Table of Contents
Hydroponics, a fascinating agricultural technique, has revolutionized the way we grow plants by eliminating the need for soil. By providing plants with a nutrient-rich water solution, hydroponic gardening offers controlled and optimized growing conditions, leading to faster growth, increased yields, and reduced environmental impact. In this article, we delve into the rich history of hydroponics, tracing its roots from ancient civilizations to the modern-day. Join us on this journey as we uncover the remarkable evolution of this soilless cultivation method.
The Ancient History of Hydroponics
The concept of soilless cultivation has ancient origins, with early civilizations experimenting with alternative farming methods. Notably, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, is often associated with hydroponics. Although historical evidence remains scarce, some theories propose that these terraced gardens employed hydroponic principles, utilizing a system of water channels and pumps.
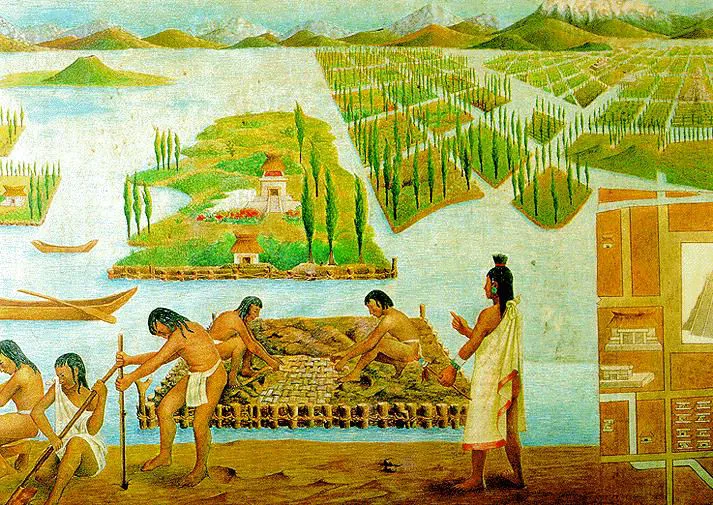
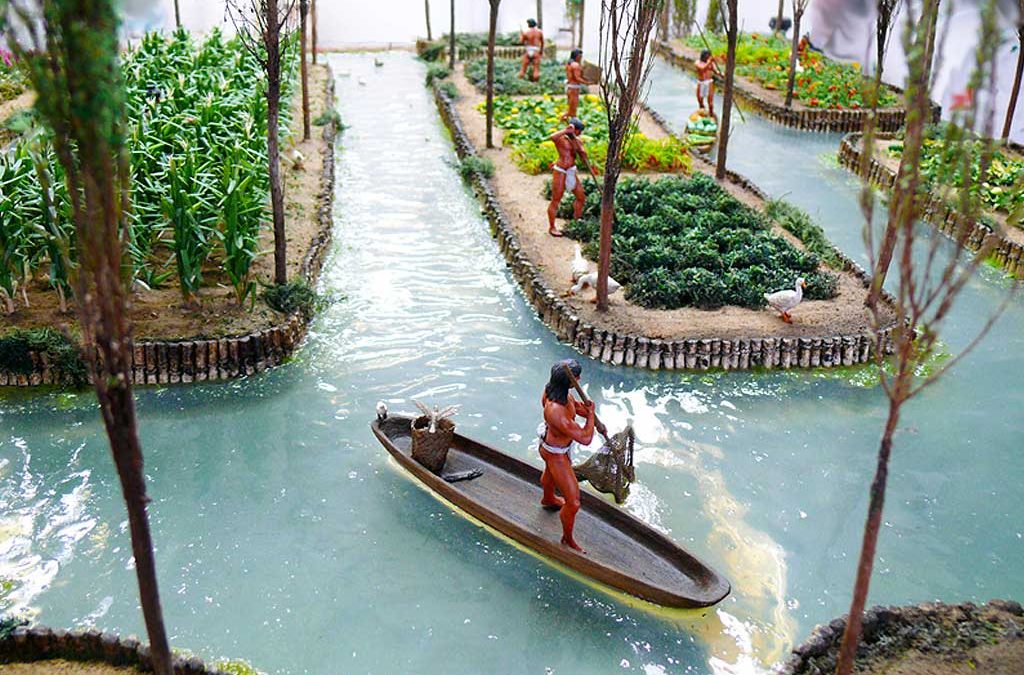
Additionally, ancient civilizations like the Chinese and Aztecs practised soilless agriculture. The Chinese developed floating gardens, where plants were grown on rafts floating on water bodies, while the Aztecs employed chinampas, man-made floating islands used for agriculture. These early examples highlight the ingenuity and resourcefulness of ancient cultures in harnessing water as a medium for plant growth.



Renaissance and Enlightenment Era Developments
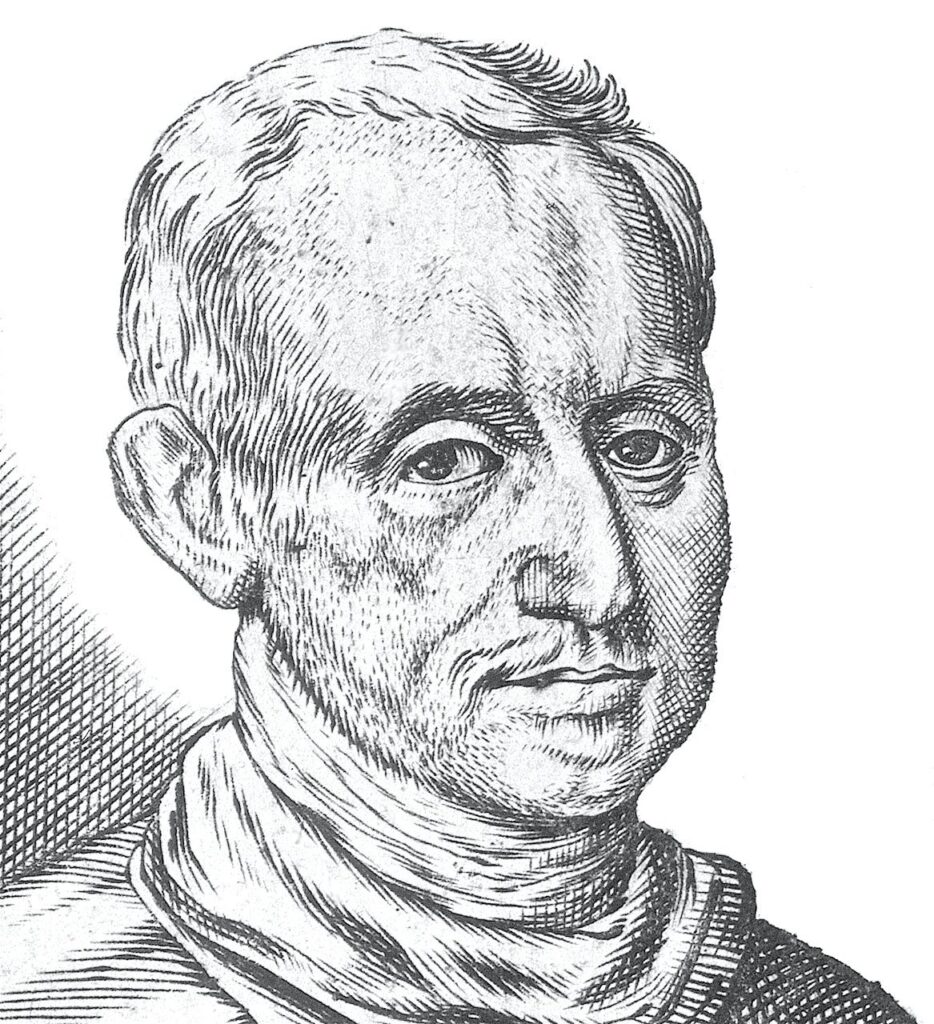
The Renaissance and Enlightenment eras witnessed significant advancements in hydroponic farming. Jan van Helmont, a Belgian chemist, conducted groundbreaking experiments in the 17th century, demonstrating that plants gain their nourishment from water rather than soil alone. Although not directly related to hydroponic, his work laid the foundation for understanding plant nutrition, which would later prove vital in the development of hydroponic systems.
In the 18th century, botanists and scientists like Stephen Hales and Carl Wilhelm Scheele delved deeper into the study of water culture techniques. They explored the role of water and nutrients in the growth of plants, setting the stage for further experimentation and innovation in the field of hydroponic farming.



The Emergence of Modern Hydroponics
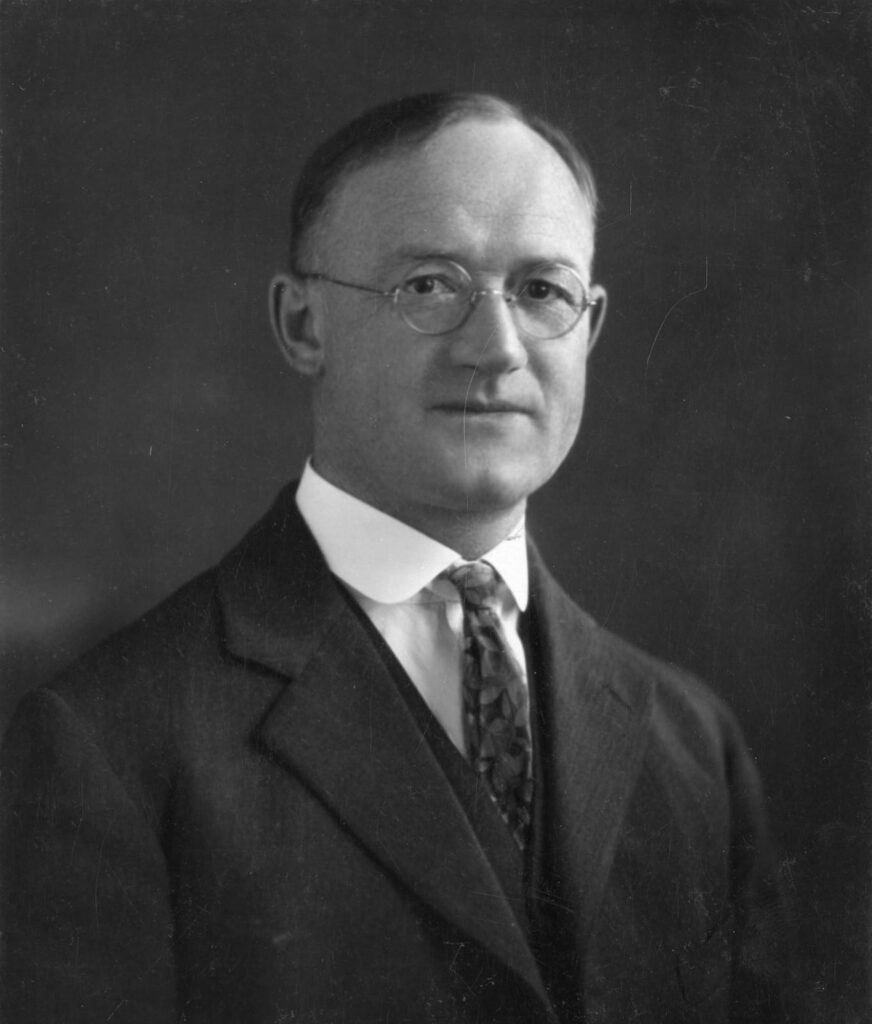
The term “hydroponics” was coined by William F. Gericke, a professor at the University of California, in the 1930s. Gericke’s research focused on soilless crop production, emphasizing the use of nutrient solutions to foster plant growth. His experiments with water-soluble mineral salts demonstrated the potential for growing crops without soil and laid the foundation for modern hydroponic practices.

During World War II, hydroponics gained prominence due to the urgent need for efficient food production. The technique was embraced by the military and civilian populations alike, enabling the cultivation of fresh produce in areas with limited arable land. This period marked a turning point in the history of hydroponics, showcasing its practicality and effectiveness in addressing food security challenges.
Advancements in Hydroponics Technology
The exploration of hydroponic gardening expanded with the involvement of NASA in the 20th century. As space travel became a reality, NASA scientists sought innovative methods to sustain plant growth in extraterrestrial environments. Hydroponic gardens emerged as a promising solution, leading to the development of advanced systems such as nutrient film technique (NFT), Deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics. These techniques allow for efficient nutrient delivery and enhanced oxygenation, optimizing plant health and growth.
Contemporary hydroponics has witnessed remarkable technological advancements. The integration of sensors, automation, and data analytics has transformed the precision and efficiency of hydroponic systems. Smart controllers regulate environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and pH levels, ensuring optimal conditions for plant growth. These technological innovations have propelled hydroponics into the realm of high-tech agriculture.
| Know more about “The Importance of pH in Hydroponic Nutrient Solutions“ |



Applications of Hydroponics
The application of hydroponic gardening spans diverse domains. Commercial hydroponic gardens have gained traction worldwide, offering a sustainable and efficient method for large-scale food production. Urban farming and vertical gardening have emerged as popular solutions for maximizing limited space in urban areas. Rooftop gardens, vertical towers, and hydroponic greenhouses are transforming cities into hubs of fresh produce, reducing the carbon footprint associated with long-distance food transportation.
It also plays a vital role in research and education. Scientists leverage its controlled environment to conduct experiments on plant behaviour, nutrition, and responses to various stimuli. Educational institutions incorporate hydroponics into curricula, exposing students to hands-on learning experiences and cultivating an appreciation for sustainable agriculture.
Benefits and Challenges of Hydroponic
The benefits of hydroponic gardening are manifold. Water conservation is a significant advantage, as hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. Additionally, the controlled environment reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, resulting in cleaner, healthier produce. Hydroponics enables year-round cultivation, independent of seasonal variations, leading to consistent yields and a more reliable food supply.
However, hydroponics is not without its challenges. Maintaining the proper nutrient balance can be complex, requiring careful monitoring and adjustment. Initial setup costs for hydroponic systems can be higher than traditional methods, although the long-term operational savings and increased yields often offset these expenses. Adequate knowledge and expertise are necessary to ensure optimal plant growth and prevent potential issues.
| Know more about “Hydroponic Nutrient Solution: The Ultimate Guide“ |
Future Prospects and Innovations
The future of hydroponic gardening holds immense promise. Sustainable practices are gaining traction, with a focus on integrating renewable energy sources and organic approaches. Solar-powered hydroponic systems and closed-loop nutrient cycles minimize reliance on external resources, making the technique even more environmentally friendly.
Advancements in technology continue to shape the landscape of hydroponic gardening. Automation and artificial intelligence enable real-time monitoring and precise control of growing conditions. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, optimizing plant nutrition and growth patterns. These advancements will streamline operations, reduce labour requirements, and make hydroponics more accessible to a wider range of growers.
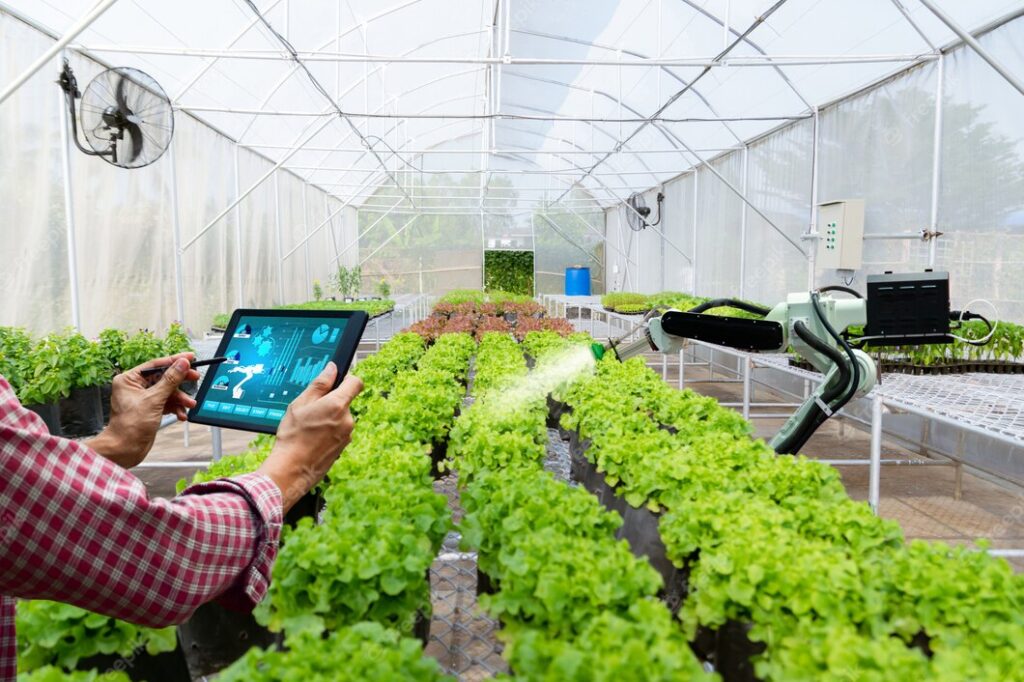
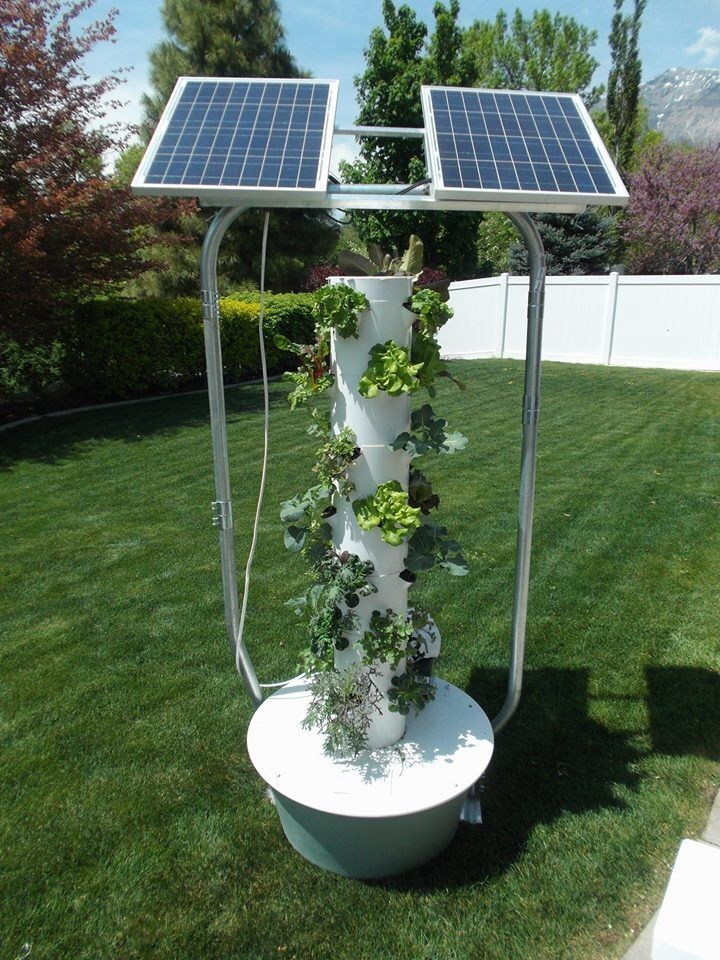



The hydroponic garden also holds the potential to address global food security concerns. With the ability to grow crops in arid regions and urban areas, a hydroponic garden offers a sustainable solution for feeding a growing population. By maximizing yields and minimizing resource consumption, it has the power to transform agriculture into a more efficient and resilient industry.
Conclusion
The history of hydroponic gardening is a testament to human ingenuity and our quest for more sustainable agricultural practices. From ancient civilizations to modern technological advancements, hydroponics has evolved into a viable solution for efficient food production, urban farming, and scientific research. As we continue to face environmental and food security challenges, it stands as a beacon of hope, offering a pathway to a more sustainable and food-secure future. Embracing this soilless revolution is not merely an option but a necessity for our planet’s well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is hydroponics?
It is an innovative agricultural technique that enables the cultivation of plants without the use of soil. Instead, plants are grown in a carefully controlled environment, with their roots immersed in a nutrient-rich water solution or supported by an inert medium. This method optimizes resource utilization, enhances plant growth, and offers a sustainable alternative to traditional soil-based cultivation.
2. How does hydroponics work?
Plants receive the necessary nutrients directly through their root systems in a water-based solution. The nutrient solution is carefully balanced to provide all the essential elements required for optimal growth. Additionally, the hydroponic environment allows for precise control over factors such as temperature, humidity, and pH levels, ensuring that plants thrive in an ideal growing environment.
3. What are the advantages of hydroponic gardens over traditional soil-based agriculture?
The hydroponic garden offers several advantages over traditional soil-based agriculture, including:
Water conservation: Hydroponic systems use significantly less water compared to traditional farming methods, as water is recirculated within the system and losses due to evaporation and runoff are minimized.
Increased crop yields: With the ability to provide plants with optimal nutrition and environmental conditions, the hydroponic garden often results in higher crop yields and faster growth rates.
Year-round cultivation: A hydroponic garden enables year-round cultivation, independent of seasonal variations, allowing for consistent harvests and a more reliable food supply.
Space efficiency: Hydroponic systems can be designed to maximize space utilization, making them suitable for urban farming and vertical gardening, where available land is limited.
Reduced pesticide use: The controlled environment of a hydroponic garden minimizes the need for pesticides and herbicides, leading to cleaner and healthier produce.
4. Is hydroponics suitable for home gardening?
Yes, hydroponics can be adapted for home gardening. There are various types of hydroponic systems, ranging from simple setups suitable for beginners to more complex systems for experienced growers. With proper knowledge and equipment, individuals can grow a wide range of crops, herbs, and even decorative plants using hydroponics.
5. Are there any challenges or limitations to hydroponics?
Initial setup costs: Setting up a hydroponic system can require an initial investment in equipment and infrastructure, although the long-term savings and increased yields often offset these expenses.
Technical knowledge required: Successful hydroponic cultivation requires a solid understanding of plant nutrition, water management, and environmental control. It is essential to monitor and adjust nutrient levels regularly to prevent imbalances.
Power dependency: Hydroponic systems often rely on electricity to power pumps, lights, and other components. In the event of power outages, backup systems or alternative power sources may be necessary to maintain the plants’ health.
6. Can hydroponics be used for organic farming?
Yes, it can be adapted to organic farming practices. Organic hydroponics utilizes organic nutrient solutions derived from natural sources, and organic pest control methods are employed to minimize the use of synthetic chemicals. The key is to ensure that the hydroponic system adheres to the organic standards set by the relevant certifying bodies.
7. Is hydroponics environmentally friendly?
It has several environmental benefits. By conserving water and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, hydroponics minimizes water pollution and the environmental impact associated with traditional agriculture. Additionally, hydroponics’ space efficiency allows for localized food production, reducing the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
8. Can hydroponic gardens help address food security challenges?
The hydroponic garden holds great promise in addressing food security challenges. Its ability to grow crops in controlled environments, independent of external factors, makes it suitable for cultivating food in arid regions, urban areas, and places with limited arable land. Hydroponics’ high productivity and year-round cultivation potential offer a sustainable solution to enhance food production and mitigate the impact of climate change on agriculture.
9. Are there any notable examples of large-scale hydroponic operations?
Yes, there are several notable large-scale hydroponic operations worldwide. One prominent example is the Netherlands, often referred to as the “global capital of hydroponics.” The country has embraced hydroponics and vertical farming to maximize food production in its densely populated areas. Additionally, commercial hydroponic farms can be found in various countries like the USA, Canada, Japan, China, the Middle East, and Europe, growing a wide range of crops, including leafy greens, strawberries, and tomatoes, on a large scale. India is also catching up with those countries. SimplyFresh and Triton Foodworks are the most notable hydroponic farms in India.
10. What does the future hold for hydroponic gardening?
The future of hydroponic gardening is promising. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further integration of automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics into hydroponic systems. This will enable even more precise control over plant growth factors and lead to further optimization of resource utilization. Hydroponic gardening is poised to play a vital role in sustainable agriculture, ensuring food security and environmental stewardship in the years to come.










