Table of Contents
Welcome to the fascinating world of hydroponics! In this blog post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of pH and EC management in hydroponic systems. Whether you’re a seasoned hydroponic enthusiast or just starting out, understanding how pH and EC affect your plants’ growth and nutrient uptake is essential for achieving exceptional results.
So, what exactly is hydroponics? It’s a revolutionary cultivation method that doesn’t rely on soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, providing them with precisely what they need to thrive. This controlled environment allows for greater control over plant health, growth, and productivity.
Now, you might be wondering, why is pH and EC management so important in hydroponics. Well, pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of the nutrient solution, while EC (electrical conductivity) measures the concentration of nutrients. Proper management of pH and EC ensures that plants can access the nutrients they need at the right levels, promoting robust growth and optimum yields.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the world of pH and EC in hydroponics. We’ll explore the significance of pH and its scale, the optimal pH range for hydroponic systems, factors affecting pH levels, testing methods and tools, as well as common pH problems and their solutions. We’ll also explore the world of EC, understanding what it measures, the optimal range, factors influencing EC levels, measurement techniques and devices, common issues, and effective strategies for adjustment.

To help you navigate the complex terrain of pH and EC management, we’ll provide you with best practices, tips for maintaining balance, and troubleshooting techniques for resolving common issues. Additionally, we’ll touch on the interrelationship between pH and EC, the importance of regular monitoring, and the tools and devices available for integrated monitoring and control.
Understanding pH in Hydroponics
What is pH?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It represents the concentration of hydrogen ions present in the solution and is expressed on a logarithmic scale ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while values below 7 indicate acidity and values above 7 indicate alkalinity.
Significance of pH in hydroponics
In hydroponics, pH plays a vital role in nutrient availability and uptake by plants. Different nutrients are optimally absorbed at specific pH levels, and any deviation from the ideal range can hinder nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies or toxicities. Therefore, maintaining the correct pH is crucial for ensuring plants receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth.
pH scale and its significance
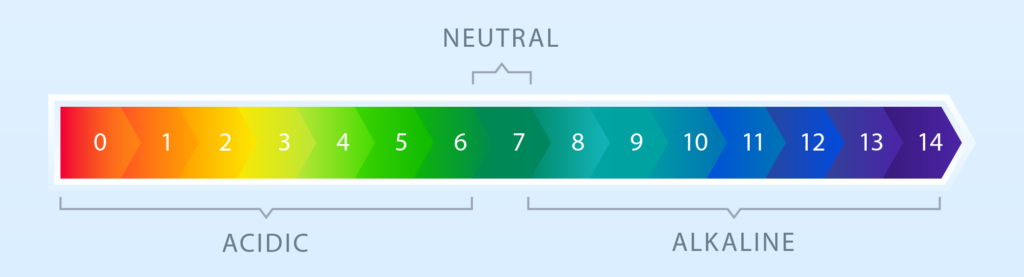
The pH scale is a visual representation of the acidity and alkalinity spectrum. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 as the neutral point. Values below 7 indicate increasing acidity, while values above 7 indicate increasing alkalinity. Understanding the pH scale helps hydroponic growers interpret pH readings and make appropriate adjustments to create an optimal growing environment for plants.
Optimal pH range for hydroponic systems
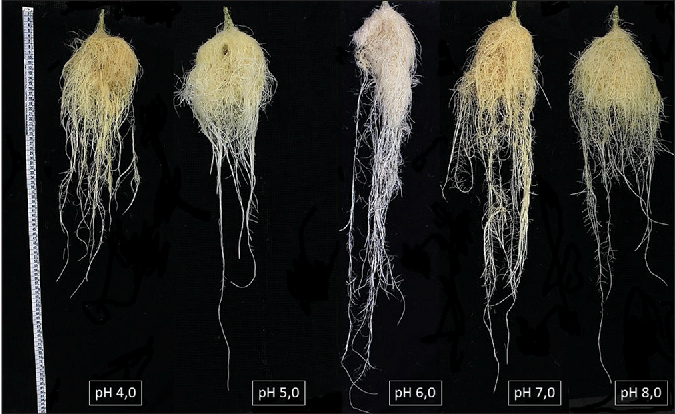
Each plant species has its preferred pH range for optimal growth. However, most hydroponic crops thrive in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. This range ensures optimal nutrient availability and uptake, promoting vigorous root development and overall plant health.
Factors affecting pH in hydroponics
Several factors influence the pH of the nutrient solution in hydroponics:
- Nutrient solution composition: The type and concentration of nutrients in the solution can impact pH. Different nutrients have varying effects on pH, either increasing or decreasing acidity. Balancing the nutrient composition is crucial for maintaining pH stability.
- Water quality: The pH of the water used in hydroponics affects the overall pH of the nutrient solution. Water sources with high mineral content or pH imbalances may require adjustment to achieve the desired pH range.
- Plant uptake and nutrient availability: As plants absorb nutrients, the pH of the nutrient solution can change. The release of hydrogen ions during nutrient uptake can influence pH, necessitating regular monitoring and adjustment.
pH testing methods and tools


Accurate pH measurement is essential for effective pH management. Hydroponic growers have various testing methods and tools at their disposal:
- pH testing strips: These strips contain indicator dyes that change color based on the pH of the solution. By comparing the strip’s color to a provided color chart, growers can estimate the pH value.
- pH meters: Digital pH meters provide precise pH measurements by measuring the electrical potential difference between the pH electrode and the solution. They offer real-time pH readings and are widely used in professional hydroponic setups.
Importance of pH monitoring and adjustment
Regular monitoring of pH levels is vital for maintaining nutrient availability and preventing nutrient imbalances. By frequently assessing pH, growers can identify deviations and take corrective actions promptly. Adjusting pH ensures optimal nutrient uptake, reduces the risk of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, and promotes healthy plant growth.
Common pH problems and their solutions
Acidic or alkaline nutrient solutions
- Problem: An acidic or alkaline nutrient solution can disrupt nutrient availability and uptake, leading to nutrient imbalances and plant stress.
- Solution: Adjust the pH of the nutrient solution using pH adjusters. Acids like phosphoric acid can lower pH, while bases like potassium hydroxide can raise pH. Gradual adjustments should be made to avoid sudden shifts that may shock plants.
pH fluctuations
- Problem: pH fluctuations can occur due to nutrient uptake, water quality changes, or insufficient pH monitoring and adjustment.
- Solution: Maintain regular pH monitoring and make adjustments as necessary. Implement automated pH dosing systems or consider using natural pH buffering substances like dolomite lime to stabilize pH and minimize fluctuations.
Alkalinity and acidity of water sources
- Problem: Water sources with high alkalinity or acidity can affect the overall pH of the nutrient solution.
- Solution: Treat water sources with high alkalinity by using acidifying agents or install water filtration systems to adjust the pH before adding nutrients. For water sources with low acidity, consider using alkaline buffers to raise pH gradually.
Techniques for adjusting pH in hydroponics
Using pH adjusters (acids and bases)

pH adjusters are chemical substances used to modify the pH of the nutrient solution. They include acids and bases that can lower or raise pH, respectively. Care should be taken when handling and measuring pH adjusters, as they are potent and must be added in small increments for gradual adjustments.
Natural methods for pH adjustment

Natural pH buffering substances can help stabilize pH and reduce fluctuations. Dolomite lime, for instance, can gradually increase pH and provide essential nutrients like calcium and magnesium. Organic matter, such as compost or worm castings, can also contribute to pH stability.
Automated pH controllers and dosing systems
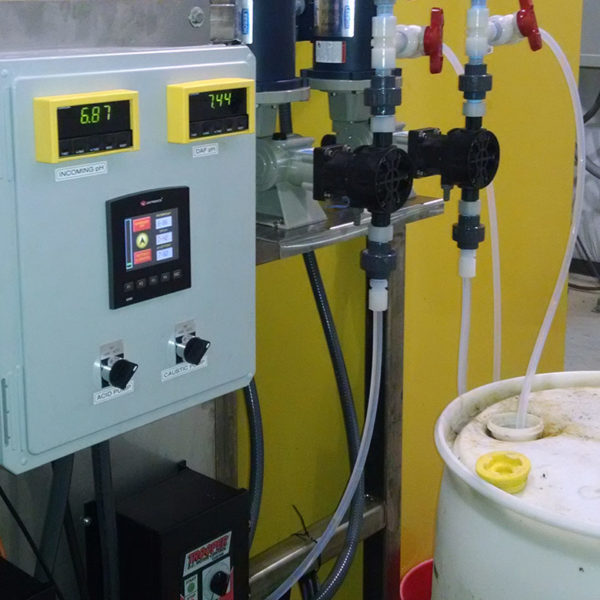

Automated pH controllers and dosing systems offer precision and convenience in maintaining pH levels. These systems monitor pH continuously and automatically adjust it by dosing the nutrient solution with the necessary pH adjuster. They are ideal for larger hydroponic systems or commercial operations.
Managing EC (Electrical Conductivity) in Hydroponics
Understanding EC in hydroponics
Electrical Conductivity (EC) is a measure of the solution’s ability to conduct electricity, which relates to its total dissolved salt concentration. EC is widely used in hydroponics to assess the nutrient strength or concentration of the nutrient solution.
What does EC measure?
EC measures the concentration of dissolved salts, including essential nutrients, in the nutrient solution. It provides an indication of the solution’s nutrient content and helps determine the appropriate nutrient concentration for plant growth.
Optimal EC range for hydroponic systems
Each plant species has its preferred EC range, which corresponds to the nutrient concentration required for optimal growth. The optimal EC range varies depending on the crop, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Growers should refer to crop-specific guidelines or consult experts to determine the ideal EC range.
Factors influencing EC in hydroponics
Several factors impact the EC of the nutrient solution:
- Nutrient concentration: The concentration of nutrients in the solution directly affects EC. Adjusting the nutrient concentration allows growers to modify EC levels based on plant requirements.
- Water quality: The mineral content of the water source affects the initial EC of the nutrient solution. Water with high mineral content may contribute to a higher baseline EC, requiring adjustments to achieve the desired range.
- Plant growth stage: Different growth stages have varying nutrient demands, leading to changes in EC requirements. Adjusting EC throughout the plant’s lifecycle ensures optimal nutrient supply for each stage.
EC measurement techniques and devices
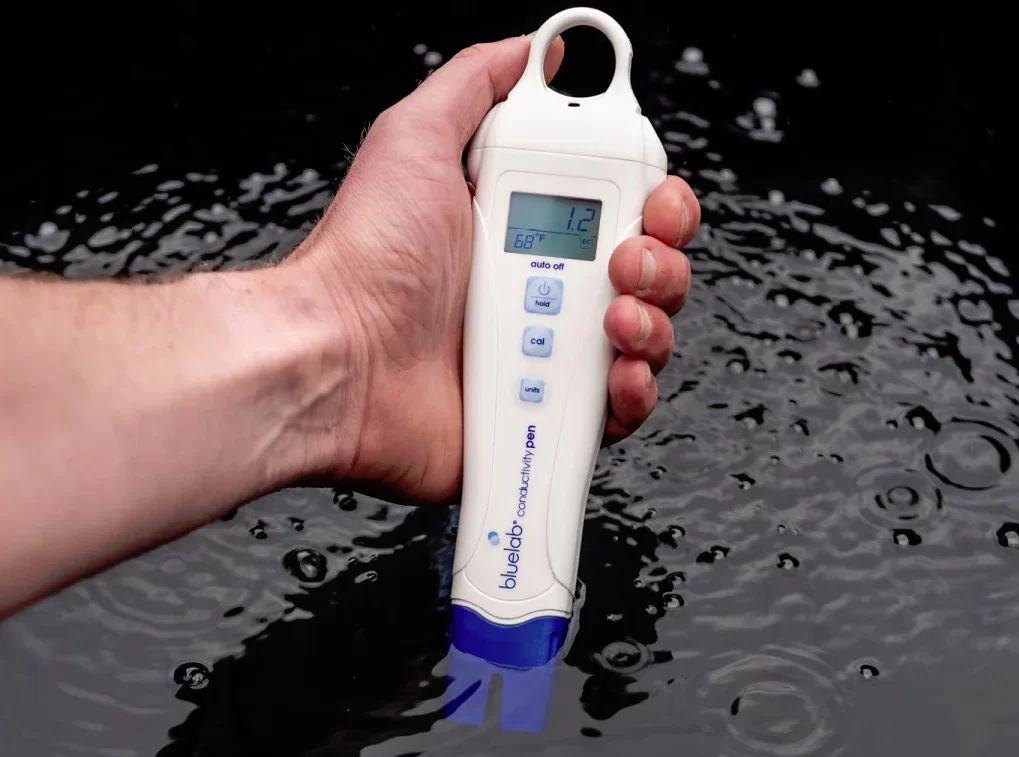

EC can be measured using various techniques and devices:
- EC meters: These handheld devices measure the electrical conductivity of the solution. They provide readings in units of millisiemens per centimeter (mS/cm) or micro siemens per centimeter (μS/cm). EC meters are commonly used in hydroponic systems for quick and accurate measurements.
- EC conductivity probes: These probes are typically connected to monitoring systems or controllers. They continuously measure the solution’s conductivity and provide real-time data for monitoring and control purposes.
Importance of EC monitoring and adjustment
Monitoring EC is essential for ensuring nutrient concentrations align with plant requirements. Maintaining the appropriate EC range promotes balanced nutrient uptake, prevents nutrient imbalances, and avoids the risk of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. Regular monitoring allows growers to adjust nutrient strength accordingly.
Common EC problems and their solutions
High or low nutrient concentrations
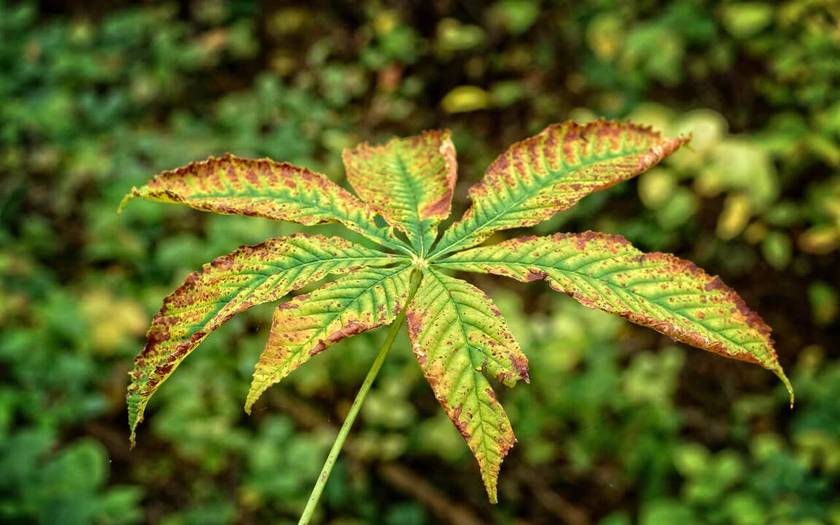
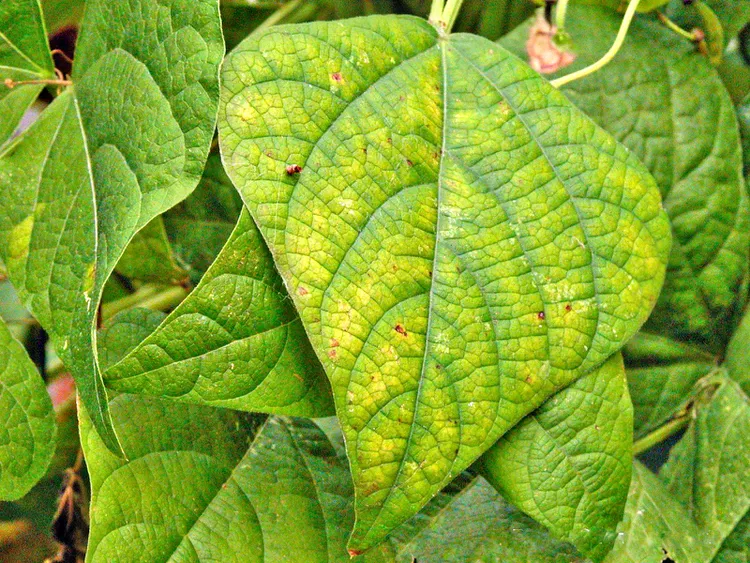


- Problem: High or low nutrient concentrations can negatively impact plant health. High concentrations may lead to nutrient burn and toxicity, while low concentrations can cause nutrient deficiencies and stunted growth.
- Solution: Adjust the nutrient concentration by diluting or increasing the nutrient solution strength. Gradual adjustments should be made, closely monitoring plant response to avoid sudden stress.
EC fluctuations
- Problem: Fluctuating EC levels can occur due to inconsistent nutrient mixing or imprecise dosing methods.
- Solution: Ensure thorough mixing of nutrient solutions to achieve uniform EC distribution. Use reliable dosing systems, such as peristaltic pumps, to maintain consistent nutrient delivery and minimize fluctuations.
Salt buildup in the growing medium
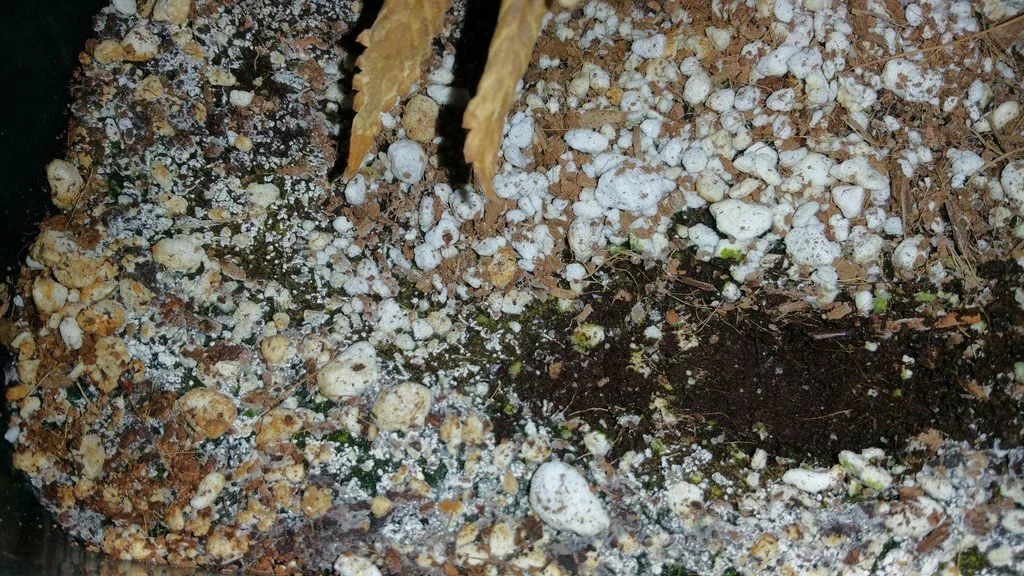

- Problem:
- Solution: Implement regular flushing and leaching practices to remove excess salts from the growing medium. Flushing with clean, pH-adjusted water helps restore the desired EC balance and prevent salt buildup.
Techniques for adjusting EC in hydroponics
Dilution and nutrient solution mixing
Diluting the nutrient solution with water is a simple method to lower EC. It allows growers to decrease the overall nutrient concentration and achieve the desired EC level.
Nutrient strength adjustment
Adjusting nutrient strength involves modifying the nutrient concentration to reach the target EC. This can be done by adding concentrated nutrients or adjusting the dosing amounts of individual nutrient components.
Flushing and leaching methods
Flushing and leaching are techniques used to reduce excessive salts in the growing medium and bring EC levels back to normal. Flushing involves saturating the growing medium with water to remove accumulated salts, while leaching involves continuous watering until the runoff carries away excess salts.
Maintaining pH and EC Balance
Interrelationship between pH and EC
pH and EC are closely interconnected in hydroponics. pH affects nutrient availability, while EC indicates nutrient concentration. Balancing both parameters ensures plants receive adequate nutrients at the optimal pH, promoting healthy growth and maximizing yields.
Importance of achieving balance
Maintaining a proper balance between pH and EC is crucial for nutrient uptake and plant health. When pH and EC are within the appropriate ranges, plants can efficiently absorb nutrients, leading to vigorous growth, strong root development, and enhanced productivity. Imbalances can result in nutrient deficiencies, toxicities, or stunted growth.
Monitoring pH and EC regularly
Regular monitoring of pH and EC is essential to detect any deviations from the desired ranges. Monitoring can be done daily or weekly, depending on the crop and system size. Consistent tracking of pH and EC allows growers to make timely adjustments and ensure optimal nutrient availability.
Adjusting pH and EC simultaneously
Simultaneous adjustment of pH and EC is crucial for maintaining balance in hydroponic systems. When making pH adjustments, it is essential to consider the impact on EC and vice versa. Integrated pH and EC controllers or monitoring systems simplify this process by allowing growers to make precise and synchronized adjustments.
Tools and devices for integrated monitoring and control
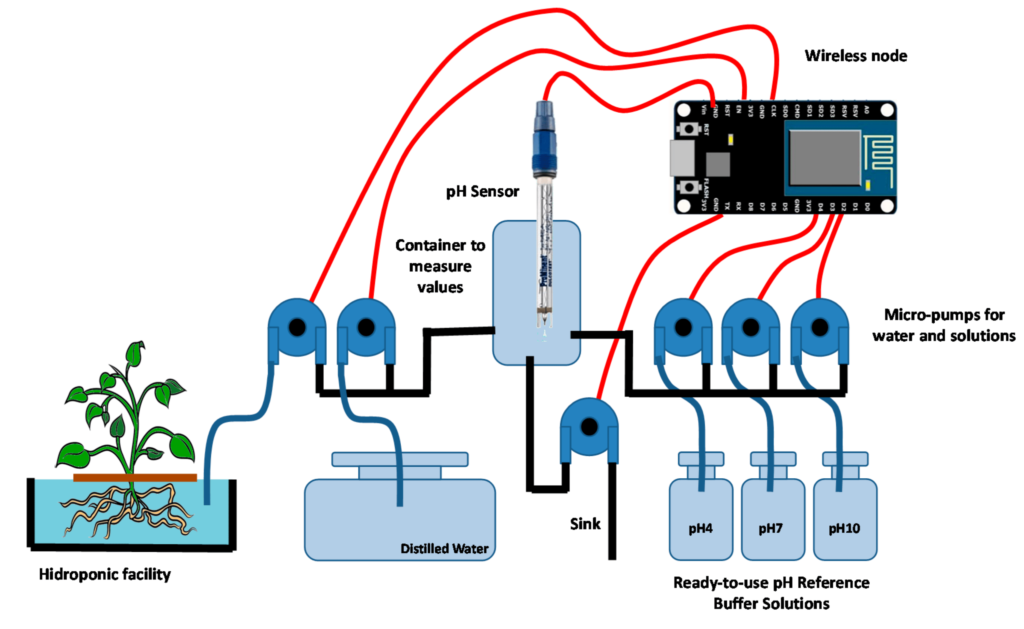
Advanced hydroponic monitoring and control systems offer integrated pH and EC measurement capabilities. These systems utilize sensors to monitor pH and EC in real-time and provide automated dosing functionality. They offer convenience and accuracy, ensuring pH and EC are continuously balanced.
Best Practices for pH and EC Management
Establishing a baseline pH and EC for specific crops
Before initiating hydroponic cultivation, it is crucial to determine the baseline pH and EC requirements for the specific crop being grown. This information can be obtained from crop-specific guidelines, scientific literature, or expert advice. Establishing the baseline provides a starting point for subsequent adjustments.
Testing and adjusting pH and EC in different growth stages
Plants have varying nutrient demands throughout their growth stages. Regularly test and adjust pH and EC based on the crop’s growth stage. Nutrient requirements are typically higher during vegetative growth and flowering stages, necessitating adjustments to maintain optimal nutrient concentrations.
Proper timing and frequency of adjustments
Timing and frequency of pH and EC adjustments depend on the specific needs of the crop, environmental conditions, and the rate of nutrient uptake. Conduct regular measurements and adjustments as needed, ensuring plants receive the appropriate nutrient concentrations and pH levels for uninterrupted growth.
Recording and tracking pH and EC data
Maintaining a record of pH and EC measurements is invaluable for long-term analysis and comparison. Record the date, time, and corresponding values of pH and EC measurements. This data can help identify trends, troubleshoot issues, and optimize nutrient management strategies.
Preventive measures to maintain stability
To maintain pH and EC stability, implement preventive measures such as regular cleaning and calibration of monitoring equipment. Proper hygiene practices, including sterilizing nutrient reservoirs and equipment, prevent contamination that can affect pH and EC levels.
Considerations for organic hydroponics
In organic hydroponics, the management of pH and EC remains crucial. Organic nutrient solutions may require additional attention to maintain balance, as natural ingredients can exhibit different pH buffering capacities. Utilize organic pH adjusters, such as citric acid or vinegar, and ensure organic nutrient inputs align with desired EC levels.
Troubleshooting pH and EC Issues in Hydroponics
Identifying and diagnosing pH and EC problems
Timely identification of pH and EC problems is vital for effective troubleshooting. Visual cues, such as nutrient deficiencies or leaf discolouration, can indicate pH or EC imbalances. Regular monitoring and observation help detect deviations and prompt further investigation.
Troubleshooting guide for common issues

- Problem: Nutrient deficiencies, toxicity, or plant stress due to pH or EC imbalances.
- Solution: Refer to a troubleshooting guide or consult experts to identify the specific issue and corrective actions. Adjust pH and EC gradually, monitor plant response, and track changes in growth and overall health.
Advanced techniques for resolving persistent problems
In some cases, persistent pH or EC issues may require more advanced techniques. These may include specialized treatments or adjustments tailored to the specific problem. Advanced techniques should be implemented under expert guidance to avoid potential risks and ensure a successful resolution.
Seeking expert advice and assistance
When faced with complex or persistent pH and EC issues, seeking advice from hydroponic experts, agronomists, or fellow growers can provide valuable insights and solutions. Experienced professionals can offer guidance, troubleshooting strategies, and recommendations based on their expertise.
Conclusion
In hydroponics, managing pH and EC is paramount to ensure optimal nutrient availability and balanced plant growth. Understanding the significance of pH and EC, along with the factors that influence them, allows growers to make informed decisions and maintain healthy hydroponic systems.
By monitoring pH and EC regularly, adjusting them simultaneously, and implementing best practices, growers can provide their plants with the ideal nutrient concentrations at the appropriate pH. This results in robust growth, high yields, and overall success in hydroponic cultivation.
Remember, maintaining pH and EC balance is an ongoing process. Continuously evaluate and fine-tune your pH and EC management techniques based on crop requirements, growth stages, and environmental factors. Apply the knowledge gained from this article to optimize your hydroponic system and achieve thriving, nutrient-rich crops.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why is pH important in hydroponics?
pH plays a crucial role in hydroponics as it affects nutrient availability to plants. Each nutrient has an optimal pH range at which it is most readily absorbed by plant roots. Maintaining the correct pH ensures that nutrients remain soluble and accessible to the plants, preventing nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
What are the common signs of pH imbalances in hydroponic systems?
pH imbalances in hydroponic systems can manifest in various ways. Some common signs include nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, stunted growth, leaf discoloration, reduced flowering or fruiting, and poor overall plant health. Regular monitoring and observation can help detect these signs and prompt pH adjustments.
Can I use household items to adjust pH in hydroponics?
While some household items, such as vinegar or citric acid, can be used to adjust pH in hydroponics, it is important to exercise caution. These items may have varying compositions and pH levels, which can affect nutrient balance. It is generally advisable to use commercial pH adjusters specifically designed for hydroponic systems.
What are the consequences of ignoring pH and EC management in hydroponics?
Ignoring pH and EC management in hydroponics can have detrimental effects on plant health and productivity. pH imbalances can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, hinder nutrient uptake, and negatively impact plant growth. EC imbalances can result in under- or over-fertilization, affecting plant development and overall yield.
Can I reuse nutrient solutions in hydroponics?
Reusing nutrient solutions in hydroponics is possible, but it requires careful monitoring and adjustment of pH and EC levels. Over time, nutrient solutions can accumulate salts or become imbalanced, affecting plant health. Regular testing and adjustments, as well as periodic replacement or rejuvenation of the nutrient solution, are recommended.
Are there any organic methods for adjusting pH and EC in hydroponics?
Yes, there are organic methods for adjusting pH and EC in hydroponics. Organic pH adjusters, such as citric acid or vinegar, can be used to lower pH levels. Additionally, organic nutrient inputs with specific pH buffering capacities can help maintain pH stability. It’s important to ensure that organic inputs are compatible with the desired EC levels.
How can I prevent salt buildup in the growing medium?
To prevent salt buildup in the growing medium, regular flushing and leaching are recommended. Flushing involves saturating the growing medium with water to remove excess salts, while leaching involves continuous watering until the runoff carries away accumulated salts. These practices help maintain a healthy nutrient balance in the root zone.
Can I automate pH and EC monitoring and adjustments in hydroponics?
Yes, automated systems are available for pH and EC monitoring and adjustments in hydroponics. These systems utilize sensors to measure pH and EC in real-time and can be connected to dosing systems that automatically adjust nutrient solutions based on pre-set parameters. Automated systems offer convenience and accuracy in maintaining pH and EC balance.
How can I troubleshoot persistent pH and EC problems in my hydroponic system?
Troubleshooting persistent pH and EC problems may require a systematic approach. Start by reviewing your nutrient solution composition, water quality, and testing methods. Ensure proper calibration of monitoring equipment and consider advanced techniques like root zone analysis or specialized treatments. Seeking advice from experts can provide additional guidance in resolving persistent issues.








