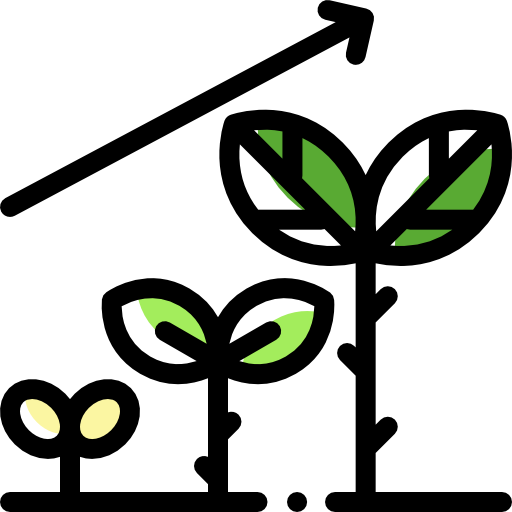
Hydroponic farming, a soilless agricultural practice, has gained significant attention in recent years. With its efficient resource utilization, controlled growing conditions, and year-round production potential, hydroponics offers enticing possibilities.
However, like any farming method, it has its advantages and disadvantages. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the pros and cons of hydroponic farming and help readers determine if it’s the right choice for their needs. By analyzing factors such as increased crop yield, control over growing conditions, reduced water usage, space optimization, and other key considerations, you will be empowered to make an educated decision about integrating hydroponics into your agricultural or gardening practices.
Table of Contents
Pros of Hydroponic Farming
Hydroponic farming offers several benefits that have attracted farmers and gardening enthusiasts alike. Let’s explore the positive aspects:
Increased Crop Yield
One of the primary advantages of hydroponic farming is its ability to maximize crop yield. By efficiently utilizing resources such as water, nutrients, and space, hydroponics can produce significantly higher yields compared to traditional farming methods. With precise control over nutrient delivery and pH balance, plants in hydroponic systems receive optimal nutrition, resulting in accelerated growth and maturation. Additionally, the elimination of soil-related issues, such as pests, diseases, and weeds, ensures healthier plants and higher yields. Furthermore, the ability to grow crops year-round and have multiple harvests significantly boosts productivity.
Efficient Use Of Water And Nutrients
Hydroponic systems recirculate water, resulting in significantly lower water consumption compared to traditional farming methods. Nutrient solutions can be precisely tailored to the plants’ needs, optimizing nutrient uptake and minimizing wastage. This efficient use of water and nutrients translates into higher crop yields.

Year-Round Production
With hydroponics, the growing environment can be controlled, allowing farmers to extend the growing season beyond traditional limitations. By adjusting factors like temperature, humidity, and light, plants can be cultivated year-round, ensuring a continuous and consistent supply of fresh produce.

Control Over Growing Conditions
Hydroponic farming provides unparalleled control over growing conditions. By eliminating soil, farmers can overcome many limitations associated with traditional agriculture. In a hydroponic system, nutrients are delivered directly to the plants’ roots, ensuring they receive precisely what they need. This targeted approach enhances the plants’ overall health and growth. Additionally, hydroponic farmers can fine-tune environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light intensity to optimize plant growth and productivity. Such control allows for the creation of an ideal environment, independent of external weather conditions.
Protection From Weather Conditions
Unlike traditional farming, hydroponic systems are not dependent on external weather conditions. Plants are shielded from extreme temperatures, heavy rain, hail, or drought, allowing for stable and reliable production. This reduces crop losses and ensures a more predictable yield.

Reduced Risk Of Pests And Diseases
Hydroponic systems can be designed to minimize the risk of pests and diseases. By excluding soil, the entry point for many pathogens, farmers can reduce the need for chemical pesticides and fungicides. Integrated pest management techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects, can further enhance pest control in these controlled environments.
Water Conservation
Hydroponic systems use significantly less water compared to traditional farming methods. Water is recirculated within the system, and excess is minimized through careful monitoring and management. This water-saving advantage is especially valuable in regions facing water scarcity or drought.

Minimal Land Requirement
Hydroponics enables vertical farming and efficient space utilization. By growing plants vertically in stacked layers or utilizing vertical towers, hydroponic farms can produce higher crop yields in a fraction of the land area required for traditional farming. This makes hydroponics suitable for urban agriculture and areas with limited arable land.

Reduced Pesticide Use
Hydroponic systems have the potential to reduce reliance on chemical pesticides. By eliminating soil-borne pests and diseases, hydroponic farmers can employ integrated pest management strategies and organic methods, minimizing the need for synthetic pesticides and promoting sustainable farming practices.

Customizable Nutrient Solutions
Hydroponic systems allow for precise control over the nutrient composition of the growing solution. By tailoring nutrient concentrations to meet specific plant requirements, growers can optimize growth, improve crop quality, and enhance nutritional value.

Enhanced Plant Growth And Quality Production
In a controlled hydroponic environment, plants can thrive without competition from weeds or nutrient limitations found in soil. With easy access to water and nutrients, plants can focus on robust growth, producing higher-quality crops with increased vitamin and mineral content.


No Weeds
Weed management is a constant challenge in traditional farming. However, hydroponic farming eliminates this concern altogether. Without soil, there is no room for weeds to take root and compete with cultivated plants. This reduces the time and effort required for weed control, allowing farmers to focus their attention on nurturing their crops.
Stress-Free Growing
Hydroponics provides plants with a stress-free growing environment. The controlled climate, balanced nutrition, and protection from pests and diseases reduce the stress on plants, promoting healthier and more vigorous growth. This can result in higher yields and better quality produce.

Cons of Hydroponic Farming
While hydroponic farming offers numerous advantages, it also has its limitations. Let’s explore some of the cons:

Cost Of Infrastructure And Equipment
Setting up a hydroponic farm requires significant upfront investment in infrastructure and specialized equipment. This includes constructing a controlled environment facility, installing lighting systems, purchasing pumps, nutrient dosing systems, and other necessary components. The initial capital expenditure can be a barrier for small-scale farmers or those with limited financial resources.

Continuous Monitoring And Adjustments Required
Hydroponic systems require constant monitoring and adjustments to ensure optimal performance. Factors such as nutrient levels, pH balance, temperature, humidity, and light intensity must be regularly assessed and adjusted as needed. This level of vigilance and attention to detail can be demanding, particularly for those new to hydroponic farming.

Technical Expertise And Learning Curve
Successfully implementing hydroponic farming techniques requires a certain level of technical expertise. Understanding the principles of hydroponics, nutrient management, and the interplay of environmental factors is essential for optimal plant growth. There is a learning curve associated with mastering these techniques, and acquiring the necessary knowledge and skills may take time and effort.

Dependency On Artificial Inputs
Hydroponic systems heavily rely on artificial inputs, including nutrient solutions and additives. The continuous supply of these inputs is crucial for the well-being and productivity of plants. However, this dependency raises concerns about the potential environmental impact associated with the use of synthetic substances. Responsible handling, disposal, and the use of environmentally friendly inputs are essential to mitigate any adverse effects.

Risk Of System Failures
As with any complex system, hydroponic setups are susceptible to failures and disruptions. Power outages can interrupt nutrient delivery and climate control, potentially affecting plant health and productivity. Equipment malfunctions can lead to downtime and require prompt repair or replacement. Additionally, while the controlled environment of hydroponics reduces the risk, diseases and pests can still pose challenges. Diligence and proactive measures are necessary to address and mitigate these risks effectively.

Limited Crop Selection
Although hydroponic farming is suitable for growing a wide range of crops, there are limitations. Root vegetables that require substantial soil volume may not thrive in hydroponic systems. Similarly, large plants with extensive root systems may pose challenges due to space restrictions. However, hydroponics excels in growing leafy greens, herbs, strawberries, tomatoes, and various other crops. It is important to carefully select crops that are well-suited for hydroponic cultivation.

Factors to Consider
Before deciding on hydroponic farming, consider the following factors:
Scale And Purpose Of Farming
Evaluate whether you intend to pursue hydroponics on a commercial scale or as a hobbyist/home gardener. The scale of farming influences the level of investment required, the complexity of the system, and the expected outcomes. Additionally, consider the specific crop requirements and market demand for your chosen crops.
Available Resources And Constraints
Assess the availability of capital, space, and necessary utilities such as water and electricity. Hydroponic systems require sufficient resources to set up and operate effectively. Additionally, consider the time commitment required for system maintenance, monitoring, and crop care.
Environmental Considerations
Take into account the environmental impact of hydroponic farming. Evaluate water availability, conservation practices, and energy consumption. Implementing sustainable practices and minimizing the carbon footprint of your hydroponic operation is essential for long-term viability.
Personal Preferences And Skills
Consider your personal interests and skills. Hydroponic farming requires a willingness to embrace technology, learn new techniques, and invest time and effort in acquiring the necessary knowledge. Assess your aptitude for technical aspects and your level of enthusiasm for innovation and experimentation.
In the end, whether hydroponic farming is the right choice for you depends on a variety of factors. Consider the scale and purpose of your farming, available resources and constraints, environmental impact, and personal preferences and skills. Conduct further research, consult experts, and learn from experienced practitioners to make an informed decision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydroponic farming offers a range of benefits and advantages, but it also presents certain challenges and limitations. Throughout this blog, we have explored the pros and cons of hydroponic farming, highlighting its potential for increased crop yield, controlled environments, resource efficiency, and optimal plant growth. We have also discussed the high initial investment, the technical knowledge required, dependency on artificial inputs, and limited crop variety as some of the challenges associated with hydroponics.
While hydroponic farming may not be suitable for every situation, it offers unique solutions for urban and space-constrained environments, areas with water scarcity, and regions where soil quality is poor. The controlled environment and precise control over nutrients and growing conditions allow for year-round production and higher yields.
To maximize the benefits and address the challenges of hydroponic farming, it is essential to continue research and development in the field. Advancements in energy-efficient technologies, sustainable nutrient solutions, and automation can further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of hydroponic systems.
By embracing hydroponics, we can reduce soil erosion, conserve water, and minimize the use of pesticides. However, it is important to strike a balance between the benefits of hydroponics and the potential environmental impacts associated with energy consumption and the reliance on artificial inputs. Exploring renewable energy sources, optimizing resource usage, and incorporating sustainable practices will contribute to a more environmentally friendly approach to hydroponic farming.
In conclusion, hydroponic farming is a promising agricultural method that offers great potential for the future. As we continue to address its challenges and further refine the technology, hydroponics can play a significant role in ensuring sustainable food production in a world with increasing population and limited resources.

FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Here are some frequently asked questions about hydroponic farming:
1. What is hydroponic farming?
Hydroponic farming is a method of growing plants without soil. Instead, plants are grown in a controlled environment using a nutrient-rich water solution. The roots are either suspended in the solution or supported by an inert medium, such as perlite or coconut coir.
2. What are the advantages of hydroponic farming?
Hydroponic farming offers several advantages, including increased crop yield, year-round production, protection from weather conditions, reduced risk of pests and diseases, efficient use of water and nutrients, minimal land requirement, and enhanced plant health and nutrition.
3. Is hydroponic farming suitable for all types of crops?
While hydroponic farming can be used to grow a wide range of crops, not all plants are equally suited for this method. Some plants with extensive root systems or specific soil requirements may not thrive in hydroponic systems. However, many leafy greens, herbs, strawberries, and certain flowering plants can be successfully cultivated using hydroponics.
4. Is hydroponic farming environmentally friendly?
Hydroponic farming has several environmental benefits. It reduces soil erosion and degradation, conserves water through efficient usage and recycling, and can potentially reduce the need for pesticides. However, energy consumption for lighting and environmental control should be considered, and efforts should be made to integrate renewable energy sources for a more sustainable approach.
5. What is the initial investment required for setting up a hydroponic farm?
Setting up a hydroponic farm requires an initial investment in infrastructure, equipment, and materials. Costs can vary depending on the scale and complexity of the system. Factors such as the type of hydroponic system, lighting, nutrient delivery systems, and climate control equipment contribute to the overall investment.
6. Do hydroponic plants taste the same as conventionally grown plants?
Hydroponic plants can have comparable or even superior taste and nutritional quality to conventionally grown plants. The controlled growing conditions allow for precise control over nutrient availability, resulting in flavorful and nutrient-dense crops. However, taste can also be influenced by the specific cultivar, post-harvest handling, and other factors unrelated to the hydroponic method itself.
7. Can hydroponic farming be done at home?
Yes, hydroponic farming can be done on a smaller scale at home. Home hydroponics systems, such as countertop or vertical systems, are available that are designed for domestic use. These systems allow individuals to grow fresh produce in a controlled environment, providing a sustainable and convenient option for home gardening.
8. Are there any certifications or regulations for hydroponic farming?
The regulations and certifications for hydroponic farming vary by region and country. It is important to consult local agricultural authorities or regulatory bodies to understand any specific requirements related to hydroponic farming practices, certifications, or labeling standards.
9. Can hydroponic farming be combined with other sustainable practices?
Yes, hydroponic farming can be integrated with other sustainable practices. This includes incorporating renewable energy sources, implementing water-saving techniques, using organic and sustainable nutrient solutions, and embracing recycling and waste reduction strategies. The combination of these practices can enhance the overall sustainability of hydroponic systems.
10. Is hydroponic farming the future of agriculture?
Hydroponic farming is one of the innovative approaches to address the challenges of traditional agriculture. While it may not replace all forms of farming, it holds great potential for urban and space-limited environments, regions with water scarcity, and areas with poor soil quality. With ongoing research and development, hydroponic farming will continue to play a significant role in sustainable food production and the future of agriculture.
If you have any more questions about hydroponic farming, feel free to reach out to us or explore the additional resources provided in this blog.








