Table of Contents
Introduction
In the dynamic world of hydroponic gardening, where plants thrive without soil, root health emerges as a cornerstone of success. While the verdant foliage aboveground may dazzle the eye, it’s the hidden network of roots that truly sustains plant vitality. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey into the intricacies of root health in hydroponic systems, unveiling strategies to cultivate robust root systems and nurture flourishing plants.
Understanding Root Health in Hydroponics
Anatomy of Plant Roots
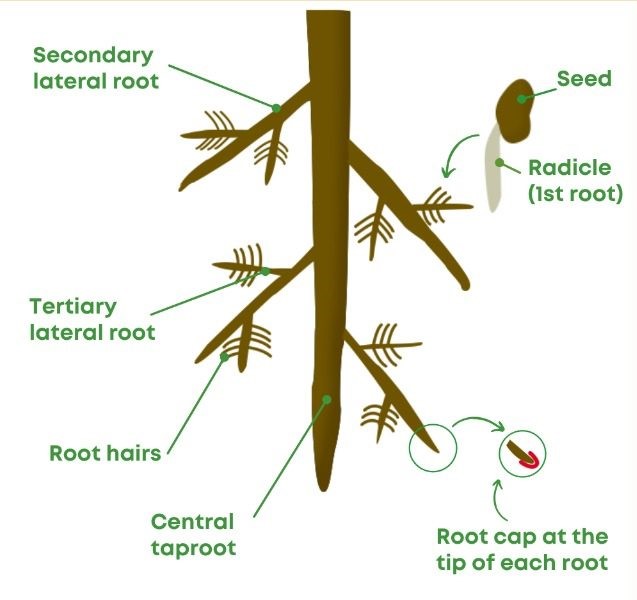
- Primary Root Structure: Root systems typically begin with a primary root, also known as a taproot, from which secondary roots branch out. This hierarchical structure anchors the plant and facilitates water and nutrient absorption.
- Root Hairs: These microscopic projections extend from the surface of roots, vastly increasing their absorptive area and enhancing nutrient uptake.
- Root Cap: Located at the tip of the root, the root cap serves as a protective barrier, shielding delicate meristematic cells as the root navigates through the growing medium.
- Meristematic Zone: Here, rapid cell division occurs, fueling root growth and contributing to overall plant development.
- Zone of Maturation: As cells mature, they differentiate into specialized tissues responsible for functions such as water and nutrient transport, bolstering the plant’s resilience and vigor.
Factors Affecting Root Health in Hydroponics
Hydroponic environments introduce unique challenges and opportunities for root health, influenced by several pivotal factors:
- Nutrient Availability: Unlike traditional soil-based systems, hydroponics necessitates precise management of nutrient solutions to meet the plant’s specific requirements at each growth stage.
- Oxygen Levels: Adequate oxygenation of the root zone is paramount for facilitating respiration and nutrient uptake. In water-based hydroponic systems, insufficient oxygen can lead to root suffocation and reduced plant vigor.
- pH Balance: pH levels profoundly influence nutrient solubility and microbial activity in the root zone, directly impacting nutrient availability and root health.
- Temperature: Root growth is intricately linked to temperature, with deviations from the optimal range impeding enzymatic activity and nutrient absorption.
- Water Quality: The purity and composition of water play a pivotal role in plant health, necessitating filtration and maintenance measures to ensure optimal conditions for root development.
Strategies for Enhancing Root Health
Proper Nutrient Management
- Understanding Nutrient Requirements: Different plant species and growth stages demand specific nutrient concentrations. Thoroughly acquaint yourself with the nutritional needs of your chosen crops to formulate customized nutrient solutions.
- Balancing Nutrient Solution: Maintain precise ratios of essential nutrients to prevent deficiencies or toxicities, fostering robust root growth and overall plant vigor.
- Monitoring Nutrient Levels: Regularly assess nutrient concentrations using tools such as electrical conductivity (EC) meters and pH meters, adjusting solutions as needed to maintain optimal nutrient levels.
- Avoiding Nutrient Imbalances: Vigilantly monitor plant responses for signs of nutrient deficiencies or excesses, such as leaf discoloration or stunted growth, and promptly address imbalances to prevent detrimental effects on root health.
Optimizing Oxygenation
- Importance of Oxygen for Root Health: Oxygen is indispensable for root respiration and nutrient uptake, fueling robust growth and metabolic activity. Ensure ample oxygen availability in the root zone to support optimal root function.
- Aeroponic Systems: Aeroponic systems represent an innovative approach to hydroponics, suspending plant roots in air and delivering oxygen directly to the root surface. This technique maximizes oxygen uptake and promotes rapid root growth.
- Oxygenation Techniques in Other Hydroponic Setups: In non-aeroponic systems, implement oxygenation methods such as air stones, oxygen pumps, or cascading waterfalls to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the root zone and sustain vigorous root development.
Maintaining pH Balance
- Impact of pH on Nutrient Uptake: pH levels exert a profound influence on nutrient availability, with deviations from the optimal range affecting nutrient solubility and uptake. Maintain pH within the appropriate range for each plant species to ensure efficient nutrient absorption.
- Monitoring and Adjusting pH Levels: Regularly monitor pH levels using pH meters or test kits, making adjustments with pH up or down solutions to maintain stable pH conditions in the nutrient solution.
- Choosing Appropriate pH Buffers: Select pH buffers compatible with hydroponic systems, opting for high-quality products that facilitate accurate and reliable pH adjustments without introducing unwanted contaminants or impurities.
Temperature Regulation
- Effects of Temperature on Root Growth: Temperature profoundly influences root growth and metabolic activity, with deviations from the optimal range impeding enzymatic function and nutrient uptake. Maintain stable temperatures conducive to root development to maximize plant health and productivity.
- Controlling Water Temperature in Hydroponic Systems: Implement measures to regulate water temperature within the desired range, such as using water chillers or insulation to mitigate temperature fluctuations and safeguard root health.
- Strategies for Temperature Management: Employ shading, cooling systems, or thermal insulation to regulate ambient temperatures in the growing environment, protecting roots from heat stress or cold shock and promoting optimal growth conditions.
Ensuring Water Quality
- Importance of Clean Water in Hydroponics: Water quality directly impacts nutrient availability and plant health, making water purification and filtration essential components of hydroponic systems. Remove impurities and pathogens through effective filtration and purification methods to create an optimal growing environment.
- Filtration and Purification Methods: Utilize a combination of sediment filters, carbon filters, UV sterilization, or reverse osmosis systems to purify water and eliminate contaminants, ensuring a pristine growing medium for healthy root development.
- Regular Maintenance of Water Reservoirs: Establish a routine maintenance schedule to clean and disinfect water reservoirs, preventing algae growth, nutrient imbalances, and pathogen proliferation. Regular maintenance is key to sustaining optimal water quality and supporting vigorous root growth.
Techniques for Root Observation and Management

Root Zone Monitoring
- Tools for Observing Root Health: Utilize specialized tools such as root inspection trays, digital microscopes, or rhizotron systems to observe root morphology and detect signs of stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies.
- Signs of Healthy and Unhealthy Roots: Familiarize yourself with indicators of root health, such as white, firm roots with abundant root hairs, as well as symptoms of root rot or decay, such as browning or slimy textures. Prompt identification of root issues enables timely intervention and corrective measures.
Tackling Root Rot in Hydroponic Systems: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
Preventative Measures
- Root Zone Sanitation: Practice strict hygiene protocols to prevent the introduction and spread of pathogens within the root zone. Sterilize growing media, equipment, and reservoirs regularly to minimize the risk of root diseases and maintain a clean, healthy growing environment.
- Preventing Root Diseases and Pathogens: Implement preventative measures such as beneficial microbial inoculants, biocontrol agents, or disease-resistant cultivars to fortify roots against pathogens and enhance overall plant resilience. Proactive disease management is essential for safeguarding root health and maximizing crop productivity.
Pruning and Trimming
- Importance of Root Pruning: Regular root pruning promotes root branching, alleviates overcrowding, and stimulates new root growth, enhancing nutrient absorption and overall plant vigour. Strategic pruning practices contribute to robust root systems and optimal plant health.
- Techniques for Root Trimming: Employ sterile tools and precise cutting techniques to prune damaged, diseased, or overgrown roots effectively. Careful trimming minimizes stress on plants and reduces the risk of secondary infections, facilitating healthy root regeneration and sustained growth.

Conclusion
In the dynamic realm of hydroponic gardening, strong roots serve as the foundation for robust, resilient plants. By implementing targeted strategies to enhance root health, growers can unlock the full potential of their hydroponic systems and cultivate vibrant, productive crops. With a deep understanding of root physiology and thoughtful management practices, hydroponic enthusiasts can embark on a journey toward sustainable, bountiful harvests, rooted in the principles of innovation and excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is root health important in hydroponics?
Root health is crucial in hydroponics as it directly impacts nutrient uptake, water absorption, and overall plant growth. Healthy roots ensure efficient nutrient delivery to the plant, leading to improved vigour, productivity, and disease resistance.
2. How can I tell if my plant’s roots are healthy?
Healthy roots typically exhibit a white or light colouration, firm texture, and abundant root hairs. Signs of unhealthy roots include discolouration, mushiness, or foul odours. Regular observation using tools like root inspection trays or digital microscopes can help detect early signs of root issues.
3. What is the optimal pH range for hydroponic nutrient solutions?
The optimal pH range for hydroponic nutrient solutions varies depending on the plant species being cultivated. However, most plants thrive in a slightly acidic pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. Monitoring and adjusting pH levels within this range is critical to ensure optimal nutrient uptake and root health.
4. Can I use organic nutrients in hydroponic systems?
Yes, organic nutrients can be used in hydroponic systems, although they may require additional considerations such as microbial activity and nutrient availability. Organic hydroponic nutrient solutions are available commercially or can be prepared using organic amendments, compost teas, or other natural inputs.
5. How can I ensure optimal oxygen levels in my hydroponic system?
To ensure optimal oxygen levels in hydroponic systems, consider using aeroponic systems, air stones, oxygen pumps, or cascading waterfalls to promote oxygenation in the root zone. Regular monitoring of dissolved oxygen levels and proper aeration techniques are essential for sustaining healthy root respiration.