Table of Contents
Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its efficiency, sustainability, and ability to maximize crop production. Among the various hydroponic systems available, the Ebb and Flow system, also known as flood and drain, has emerged as a favoured choice for both home gardeners and commercial growers. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the Ebb and Flow hydroponic system, delving into its definition, historical background, mechanism of operation, advantages, setup process, maintenance requirements, plant selection, and real-life success stories.
In this article, we will explore the principles behind the Ebb and Flow system, its components, and their functions. We will discuss the importance of selecting the right location, determining the appropriate grow tray size, and configuring the submersible pump and timer. We will also delve into maintaining the system, monitoring nutrient solution levels, troubleshooting common issues, and ensuring cleanliness and sanitation. Furthermore, we will provide insights into choosing suitable plants, considering their space requirements, nutrient demands, and growth habits.
Throughout the article, real-life examples and success stories will illustrate the practical applications of Ebb and Flow systems, ranging from small-scale home setups to large commercial operations. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a solid understanding of Ebb and Flow hydroponics and the potential it holds for revolutionizing agriculture and food production.
How Does an Ebb and Flow Hydroponic System Work?
At its core, the Ebb and Flow system utilizes an alternate flooding and draining mechanism to provide plants with water and nutrients. This cyclic process aids in oxygenating the roots, promoting nutrient absorption, and minimizing the risk of root-related issues such as rot. Let’s dive into the fundamental principles and components of this system.
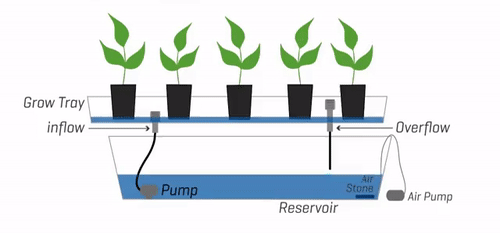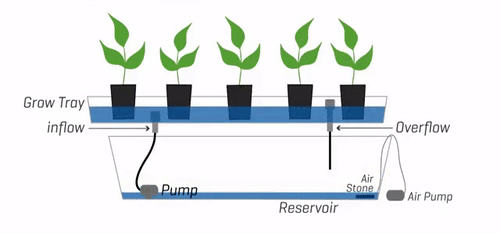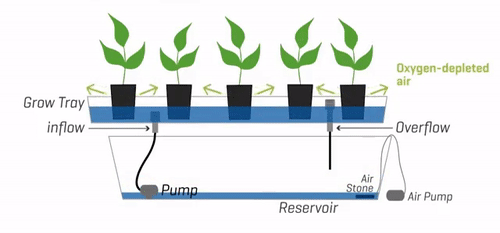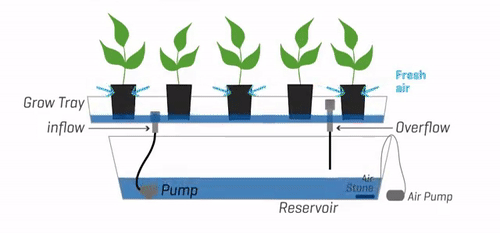
Explanation of the Basic Principles Behind Ebb and Flow Systems
The Ebb and Flow system operates on the principle of periodically flooding the grow tray with a nutrient-rich water solution and then allowing gravity to drain the excess water back into the reservoir. This flood and drain cycle is crucial for delivering oxygen, nutrients, and moisture to the plant’s roots, fostering healthy growth and development.
Components of the System
To set up an Ebb and Flow system, several components are essential:
Water reservoir:
The water reservoir serves as a container for the nutrient solution. It should be adequately sized to accommodate the needs of your plants and maintain a stable environment for the system.
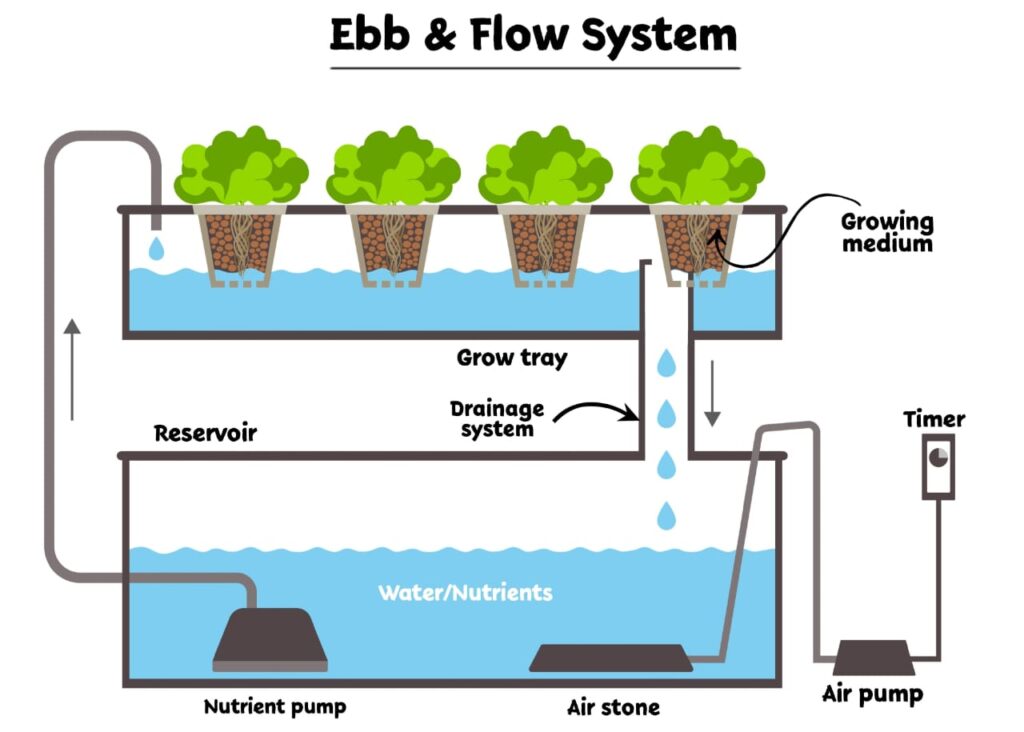
Submersible pump:
A submersible pump is responsible for flooding the grow tray with the nutrient solution during the flood phase. It is connected to a timer to automate the flooding and draining cycles.
Timer:
The timer controls the frequency and duration of the flood phase. It ensures consistent cycles, reducing manual intervention and allowing plants to receive water and nutrients at regular intervals.
Grow tray:
The grow tray holds the plants and the growing medium. It should be designed to facilitate efficient drainage and ensure proper oxygenation of the roots.
Growing medium:
Various options exist for the growing medium, including coco coir, clay pellets, and rock wool. Each medium offers specific benefits such as moisture retention, root support, and pH stability. The choice of medium depends on the crop’s requirements and the grower’s preferences.
Drainage system:
An overflow drain is essential to prevent water accumulation in the grow tray. Excess water flows through the drain and returns to the water reservoir for reuse in subsequent flood cycles.
Operation of an Ebb and Flow System
The Ebb and Flow system operates in two primary phases: the flood phase and the rest phase.
Flood phase:
During the flood phase, the submersible pump activates, delivering the nutrient solution from the water reservoir to the grow tray. The nutrient-rich water floods the tray, submerging the plant roots for a specified duration.
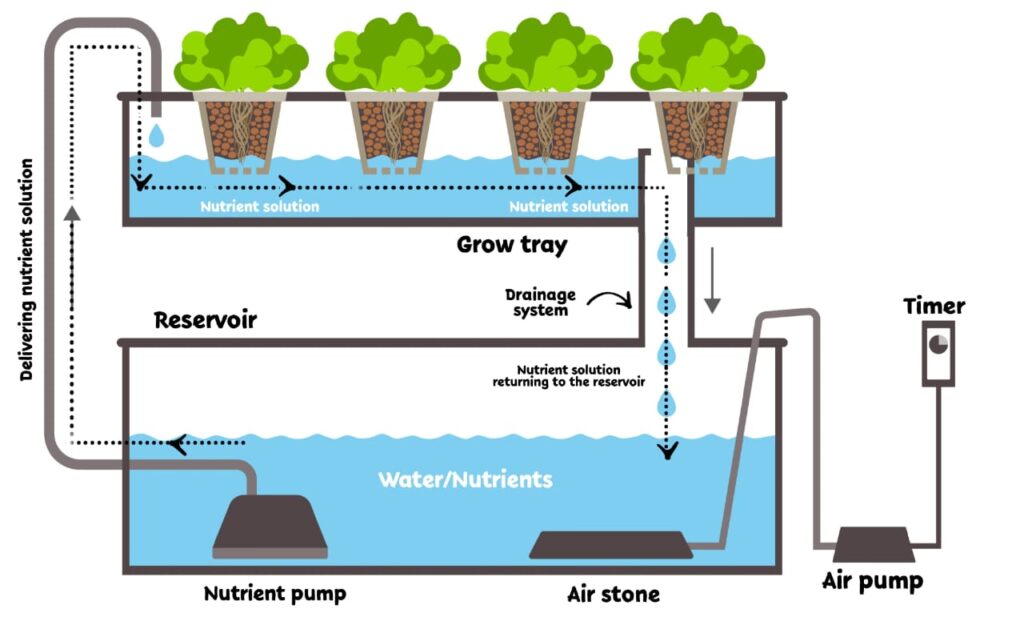
Rest phase:
Once the flood phase concludes, gravity comes into play. The excess water gradually drains from the grow tray, returning to the reservoir through the overflow drain. This resting phase allows the roots to receive oxygen and prevents waterlogging, creating an optimal environment for nutrient absorption.
The repetitive nature of these flood and drain cycles ensures that plants receive a consistent supply of water, nutrients, and oxygen, promoting robust growth and yield.
Benefits of the Cycle for Plant Growth
The cyclic nature of the Ebb and Flow system provides several benefits for plant growth and development. These include:
Oxygenation:
During the rest phase, as the water drains from the grow tray, oxygen is pulled into the root zone. This oxygenation is crucial for the roots’ health, as it helps prevent anaerobic conditions and promotes efficient nutrient uptake.
Nutrient absorption:
The flood phase saturates the root zone with nutrient-rich water, ensuring that the plant’s requirements are met. The nutrients are absorbed by the roots during this phase and stored for use during the subsequent rest phase. This balanced uptake of nutrients promotes healthy plant growth and reduces the risk of deficiencies.
Example: Let’s consider an Ebb and Flow system growing lettuce. During the flood phase, the tray is filled with the nutrient solution, immersing the lettuce roots. The roots absorb the essential nutrients required for growth, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. As the water drains, fresh oxygen enters the root zone, aiding in nutrient absorption and preventing root suffocation. This cycle is repeated multiple times throughout the day, ensuring the lettuce plants receive consistent nourishment and oxygen supply.
Setting Up an Ebb and Flow Hydroponic System
The success of an Ebb and Flow system relies on proper setup. Consider the following factors when embarking on your system installation.
Choosing the Right Location for Your System
Selecting an appropriate location is crucial for the success of your Ebb and Flow system. Look for a spot with the following characteristics:
Adequate light:
Most plants require sufficient light for photosynthesis. Choose a location that receives ample natural light or install artificial grow lights if necessary.
Stability:
Ensure the chosen area provides a stable surface to support the weight of the system, including the grow tray, water reservoir, and plants.
Accessibility:
Position the system in a convenient location, allowing easy access for maintenance, monitoring, and harvest.
Selecting Appropriate Grow Tray Size and Materials
The size and material of the grow tray depend on factors such as available space and the number of plants you intend to cultivate. Consider the following when selecting a grow tray:
Space utilization:
Optimize the available space by choosing a grow tray size that maximizes the number of plants without overcrowding. Adequate spacing between plants allows for proper airflow and prevents the spread of diseases.

Sturdiness and durability:
The grow tray should be made of sturdy materials that can withstand the weight of the plants and the constant flooding and draining cycles. Popular options include plastic, fibreglass, or metal trays.
Determining the Optimal Capacity of the Water Reservoir
Choosing the appropriate water reservoir capacity is essential to maintain stability in the Ebb and Flow system. Consider the following factors when determining the reservoir size:
Plant water requirements:
Calculate the total water needs of the plants based on factors like species, growth stage, and environmental conditions. This calculation will help determine the minimum water reservoir capacity required.
System stability:
A larger water reservoir provides stability in the system by maintaining a consistent water supply, especially during periods of power outages or pump failures.
Maintenance frequency:
A larger water reservoir requires less frequent refilling and monitoring, providing convenience and reducing the risk of interruptions.
Installing and Configuring the Submersible Pump and Timer
The submersible pump and timer play pivotal roles in automating the flood and drain cycles. Follow these steps for proper installation and configuration:
Submersible pump installation:
Place the submersible pump in the water reservoir, ensuring it is fully submerged. Position it at a height that allows for efficient water distribution during the flood phase.
Timer setup:
Connect the timer to the submersible pump and set the desired intervals and durations for the flood and rest phases. Consider the specific requirements of your plants when configuring the timer.
Testing and adjustment:
Once the pump and timer are connected, perform a test run to ensure the flood and drain cycles are functioning as intended. Make adjustments to the timer settings if necessary.
Selecting and Preparing a Suitable Growing Medium
The choice of a suitable growing medium depends on factors such as crop type, water retention capacity, pH stability, and availability. Here are a few popular options:
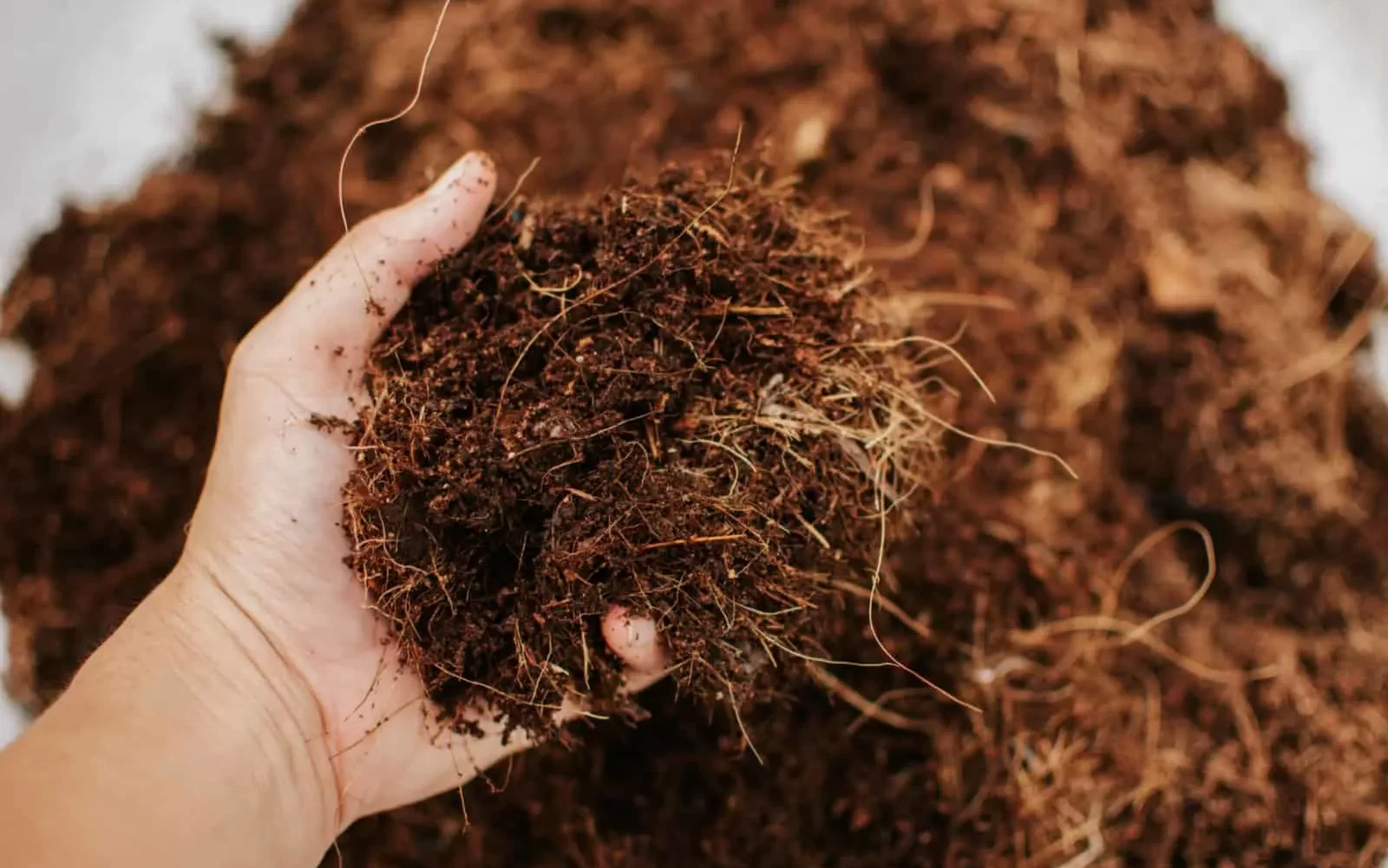
Coco coir:
Made from coconut husks, coco coir offers excellent moisture retention, aeration, and pH stability. It provides a supportive environment for plant roots and can be reused across multiple growing cycles.

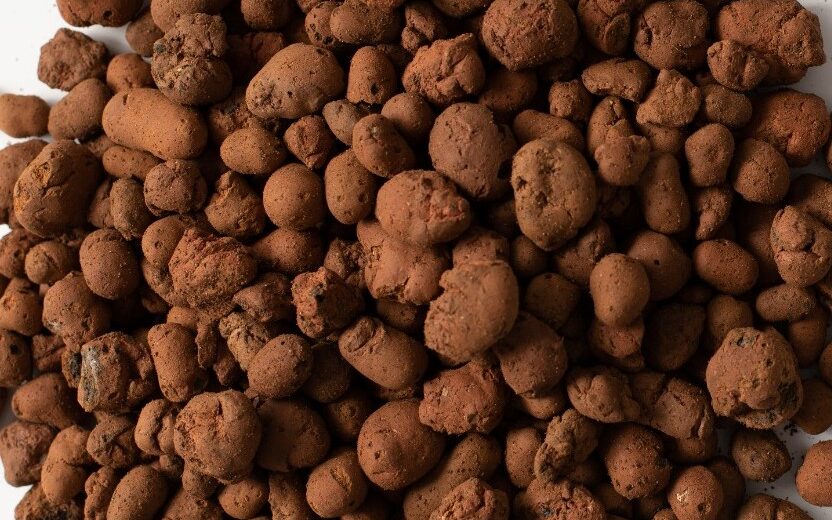
Clay pellets:
Clay pellets, also known as hydroton or expanded clay, are lightweight and porous. They provide excellent drainage, allowing for ample oxygenation of the roots.

Rockwool:
Rockwool is a mineral fibre material that provides good water retention while maintaining proper aeration. It is often used for starting seeds and propagating cuttings.

Before using any growing medium, it’s essential to properly prepare and condition it as per the manufacturer’s instructions to remove any impurities or excessive salts.
Proper Positioning of Plants and Transplanting Seedlings into the System
Once the Ebb and Flow system is set up and ready, it’s time to position the plants and transplant seedlings into the grow tray. Follow these steps for successful transplanting:
Plant spacing:
Determine the optimal spacing between plants based on their growth habits, size, and nutrient requirements. Providing sufficient space ensures better light penetration, and airflow, and prevents the spread of diseases.
Transplanting process:
Gently remove seedlings from their starter pots or seed trays, taking care not to damage the roots. Place the seedlings in the grow tray, ensuring the roots are in contact with the growing medium. Firmly secure the seedlings to maintain stability.
Post-transplant care:
After transplanting, monitor the seedlings closely for the first few days to ensure they adjust well to the new environment. Make any necessary adjustments to the flood and drain cycles based on plant response.
Maintaining an Ebb and Flow Hydroponic System
Regular maintenance is crucial for the smooth operation and success of an ebb-and-flow system. Pay attention to the following aspects to ensure optimal plant health and productivity.
Monitoring and Adjusting Nutrient Solution pH and EC Levels
Maintaining the appropriate pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels of the nutrient solution is vital for nutrient availability and absorption. Monitor these levels regularly using a pH meter and EC meter. Adjust the solution as necessary using pH up or pH down solutions and additional nutrients to achieve the desired range suitable for your crop.
Managing the Flood and Drain Cycles Based on Plant Requirements and Growth Stage
The flood and drain cycles should be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the plants and their growth stage. Factors to consider include:
Plant species:
Different plants have varying water and nutrient needs. Research the optimal flood and drain cycles for the specific crop you are cultivating.
Growth stage:
As plants progress through different growth stages, their water and nutrient requirements change. Adjust the flood and drain frequency and duration accordingly to meet their evolving needs.
Example: For lettuce plants in the vegetative stage, a flood cycle of 15 minutes every 2 hours may be suitable. However, as the plants transition to the flowering stage, reducing the flood cycle to 10 minutes every 3 hours might be more appropriate to accommodate their changing water demands.
Preventing and Troubleshooting Common Issues
While Ebb and Flow systems offer numerous benefits, certain issues can arise. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting measures:
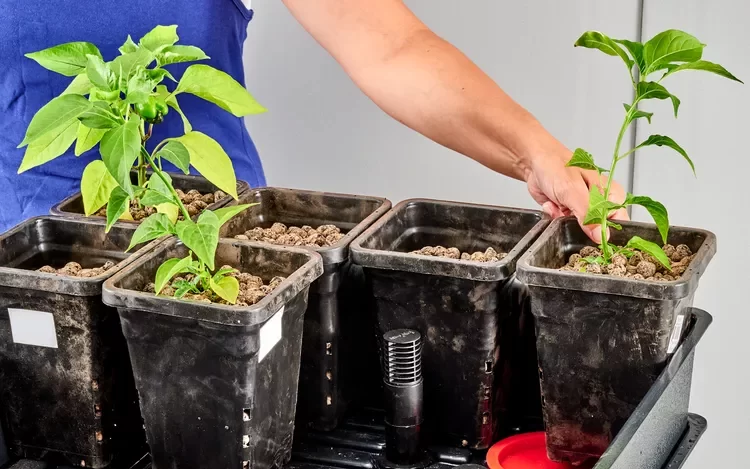

Root rot:
To prevent root rot, maintain proper oxygenation by ensuring adequate drainage and avoiding overwatering. Monitor the moisture levels in the grow tray and adjust the flood and drain cycles accordingly.
Nutrient deficiencies:
Regularly monitor plant health and appearance to detect any signs of nutrient deficiencies. Adjust the nutrient solution composition or concentration as necessary to address specific nutrient imbalances.
| Know more about “How to Troubleshoot Problems in Hydroponic Nutrients Solution“ |
Pump failures:
To prevent pump failures, regularly inspect and clean the pump to remove any debris or clogs. Have a backup pump ready in case of emergencies.
Cleaning and Sanitizing the System Components Regularly
Maintaining a clean and sanitary environment is crucial for preventing diseases and maintaining optimal plant health. Regularly clean and sanitize the system components, including the grow tray, water reservoir, and pump, to remove algae, biofilm, and other contaminants. Use a mild bleach solution or a recommended disinfectant to ensure thorough cleaning.
Avoiding Nutrient Buildup and Deficiencies
Over time, nutrient buildup or deficiencies can occur in the growing medium. To avoid these issues:
Flushing:
Periodically flush the growing medium with plain water to remove any excess salts or nutrient buildup.
Nutrient solution replenishment:
Regularly monitor the nutrient solution’s strength and replenish it with a fresh solution as needed to maintain the appropriate nutrient levels.
Flushing and Replacing Nutrient Solutions
Regularly flushing and replacing the nutrient solution helps maintain its freshness, balance, and effectiveness. Empty and clean the water reservoir, refill it with fresh water, and mix in the appropriate amount of nutrients based on the stage of plant growth and their nutrient requirements.

Choosing Suitable Plants for Ebb and Flow Systems
Ebb and Flow hydroponic systems are versatile and can accommodate a wide range of plant species. Consider the following factors when selecting plants for your system:
Overview of Plant Types Suitable for Ebb and Flow Hydroponics
Leafy greens:
Lettuce, spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are well-suited for Ebb and Flow systems due to their shallow root systems and fast growth.
Herbs:
Basil, mint, parsley, and other herbs thrive in Ebb and Flow setups, offering a continuous supply of fresh, aromatic leaves.
Flowering plants:
Certain flowering plants, such as tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries, can be successfully grown in Ebb and Flow systems. Ensure adequate support is provided as they grow and develop.

Factors to Consider When Selecting Plants
When selecting plants for an Ebb and Flow system, consider the following factors:
Space requirements:
Choose plants that fit within the available grow tray space and do not overcrowd the system.
Nutrient demands:
Different plants have varying nutrient requirements. Select crops that can be supported by the nutrient solution available and adjust the solution composition accordingly.
Growth habits:
Consider the growth habits of plants, such as vine-like growth, bushy growth, or compact growth. This knowledge will help you plan for adequate support structures and spacing.
Example: If you have a small-scale Ebb and Flow system and limited space, you might choose to grow a variety of herbs, such as basil, mint, and oregano. These herbs are well-suited for hydroponic cultivation and can be harvested frequently for culinary use. Their compact growth habits and shallow root systems make them ideal for the system’s flood and drain cycles.
Advantages of Ebb and Flow Hydroponic Systems
Ebb and Flow hydroponic systems offer several advantages that contribute to their popularity and widespread use. Understanding these benefits can help you make an informed decision about implementing this system.
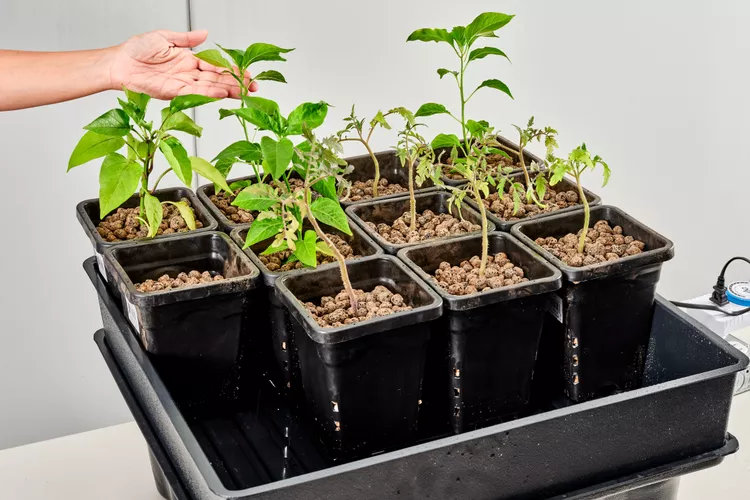

Increased Oxygenation and Nutrient Absorption
The cyclic nature of the flood and drain cycles in Ebb and Flow systems promotes oxygenation of the root zone. This oxygen availability enhances nutrient uptake efficiency and prevents anaerobic conditions, leading to healthier and more vigorous plant growth.
Reduced Risk of Root Rot and Nutrient Imbalances
The alternating flood and drain cycles prevent waterlogging and ensure proper drainage, reducing the risk of root rot. Additionally, monitoring and adjusting the nutrient solution composition in Ebb and Flow systems minimize the occurrence of nutrient imbalances, helping plants thrive.
Versatility in Crop Types and Growth Stages
Ebb and Flow systems are highly versatile and can accommodate a wide range of plant species, including leafy greens, herbs, and flowering plants. They can be used for both seed-starting and full growth cycles, making them suitable for various growth stages.
Ease of Maintenance and Scalability
Ebb and Flow systems are relatively easy to set up and maintain compared to other hydroponic systems. Once the system is established, the automated flood and drain cycles reduce the need for constant manual intervention. Additionally, these systems can be easily scaled up or down to fit available space and desired production capacity.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Other Hydroponic Systems
Ebb and Flow systems are known for their cost-effectiveness, as they require minimal equipment and resources. The simplicity of the setup, along with the ability to reuse the nutrient solution and growing medium, contributes to overall savings in the long run.
Disadvantages of Ebb and Flow Hydroponic Systems
While Ebb and Flow systems offer numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of potential disadvantages as well:
Equipment failure risks:
The reliance on pumps and timers in the Ebb and Flow system makes them susceptible to equipment failures. Having backup equipment and regular maintenance can mitigate these risks.
Root disturbance during flooding:
The periodic flooding can cause minor root disturbance, especially in young seedlings. Care should be taken during the flood phase to avoid damaging delicate roots.
Limited scalability:
Although Ebb and Flow systems can be scaled up to a certain extent, large-scale production may require more complex and efficient hydroponic setups.
Example: A small-scale indoor grower using an Ebb and Flow system might encounter occasional equipment failures, such as a malfunctioning timer. To mitigate this risk, the grower could invest in a backup timer and perform regular maintenance checks on the system to ensure smooth operation.
Conclusion
Ebb and Flow hydroponic systems provide a versatile, cost-effective, and efficient way to cultivate a wide range of plants. Their alternate flooding and draining mechanism promotes oxygenation, reduces the risk of root rot, and accommodates varying growth stages. With proper setup, maintenance, and plant selection, Ebb and Flow systems offer excellent opportunities for home gardeners and commercial growers alike.
Implementing an Ebb and Flow system empowers individuals to take control of their food production, enhance sustainability, and explore innovative agricultural practices. As technology and knowledge continue to advance, the future prospects of Ebb and Flow systems in agriculture are promising, contributing to a greener and more food-secure world.

FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Is the Ebb and Flow hydroponic system suitable for beginners?
Yes, the Ebb and Flow system is considered beginner-friendly due to its relatively simple setup and maintenance. With proper guidance and understanding of the system’s principles, beginners can successfully implement and operate an Ebb and Flow system.
2. What types of plants can be grown using the Ebb and Flow system?
The Ebb and Flow system is versatile and can accommodate various plant types. Leafy greens, herbs, and flowering plants are commonly grown in this system. However, it is important to consider the space requirements, nutrient demands, and growth habits of the plants when making selections.
3. How often should I flood the grow tray in an Ebb and Flow system?
The frequency of flooding the grow tray depends on factors such as plant type, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Typically, the flood cycle lasts for a few minutes to an hour, and the rest period allows the excess water to drain back into the reservoir. It is important to monitor the moisture levels in the growing medium and adjust the flood and drain cycles accordingly.
4. Can I reuse the nutrient solution in an Ebb and Flow system?
nutrient solution. After each flood and drain cycle, the excess water returns to the reservoir, where it can be replenished with fresh nutrients as needed. Regular monitoring and adjustments ensure the nutrient solution remains balanced for optimal plant growth.
5. How often should I clean and sanitize the Ebb and Flow system?
Regular cleaning and sanitization of the Ebb and Flow system are essential to prevent contamination and maintain plant health. It is recommended to clean the system between growing cycles and sanitize it periodically to remove any potential pathogens or buildup. The frequency may vary based on individual circumstances, but it is good practice to establish a routine cleaning schedule.
6. Can the Ebb and Flow system be used outdoors?
Yes, the Ebb and Flow system can be used outdoors. However, it is important to consider factors such as temperature fluctuations, sunlight exposure, and protection from pests and extreme weather conditions. Providing suitable covers, shading, or greenhouse structures can help create an optimal outdoor environment for the system.
7. Can I automate the flood and drain cycles in an Ebb and Flow system?
Yes, the flood and drain cycles can be automated using timers and submersible pumps. These components allow you to set the desired frequency and duration of the flood cycles, making the system more efficient and convenient to manage.
8. How do I adjust the nutrient solution pH in an Ebb and Flow system?
Maintaining the proper pH level of the nutrient solution is crucial for plant health and nutrient uptake. To adjust the pH, you can use pH testing kits or meters to monitor the solution’s acidity or alkalinity. If the pH deviates from the desired range, pH adjusters such as pH-up or pH-down solutions can be used to bring it back to the optimal level.
9. What is the lifespan of the growing medium in an Ebb and Flow system?
The lifespan of the growing medium in an Ebb and Flow system can vary depending on factors such as the type of medium used, plant selection, and maintenance practices. Some growing mediums, like clay pellets, can be reused multiple times, while others, such as coco coir, may need periodic replacement or rejuvenation to maintain their effectiveness. Regular inspection and observation of the growing medium’s condition will help determine when it needs to be replaced.
10. Can I integrate additional hydroponic techniques with the Ebb and Flow system?
Absolutely! The Ebb and Flow system can be combined with other hydroponic techniques to enhance its capabilities. For instance, incorporating aeroponics or drip irrigation in conjunction with the Ebb and Flow system can provide additional oxygenation and precise nutrient delivery to the plants. These hybrid systems offer growers the flexibility to customize their setups according to specific plant requirements and optimize growth.
11. How can I prevent or manage common issues like root rot in an Ebb and Flow system?
To prevent or manage root rot in an Ebb and Flow system, it is essential to maintain proper oxygenation and drainage. Ensure that the flood and drain cycles are appropriately timed to avoid waterlogging and excess moisture. Using a well-draining growing medium, providing adequate airflow around the roots, and maintaining a clean and sanitary system can help minimize the risk of root rot.
12. Can I grow plants with different nutrient requirements together in the same Ebb and Flow system?
It is generally recommended to group plants with similar nutrient requirements together in an Ebb and Flow system to ensure optimal nutrient delivery. However, if you choose to grow plants with different nutrient needs in the same system, it is important to carefully monitor and adjust the nutrient solution accordingly. Regular testing of nutrient levels and observation of plant health will help you tailor the system’s parameters to meet the diverse needs of different plant species.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only. Consult local experts and reputable sources before implementing any hydroponic system or making significant changes to your gardening practices.








