Table of Contents
In today’s world, where sustainability and efficient resource utilization are paramount, the agricultural industry is undergoing a transformation. Traditional farming practices, while vital for centuries, are now facing challenges due to land scarcity, water limitations, and environmental concerns. As a result, alternative farming methods like hydroponic farming are gaining popularity. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the comparison between hydroponic farming and traditional farming, with a focus on sustainability. By exploring the advantages and limitations of both approaches, we aim to provide insights into how hydroponics can revolutionize agriculture for a greener future.
What is Hydroponic Farming?
Hydroponics is a soil-less farming technique that allows plants to grow in nutrient-rich water solutions, with their roots supported by an inert medium or suspended in the air. This method provides controlled environmental conditions to optimize plant growth. Various types of hydroponic systems exist, including nutrient film technique, deep water culture, and aeroponics.
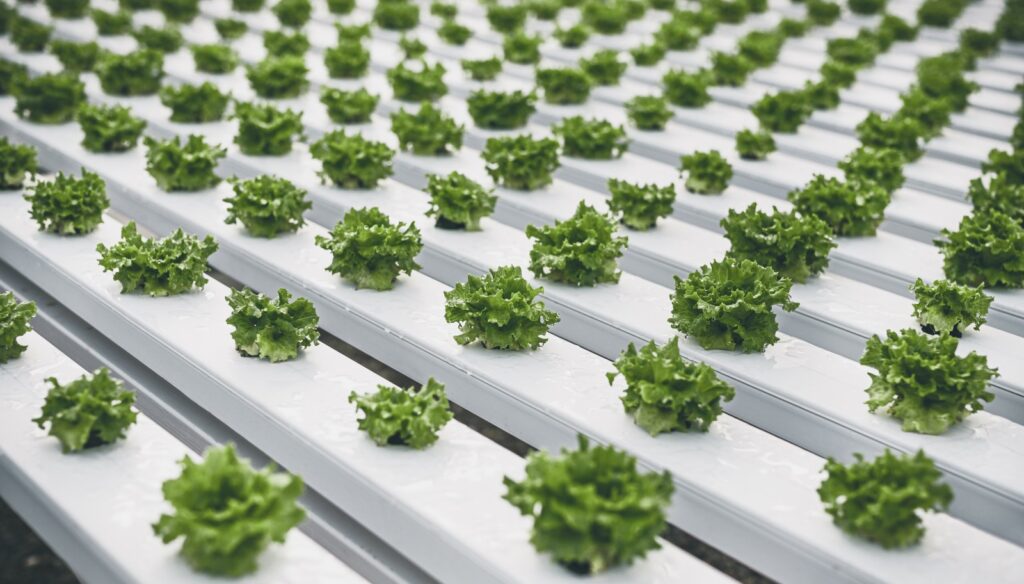
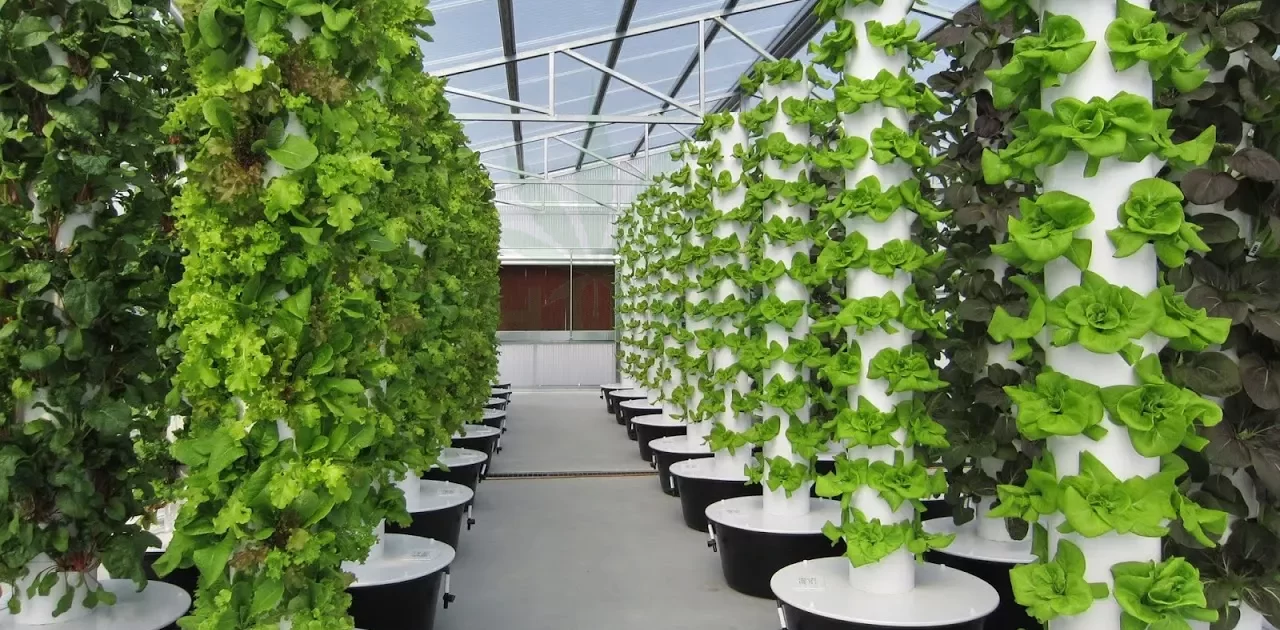
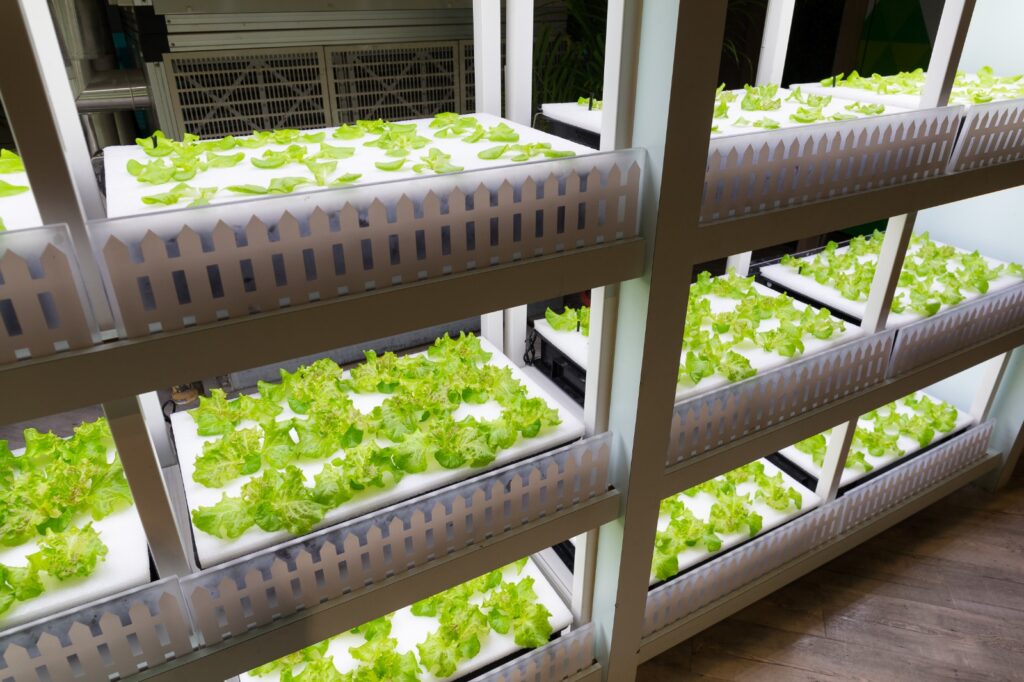



For example, the nutrient film technique involves a continuous flow of a thin film of nutrient solution that circulates around the plant roots, providing essential nutrients. In deep water culture, the plant roots are submerged in a nutrient solution, while aeroponics relies on misting the roots with a nutrient solution.
The controlled environment in hydroponics enables year-round cultivation, independent of climate conditions and soil quality, making it suitable for urban areas, deserts, or regions with limited arable land.
While traditional farming has been successful in increasing crop yields, it has some drawbacks. For one, the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can have negative effects on the environment. Chemical fertilizers can pollute water sources, leading to the growth of harmful algae and fish kills. Pesticides can also be harmful to wildlife and beneficial insects, disrupting the natural balance of the ecosystem.
Furthermore, the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can also affect human health. Pesticides can be toxic and can cause a range of health problems, including cancer, birth defects, and neurological disorders.
Traditional Farming: Pros and Cons
Traditional farming, which relies on soil cultivation and crop rotation, has been the backbone of agriculture for centuries. While it has several advantages, it also faces significant challenges in terms of sustainability.
Advantages of Traditional Farming
One of the notable advantages of traditional farming is its established infrastructure, allowing farmers to leverage existing knowledge, techniques, and equipment. Additionally, traditional farming often has lower initial setup costs compared to hydroponics, making it more accessible for small-scale farmers.
Certain crops also fare better in traditional farming systems, especially those that require deep soil for extensive root growth or have a symbiotic relationship with soil microorganisms. These crops can take advantage of the natural ecosystem services provided by the soil.
Limitations of Traditional Farming
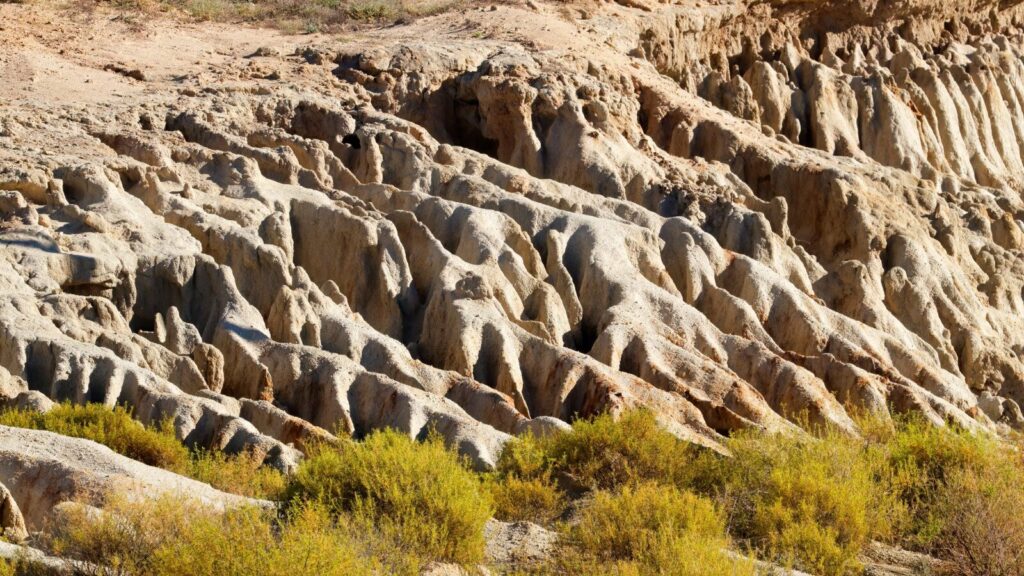

However, traditional farming practices face significant limitations. One key challenge is the scarcity of arable land, as urbanization and land degradation reduce the available space for cultivation. Soil erosion, depletion of nutrients, and the loss of topsoil further threaten the productivity of traditional farming systems.
Moreover, traditional farming often relies on chemical pesticides and fertilizers to control pests and enhance crop yields. However, the excessive use of these inputs can lead to water pollution, soil degradation, and adverse effects on human health and biodiversity.

Hydroponics Farming: Pros
Hydroponics offers several sustainable advantages over traditional farming methods, addressing the limitations associated with land, water, and environmental impact. Let’s explore these advantages in detail.
Resource Efficiency
Water Conservation
Water scarcity is a global concern, particularly in regions prone to droughts. Hydroponics presents an efficient solution by using significantly less water than traditional farming methods. Research has shown that hydroponics can reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to soil-based cultivation.
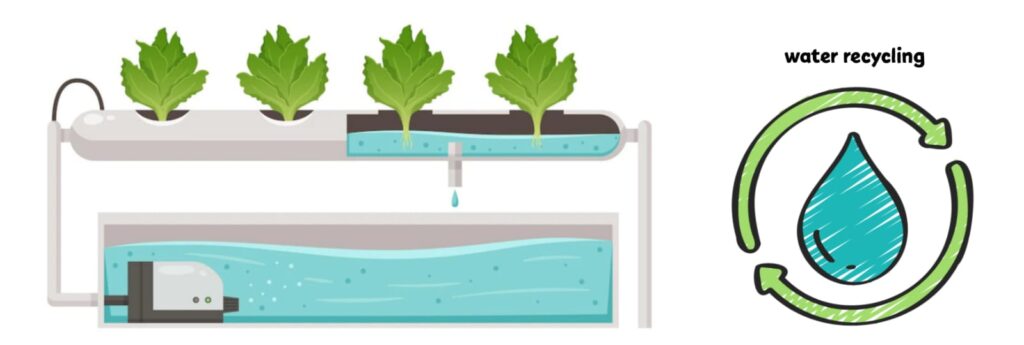
In hydroponic systems, water is recirculated, reducing wastage and allowing for precise control of water delivery to plants. Moreover, the closed-loop system ensures that nutrients are not lost through leaching, leading to further water conservation.
Land Utilization
As urbanization continues to expand, arable land becomes scarce. Hydroponics offers a solution by maximizing land utilization through vertical farming. Vertical hydroponic systems allow crops to be stacked, utilizing vertical space in urban environments or regions with limited land availability.
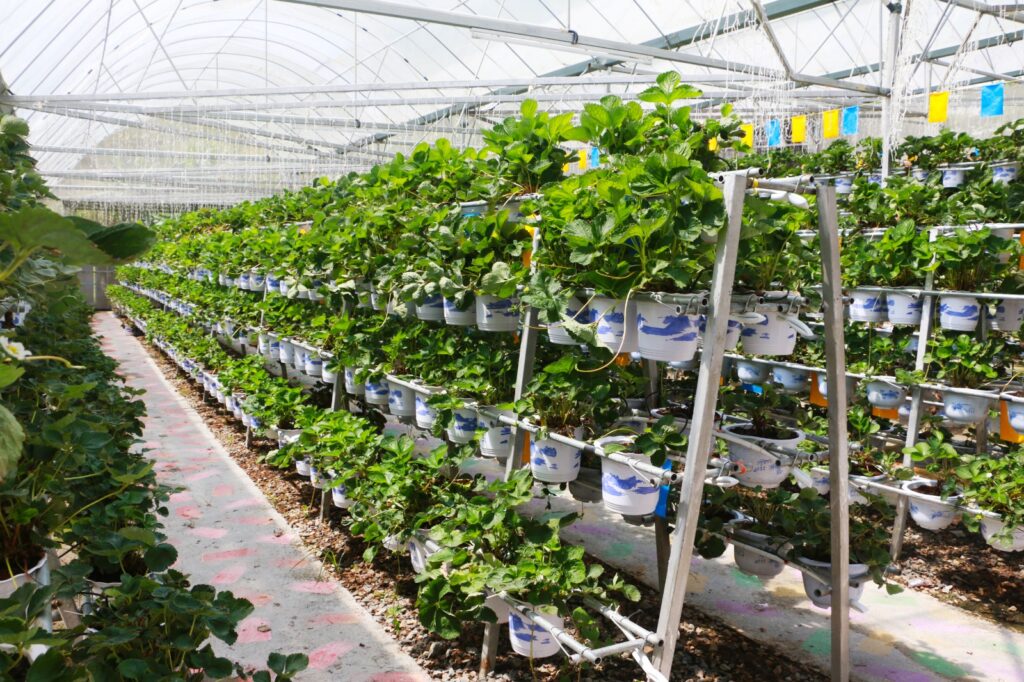
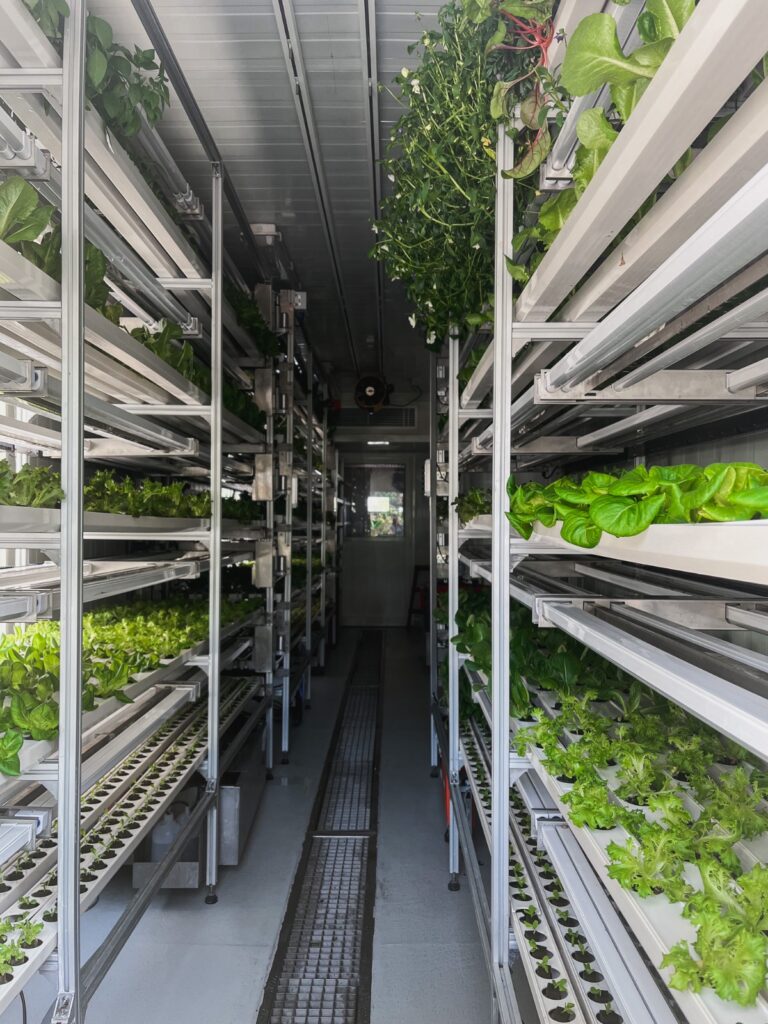
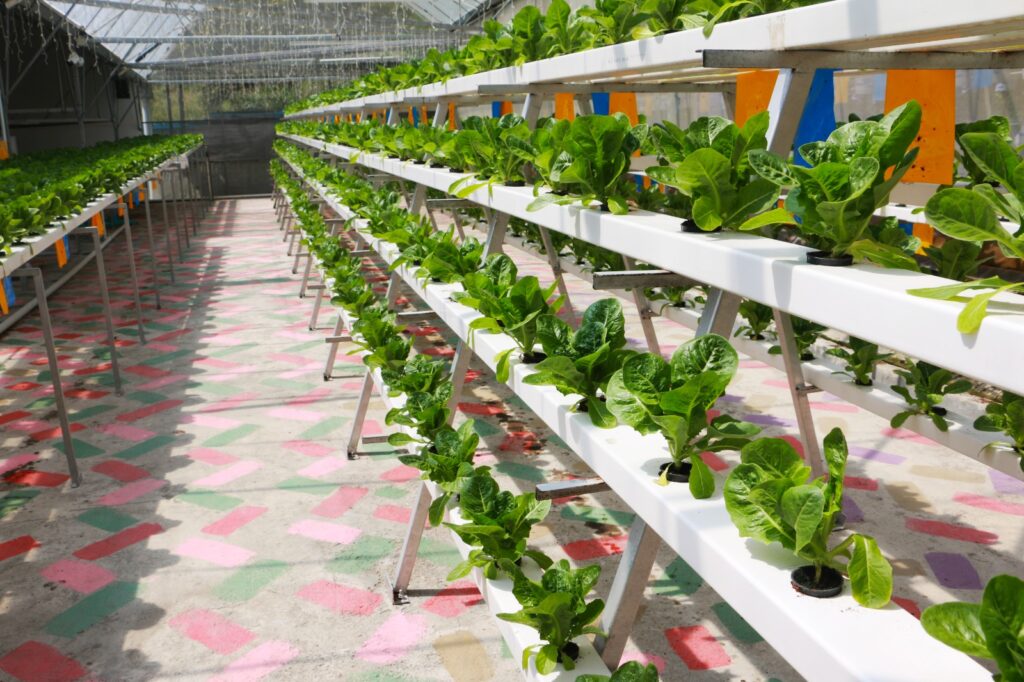



Vertical farming not only increases crop productivity per unit area but also reduces the need for land conversion, conserving natural habitats and promoting urban agriculture.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Pesticide and Fertilizer Usage
One of the significant environmental benefits of hydroponics is the reduction or elimination of chemical pesticides and fertilizers. Integrated pest management (IPM) techniques, such as biological control methods, are often employed in hydroponic systems to manage pests without relying on harmful chemicals.

By minimizing pesticide usage, hydroponics reduces environmental pollution and minimizes health risks for farmers and consumers. Furthermore, the absence of synthetic fertilizers in hydroponic systems prevents nutrient runoff and associated water pollution.
Soil Conservation
Soil erosion and degradation pose significant threats to traditional farming practices. However, hydroponics eliminates these concerns altogether, as plants are not grown in soil. By removing the dependence on soil, hydroponic systems prevent soil erosion, maintain soil structure, and minimize nutrient depletion.

Additionally, hydroponics can be integrated with sustainable soil management practices in traditional farming, such as using hydroponic systems to propagate seedlings before transplanting them into soil-based systems. This approach reduces the reliance on chemical inputs and improves the overall sustainability of traditional farming.
Energy Efficiency
Hydroponic systems require energy for lighting, climate control, and water circulation. However, innovative technologies and practices can optimize energy efficiency in hydroponics. LED lighting, for instance, offers energy-efficient alternatives to traditional lighting sources, reducing electricity consumption.

Compared to traditional farming, where machinery, irrigation pumps, and transportation contribute to significant energy consumption, hydroponics can potentially be more energy-efficient overall.
Challenges and Considerations
While hydroponics offers numerous sustainability advantages, it also presents certain challenges and considerations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
Establishing a hydroponic farm requires an initial investment in infrastructure, equipment, and nutrient solutions. The cost of setting up a hydroponic system can be higher than traditional farming methods. However, it is important to consider the long-term benefits and potential returns on investment that hydroponics offers.
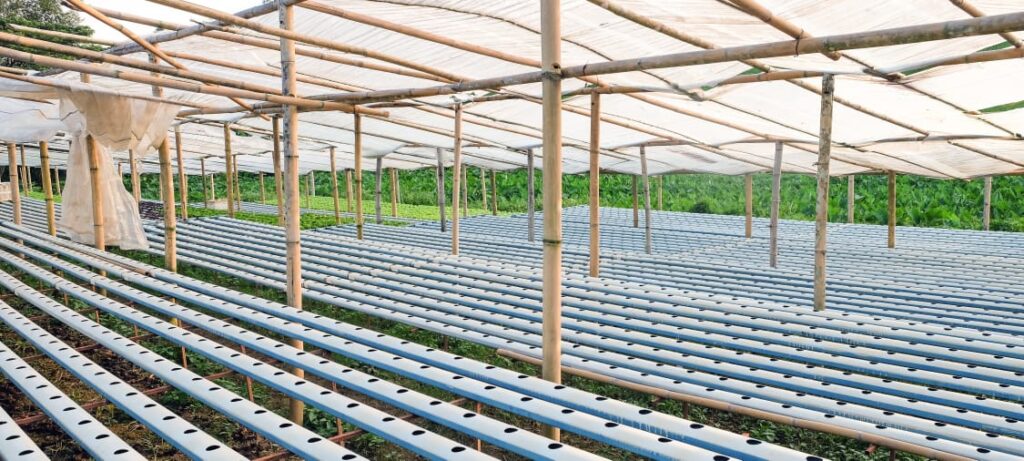

Technical Expertise and Training
Operating a successful hydroponic system requires specialized knowledge and skills. Farmers need to understand the principles of hydroponics, nutrient management, pH balancing, and pest control strategies specific to hydroponic systems. Training programs and educational resources are available to support farmers in acquiring the necessary expertise.
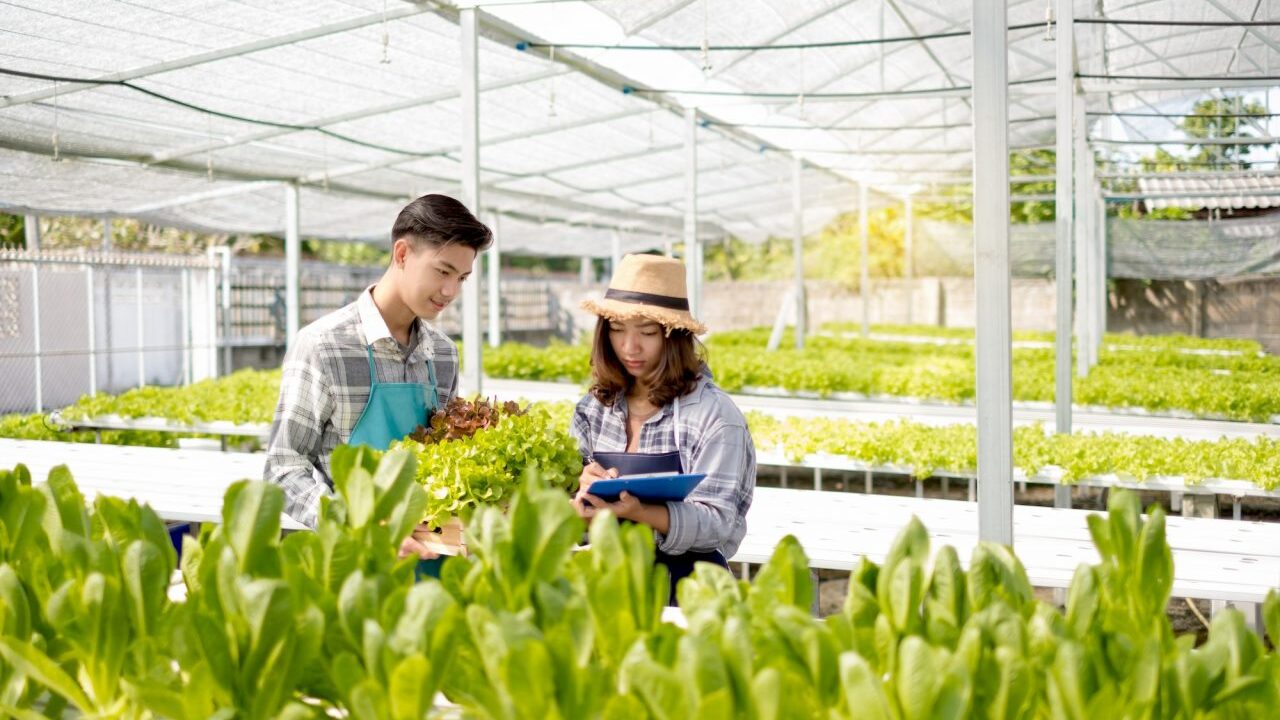

Crop Selection and Adaptability
While hydroponics is suitable for growing a wide range of crops, certain crops may have specific requirements that make them less suitable for hydroponic cultivation. For example, crops with extensive root systems may require modifications to hydroponic systems or alternative cultivation methods.
It is crucial to consider crop selection and adaptability when planning a hydroponic farm. Conducting thorough research and seeking expert advice can help farmers make informed decisions about which crops are best suited for hydroponics.
Conclusion
Hydroponics represents a sustainable and efficient approach to agriculture, offering numerous advantages over traditional farming methods. Through its resource efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and energy efficiency, hydroponics holds great potential to address the challenges faced by the agricultural industry.
By conserving water, minimizing land utilization, reducing chemical inputs, and preventing soil degradation, hydroponics can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
As farmers and consumers alike become increasingly conscious of the need for sustainable practices, hydroponics offers an exciting pathway to meet the growing demand for food while minimizing environmental harm. Embracing hydroponics can empower us to build a resilient and sustainable food system for generations to come.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is hydroponic farming suitable for all types of crops?
While hydroponics is suitable for growing a wide range of crops, certain crops may have specific requirements that make them less suitable for hydroponic cultivation. Crops with extensive root systems or those that have a symbiotic relationship with soil microorganisms may require modifications to hydroponic systems or alternative cultivation methods. It is important to consider crop selection and adaptability when planning a hydroponic farm. Conducting thorough research and seeking expert advice can help farmers make informed decisions about which crops are best suited for hydroponics.
2. Does hydroponic farming require a lot of water?
No, hydroponics actually reduces water usage compared to traditional farming methods. Research has shown that hydroponics can reduce water usage by up to 90%. This is achieved through efficient water management in hydroponic systems, such as recirculating water and precise control of water delivery to plants. The closed-loop system also prevents nutrient leaching, further conserving water.
3. How does hydroponics reduce the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers?
Hydroponics relies on integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to manage pests without relying on harmful chemicals. Biological control methods, such as the introduction of beneficial insects or the use of natural predators, are commonly employed in hydroponic systems. By minimizing pesticide usage, hydroponics reduces environmental pollution and minimizes health risks for farmers and consumers. Additionally, the absence of soil in hydroponic systems eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, preventing nutrient runoff and associated water pollution.
4. Does hydroponic farming require a lot of energy?
Hydroponic systems do require energy for lighting, climate control, and water circulation. However, innovative technologies and practices can optimize energy efficiency in hydroponics. For instance, LED lighting offers energy-efficient alternatives to traditional lighting sources, reducing electricity consumption. Compared to traditional farming, where machinery, irrigation pumps, and transportation contribute to significant energy consumption, hydroponics can potentially be more energy-efficient overall.
5. Is hydroponic farming expensive to set up and maintain?
Establishing a hydroponic farm does require an initial investment in infrastructure, equipment, and nutrient solutions. The cost of setting up a hydroponic system can be higher than traditional farming methods. However, it is important to consider the long-term benefits and potential returns on investment that hydroponics offers. Moreover, as the popularity of hydroponics grows, the availability of affordable equipment and resources is increasing, making it more accessible to farmers of different scales.
6. Are there any training programs available for hydroponic farming?
Yes, we offer training programs and educational resources to support farmers in acquiring the necessary knowledge and skills for successful hydroponic farming. This program covers various aspects of hydroponics, including system setup, nutrient management, pH balancing, and pest control strategies specific to hydroponic systems. Farmers can participate in workshops, attend training sessions, or access online courses to enhance their understanding of hydroponics and improve their farming practices. Click here to join The Best Hydroponic Training in India.
7. Can hydroponics be combined with traditional farming practices?
Yes, hydroponics can be integrated with traditional farming practices to maximize sustainability. For example, hydroponic systems can be used to propagate seedlings before transplanting them into soil-based systems. This approach reduces the reliance on chemical inputs, optimizes resource usage, and improves the overall sustainability of traditional farming. Additionally, hydroponics can be utilized for niche crops or in urban environments where space is limited, complementing traditional farming methods.
8. How does hydroponic farming contribute to a greener future?
Hydroponic farming offers numerous sustainability advantages that contribute to a greener future. By conserving water, minimizing land utilization, reducing chemical inputs, and preventing soil degradation, hydroponics helps to address the challenges faced by the agricultural industry. Additionally, hydroponics reduces environmental pollution by minimizing pesticide usage and preventing nutrient runoff. With its resource efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and energy efficiency, hydroponics offers a pathway to meet the growing demand for food while minimizing harm to the environment.








