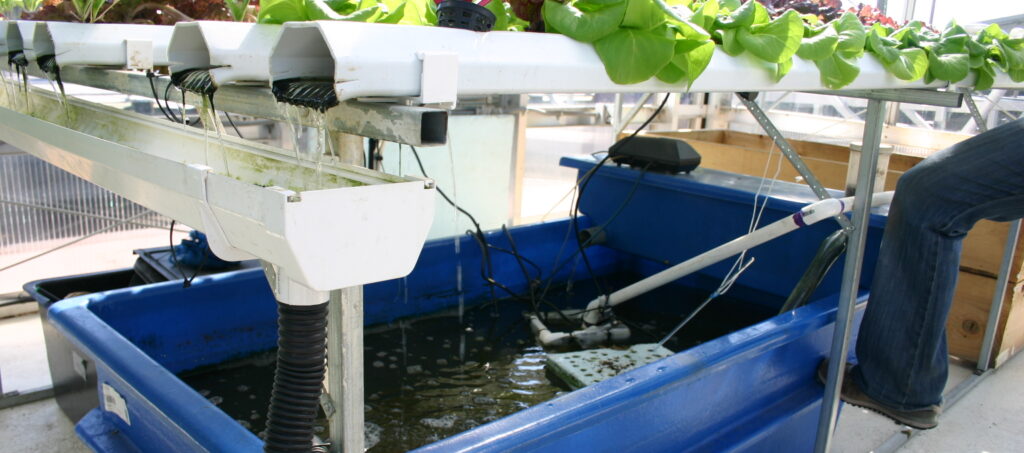

A. Overview of Nutrient Requirements
Plants rely on various essential nutrients to support their growth, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and micronutrients like iron and zinc. In hydroponic systems, these nutrients are dissolved in water, allowing for direct uptake by the plant’s roots.
B. Traditional vs. Hydroponic Systems
Traditional soil-based agriculture relies on the complex interactions within the soil to deliver nutrients to plants. In contrast, hydroponic systems provide precise control over nutrient concentrations, ensuring optimal uptake by plants and minimizing nutrient wastage.
C. Challenges in Nutrient Management
Maintaining optimal nutrient levels in hydroponic systems presents unique challenges. Factors such as pH fluctuations, nutrient imbalances, and the accumulation of salts can affect plant health and productivity. Effective nutrient management strategies are essential to address these challenges.
Supporting Media: Comparison chart illustrating the differences in nutrient uptake mechanisms between traditional and hydroponic systems.
Benefits of Nutrient Recycling and Reuse
A. Environmental Sustainability
Nutrient recycling and reuse minimize the environmental impact of hydroponic farming by reducing nutrient runoff and minimizing the use of finite resources. By closing the nutrient loop, hydroponic systems contribute to a more sustainable agricultural model.
B. Economic Efficiency
The reuse of nutrients in hydroponic systems reduces the need for frequent replenishment of nutrient solutions, leading to cost savings for farmers. Additionally, efficient nutrient management can increase crop yields and profitability.
C. Waste Reduction
Nutrient recycling minimizes waste by utilizing excess nutrients from runoff or unused portions of the nutrient solution. This reduces the overall environmental footprint of hydroponic farming and promotes resource conservation.
Supporting Media: Infographic showcasing the environmental and economic benefits of nutrient recycling and reuse in hydroponic systems.
Strategies for Nutrient Recycling in Hydroponic Systems
A. Collection and Filtration
Implementing systems to collect and filter nutrient solution runoff allows for the reuse of excess nutrients. This prevents nutrient wastage and ensures that nutrients are available for plant uptake.
B. Closed-Loop Systems
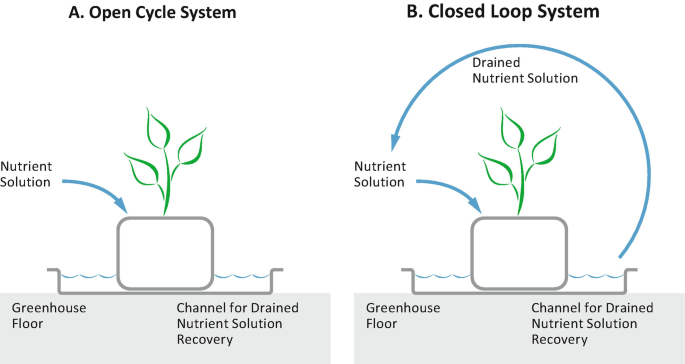
Closed-loop hydroponic systems recycle and reuse nutrient solutions, minimizing the need for external inputs. By continuously circulating and replenishing the nutrient solution, these systems optimize nutrient availability for plants.
C. Organic Matter Integration
Integrating organic matter, such as compost or organic fertilizers, into hydroponic systems promotes nutrient cycling and enhances soil health. Microbial processes within the organic matter help break down nutrients and make them available to plants.
Supporting Media: Diagram illustrating the components and processes of a closed-loop hydroponic system, including organic matter integration.
Techniques for Nutrient Reuse in Hydroponic Systems

A. Nutrient Solution Treatment
Treating recycled nutrient solutions with sterilization methods, such as UV sterilization or ozonation, ensures the removal of pathogens and contaminants. This safeguards plant health and prevents the spread of diseases.
B. pH and EC Adjustment
Monitoring and adjusting the pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of nutrient solutions optimize nutrient uptake by plants. Maintaining the correct pH and EC levels ensures that nutrients are available in the appropriate forms and concentrations for plant absorption.
C. Nutrient Monitoring and Balancing
Regular monitoring of nutrient levels in hydroponic systems allows for timely adjustments to maintain optimal nutrient concentrations. This ensures that plants receive the right balance of nutrients for healthy growth and development.
Supporting Media: Video tutorial demonstrating nutrient solution treatment and pH adjustment techniques in hydroponic systems.
Case Studies and Examples
A. Successful Implementations
Explore case studies of hydroponic farms that have successfully implemented nutrient recycling and reuse strategies. These examples showcase the practical application of nutrient management techniques and their impact on crop production and sustainability.
B. Challenges and Solutions
Examine common challenges faced in implementing nutrient recycling strategies and the innovative solutions developed to overcome them. Understanding these challenges and solutions can provide valuable insights for farmers looking to optimize nutrient management in their hydroponic systems.
C. Lessons Learned
Reflect on lessons learned from past experiences with nutrient recycling and reuse in hydroponic farming. By sharing these insights, we can improve our understanding of effective nutrient management practices and drive further innovation in hydroponic agriculture.
Supporting Media: Interactive timeline featuring case studies, challenges, and solutions in nutrient recycling and reuse in hydroponic farming.
Future Directions and Innovations
A. Emerging Technologies
Explore emerging technologies and innovations in nutrient recycling and reuse for hydroponic systems. These advancements hold the potential to further improve nutrient management efficiency and sustainability in hydroponic farming.
B. Advancements in Closed-Loop Systems
Investigate potential advancements in closed-loop hydroponic systems, such as automated nutrient monitoring and dosing systems. These advancements aim to streamline nutrient management processes and optimize plant growth.
C. Research Areas
Identify key research areas for further exploration in hydroponic nutrient recycling and reuse. By addressing gaps in knowledge and understanding, researchers can contribute to the development of more sustainable and efficient hydroponic farming practices.
Supporting Media: Infographic highlighting upcoming technologies and research areas in hydroponic nutrient recycling and reuse.
Practical Tips for Implementation
A. Best Practices
Provide practical tips and best practices for implementing nutrient recycling and reuse strategies in hydroponic systems. These guidelines can help farmers optimize nutrient management and maximize the benefits of nutrient recycling.
B. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Offer guidance on maintenance and troubleshooting of nutrient recycling systems in hydroponic setups. Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of nutrient-recycling strategies.
C. Additional Resources
Direct readers to additional resources, such as manuals, forums, and expert consultations, for further support and guidance on nutrient recycling and reuse in hydroponic farming.
Supporting Media: Printable checklist summarizing best practices for nutrient recycling implementation in hydroponic systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nutrient recycling and reuse play a vital role in sustainable hydroponic farming. By adopting effective nutrient management strategies and embracing innovative technologies, we can minimize waste, conserve resources, and maximize crop productivity. Let us work together to close the loop in hydroponic systems and cultivate a greener, more sustainable future for agriculture.
FAQ Section
1: What is nutrient recycling in hydroponic systems?
Nutrient recycling involves collecting and reusing excess nutrient solutions in hydroponic systems to minimize waste and optimize nutrient efficiency.
2: Why is nutrient recycling important in hydroponics?
Nutrient recycling promotes environmental sustainability by reducing nutrient runoff and conserving resources. It also enhances economic efficiency by minimizing the need for frequent nutrient replenishment.
3: How can I collect and filter nutrient solution runoff?
Implementing systems such as sediment filters or settling tanks can help collect and filter nutrient solution runoff for reuse in hydroponic systems.
4: What are closed-loop hydroponic systems?
Closed-loop hydroponic systems continuously recirculate and reuse nutrient solutions, minimizing the need for external inputs and optimizing nutrient availability for plants.
5: How do I adjust pH and EC levels in hydroponic systems?
Regular monitoring and adjustment of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels using pH meters and EC meters ensure optimal nutrient uptake by plants.
6: What are some common challenges in nutrient recycling?
Common challenges include maintaining nutrient balance, preventing nutrient imbalances, and addressing pH fluctuations in hydroponic systems.
7: Can I use organic matter in hydroponic systems?
Yes, incorporating organic matter such as compost or organic fertilizers can promote nutrient cycling and microbial activity in hydroponic systems, enhancing plant health.
8: Are there any resources available for further guidance on nutrient recycling?
Yes, there are various manuals, forums, and expert consultations available to provide additional support and guidance on implementing nutrient recycling and reuse strategies in hydroponic farming.