Table of Contents
Hydroponics, the method of growing plants without soil, has revolutionized the way we cultivate crops. By using nutrient-rich water solutions, hydroponic systems allow us to grow plants in controlled environments, often yielding better results than traditional soil-based agriculture. However, the water used in hydroponics plays a significant role in the success of the cultivation process, and this is where the importance of water quality comes into the picture.
One of the most effective ways to ensure optimal water quality is through the use of Reverse Osmosis, a water purification technology that has significant implications for hydroponics. This article provides an in-depth understanding of RO, the critical role of reverse osmosis in hydroponics, how to choose the right RO system, the environmental and economic impacts, and the future perspectives of RO in hydroponics.
Understanding Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification technique that employs a semipermeable membrane to remove larger particles and impurities from water. The principle behind reverse osmosis is relatively straightforward, yet the process and its implications are multifaceted.
The RO Process
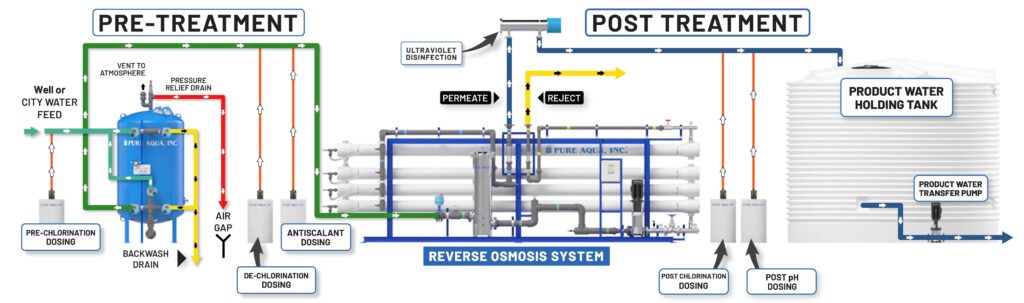
- Pre-filtration: The first stage involves removing large particles such as sediment and chlorine that might damage the RO membrane. This is typically done with a sediment filter and a carbon filter.
- Reverse Osmosis: The water is then forced under pressure through the semipermeable membrane, which removes a vast majority of the remaining contaminants. The membrane’s small pore size (around .0001 microns) ensures that only water molecules can pass through, leaving larger particles and ions behind.
- Post-filtration: After the RO stage, the water goes through another activated carbon filter. This post-filtration process polishes the water, removing any remaining tastes or odours.
Limitations of Reverse Osmosis
While the benefits of reverse osmosis are numerous, it does have a few limitations:
- Water Waste: During the RO process, a significant amount of water is wasted. For every gallon of purified water, 2 to 4 gallons are typically discharged as waste.
- Slow Process: The RO process is relatively slow, and without a storage tank, it could take a while to generate a considerable amount of purified water.
- Removal of Beneficial Minerals: The RO process doesn’t distinguish between harmful and beneficial minerals, meaning it removes both. As a result, RO water can be devoid of essential minerals like calcium and magnesium.
Importance of Water Quality in Hydroponics
In hydroponic systems, the role of water isn’t just to provide hydration for plants; it’s also the medium through which plants receive essential nutrients. The quality of water is crucial for several reasons.
Nutrients and Mineral Content in Water
The mineral content in water plays a significant role in the health and productivity of hydroponic plants. The water needs to contain the right balance of macro and micronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and trace elements.
Problems with Poor Quality Water
- Nutrient Imbalance: Poor quality water can contain excessive or insufficient amounts of certain minerals, causing nutrient imbalances that can lead to deficiencies or toxicities in plants.
- Contaminants: Water of poor quality might also contain harmful substances such as heavy metals, pesticides, or harmful microorganisms, which can adversely affect plant health and crop yield.
- pH Imbalances: The pH of the water can significantly affect nutrient availability. Poor quality water can often have a pH level that’s too high or too low, which can result in nutrient lockout—where plants can’t absorb the nutrients they need.
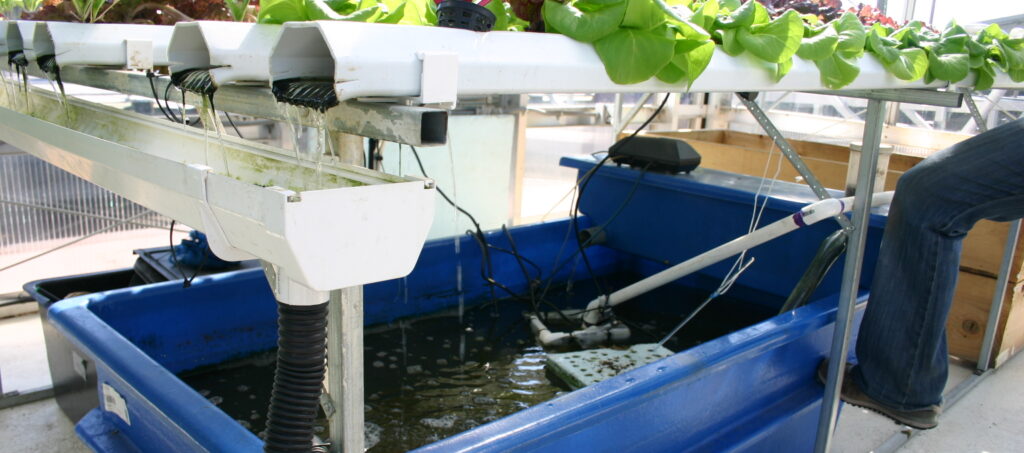
The Role of Reverse Osmosis in Hydroponics
Reverse Osmosis (RO) plays an integral role in hydroponic systems, helping to overcome the issues related to water quality.
How RO Systems Work in Hydroponics
RO systems in hydroponic farming work much the same way as they do for household water filtration. They take source water, filter out the majority of contaminants, and produce purified water suitable for use in the hydroponic system.
The Impact of RO Water on Plant Growth
The use of RO water can have a significant positive impact on plant growth and productivity in hydroponic farming:
- Improved Nutrient Uptake: Since RO water is virtually free of contaminants and unnecessary minerals, it can be easily customized with the ideal nutrient mix for specific plants. This can lead to improved nutrient uptake and healthier, more productive plants.
- Reduced Risk of Disease: By removing harmful bacteria and viruses, RO water can reduce the risk of plant disease in hydroponic systems.
- Better pH Control: RO water is typically neutral (pH 7) or slightly acidic, making it easier to adjust to the optimal pH range for nutrient absorption in hydroponics, typically around 5.5 to 6.5.

Choosing a Reverse Osmosis System for Hydroponics
Selecting the right reverse osmosis (RO) system for your hydroponic garden is a decision that can significantly influence the health and productivity of your plants. Here are some key factors to consider:
Water Quality
Testing the quality of your source water is an essential first step. The level of contaminants and their type will determine the kind of RO system you’ll need. Some systems come with additional filters for specific contaminants, such as iron or chloramine.
System Capacity
Consider the size of your hydroponic setup and how much-filtered water you’ll need daily. RO systems have varying capacities, usually indicated by the amount of filtered water they can produce per day.
Cost and Maintenance
Cost is another significant factor. This doesn’t just involve the initial cost of the system, but also the long-term cost of replacement filters and maintenance. Some systems might be cheaper upfront but require more frequent and costly maintenance.
Efficiency and Waste
RO systems also vary in their efficiency — specifically, the ratio of purified water to wastewater they produce. More efficient systems can save a considerable amount of water in the long run.

Environmental and Economic Implications of Using RO
The use of reverse osmosis in hydroponic system has implications that extend beyond the health of your plants.
Environmental Considerations
While RO systems are highly effective at purifying water, they’re known for producing a significant amount of wastewater. However, strategies can be employed to minimize this waste, such as reusing the wastewater for other purposes like outdoor irrigation or choosing an RO system with built-in water-saving technology.
Economic Implications
An RO system is an investment. While there’s an upfront cost involved, the potential returns in terms of improved plant growth, yield, and reduced losses due to disease, can be substantial. It’s also worth considering the savings from potentially reduced water usage in the long term, especially in areas where water costs are high.
Future Perspectives of RO in Hydroponic system
The use of reverse osmosis in hydroponic farming is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research and innovation promising exciting developments.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are making RO systems more efficient and accessible. New membrane materials are increasing efficiency, reducing waste, and lowering energy demands. Smart RO systems with automated monitoring and control systems are also emerging.
Sustainability
The integration of renewable energy sources in running RO systems, like solar power, is a trend likely to grow. Such advancements could make RO systems more sustainable and less dependent on conventional energy sources.
Addressing Global Challenges
As freshwater resources continue to diminish and the global population rises, the combination of hydroponics and efficient water purification methods like RO could play a significant role in sustainable food production and water management.
Conclusion
The application of Reverse Osmosis in hydroponic farming is much more than a simple step in water purification. It’s a game-changing approach that ensures the water used provides the perfect blank slate upon which a precise and optimal nutrient solution can be built. While it comes with its own set of challenges, the ongoing innovations promise to make RO more efficient and more accessible to hydroponic farmers.
As we look to the future, it becomes clear that RO, when used responsibly and sustainably, has the potential to be a major contributor to successful hydroponic practices and an integral part of the solution to our global food and water challenges. If you are a hydroponic grower or planning to become one, consider how incorporating an RO system could significantly improve your yield and overall crop health.
We’d love to hear about your experiences with the use of RO in hydroponics. Has it made a significant difference in your crop yield or quality? Do you have any tips or suggestions for other readers? Please share your thoughts in the comments section below. Additionally, if there are any specific topics related to hydroponics and water purification that you would like us to cover in future articles, do let us know.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use tap water for my hydroponic system without an RO filter?
While tap water can be used in hydroponic systems, it may contain contaminants or have a mineral composition that is not ideal for your plants. Using tap water without filtration can lead to imbalances in nutrient availability, potentially harming your plants.
Does RO water need to be re-mineralized for use in hydroponic farming?
Yes, because RO water is almost completely free of minerals, you’ll need to add a hydroponic nutrient solution to provide your plants with the necessary nutrients.
Are there alternatives to reverse osmosis for water purification in hydroponic farming?
Yes, there are several other methods for water purification that can be used in hydroponic farming, such as activated carbon filters, ceramic filters, and UV sterilization. However, these methods may not be as effective as RO in removing certain types of contaminants.
How often do I need to replace the RO membrane in my system?
The frequency of membrane replacement depends on the quality of your source water and how much water you filter. Generally, RO membranes need to be replaced every 2-3 years, but it’s best to check with the manufacturer’s instructions.
How can I determine the size of the RO system I need for my hydroponic system setup?
The size of the RO system you need will depend on the size of your hydroponic system setup and the amount of water you need to filter each day. For a small home setup, a system with a capacity of 50-100 gallons per day might be sufficient. For larger commercial operations, you’ll need a system with a much higher capacity.
How can I minimize the environmental impact of using an RO system in my hydroponic setup?
You can minimize the environmental impact by reusing the wastewater produced by your RO system for other purposes, such as outdoor irrigation. Some modern RO systems also come with water-saving technology that can significantly reduce the amount of wastewater produced.








