Table of Contents
Get ready to embark on an exciting adventure into the world of hydroponics! We’re about to uncover the secrets of nurturing thriving plants without soil in our ultimate guide on hydroponic nutrients. Don’t worry, we promise it’s not rocket science… well, maybe just a little bit! In this guide, we’ll dive into the importance of nutrient solutions in hydroponic systems and equip you with all the knowledge and tools you need to create your own flourishing hydroponic garden. It’s time to ditch the traditional dirt and let your plants enjoy the high life of nutrient-rich liquids.
Forget about your grandma’s gardening methods—hydroponics is all about delivering the perfect blend of essential nutrients to your plants, ensuring they grow strong and healthy. We’ll walk you through the nitty-gritty details of nutrient solutions, from macro and micronutrient balance to different types of solutions that will make your plants sing with joy.
Whether you’re a newbie with a budding green thumb or a seasoned hydroponic expert looking to level up your nutrient game, this guide has got your back. Prepare to unlock the secrets to bountiful harvests and become the envy of your plant-loving friends. So, get your lab coat ready and your sense of adventure in full swing. It’s time to dive headfirst into the world of hydroponic nutrient solutions. Let’s get growing, shall we?
What is a Hydroponic Nutrient Solution?
Let’s start by unravelling the mystery of a hydroponic nutrient. Simply put, it’s a tailored concoction of essential elements that serve as the primary source of nutrition for your plants in a hydroponic system. Instead of relying on soil, which acts as a natural reservoir of nutrients, hydroponics provides a controlled environment where plants receive their required nourishment directly through a nutrient solution.
Components of a Nutrient Solution
A nutrient solution consists of two main types of components: macro and micro-nutrients. Macro-nutrients are the primary elements that plants need in relatively large quantities, including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). These macro-nutrients play vital roles in plant growth, such as promoting leaf development, supporting root health, and facilitating the production of flowers and fruits.
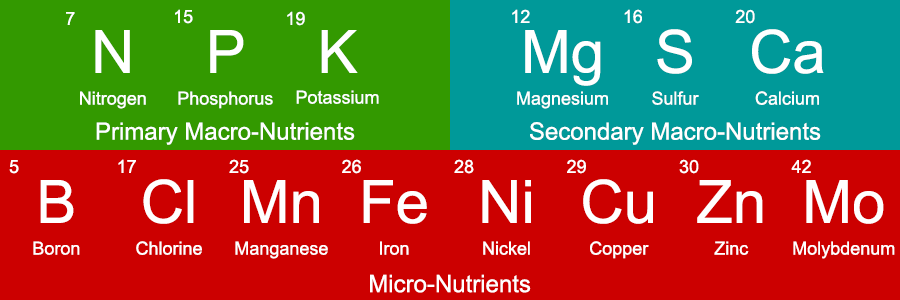
On the other hand, micro-nutrients are trace elements that plants need in smaller quantities but are equally essential for their overall health. These micro-nutrients include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), molybdenum (Mo), boron (B), and chlorine (Cl). Despite being required in smaller amounts, micro-nutrients play crucial roles in enzyme activation, photosynthesis, and overall metabolic processes.
Absorption of Nutrients in Hydroponic Systems
In a hydroponic system, plants absorb nutrients differently compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. Instead of searching for nutrients in the soil, the plant’s roots are directly exposed to the nutrient solution. This direct access allows for efficient nutrient uptake, as plants can readily absorb the required elements.
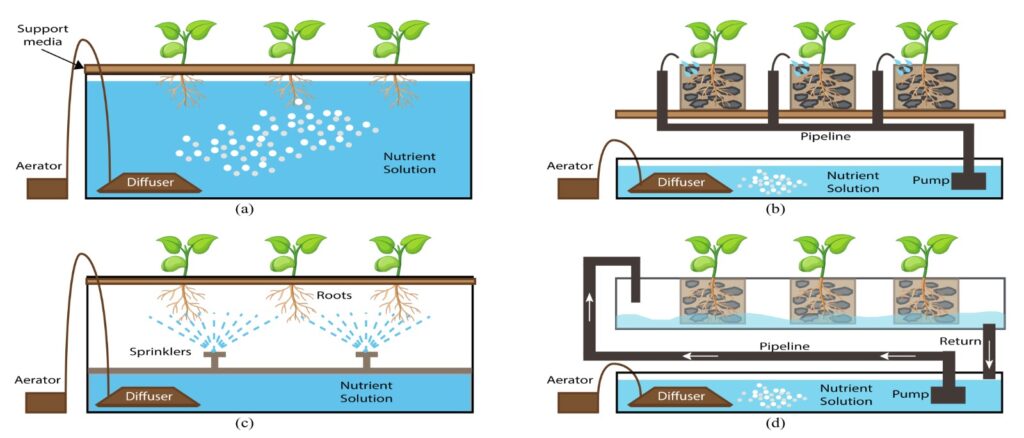
The nutrient solution is designed to provide the necessary nutrients in a readily available form, ensuring that plants receive optimal nutrition without exerting excess energy on root growth. This efficiency enables plants to allocate more resources to above-ground growth, resulting in faster growth rates and higher yields.
Importance of pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC) Levels
Maintaining proper pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels in the nutrient solution is crucial for the success of a hydroponic system. pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of the solution, while EC measures its electrical conductivity, which indicates the concentration of dissolved nutrients.
pH levels affect nutrient availability, as different elements are absorbed optimally within specific pH ranges. Deviations from the ideal pH can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, hindering plant growth and health. Monitoring and adjusting pH levels accordingly are essential for ensuring nutrient uptake efficiency.
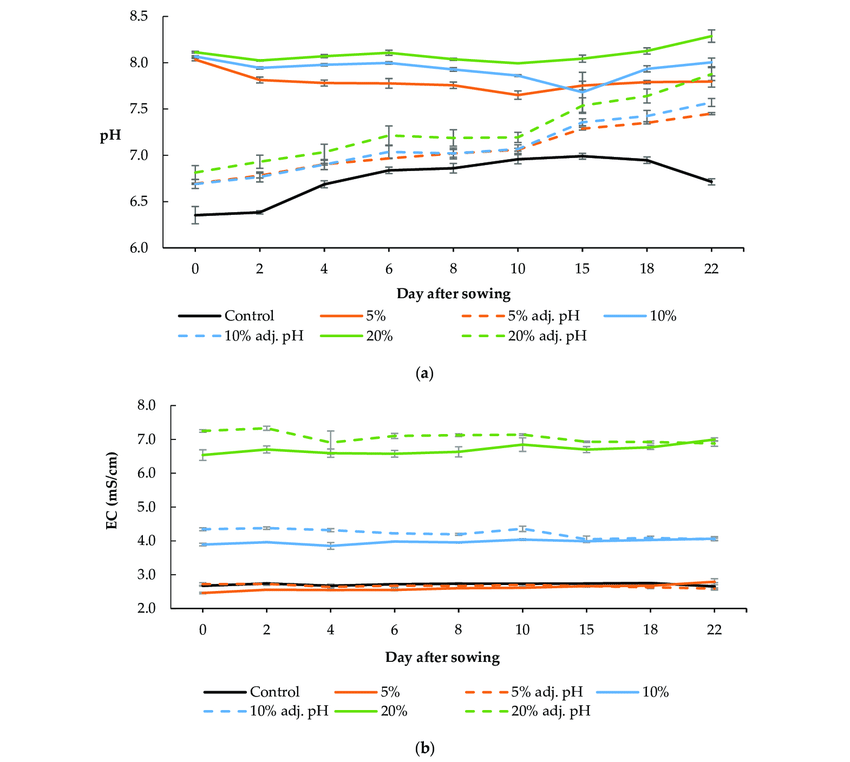
Electrical conductivity (EC) levels, on the other hand, provide insights into the nutrient concentration in the solution. It helps maintain the proper balance of nutrients, preventing nutrient imbalances that can impede plant growth or lead to nutrient toxicity. Regular monitoring and adjustment of EC levels enable precise control over nutrient delivery, promoting optimal plant development.
Understanding the intricacies of a hydroponic nutrient solution is essential for achieving successful hydroponic gardening. By providing plants with precisely balanced macro and micro-nutrients, while also monitoring pH and EC levels, you can create an environment where plants thrive and flourish.
Types of Hydroponic Nutrient Solutions
Now that we have a solid understanding of the importance of nutrient solutions in hydroponics let’s explore the different types available. From liquid solutions to powdered options and even organic alternatives, there’s a wide array of choices to suit your gardening preferences and goals.
Liquid Nutrient-Solutions
Pre-mixed Nutrient Solutions
Pre-mixed nutrients are a popular choice among hydroponic enthusiasts, especially beginners. These solutions come ready to use, conveniently mixed with the necessary macro and micro-nutrients in the proper ratios. They offer convenience and ease of use, as you simply need to dilute the solution in water according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Pre-mixed solutions are often formulated to cater to specific plant types or growth stages, making it simpler for beginners to provide the appropriate nutrition.
Two-part Nutrient Solutions
Two-part nutrients consist of two separate components: Part A and Part B. Each part contains a different set of nutrients, usually divided into the essential macro and micro-nutrients. This approach allows for greater control over nutrient ratios and allows you to customize the nutrient solution based on your plant’s specific requirements. By adjusting the proportions of Part A and Part B, you can fine-tune the nutrient levels to achieve optimal growth and maximize yields.
Single-part Nutrient Solutions
Single-part nutrients, as the name suggests, are a complete blend of all necessary nutrients in a single bottle. These solutions are convenient and straightforward to use, as you don’t need to mix separate parts. While they may offer less flexibility compared to two-part solutions, single-part nutrients are suitable for growers who prefer a more straightforward approach to nutrient management.
Powdered Nutrient Solutions
Pros and Cons of Powdered Nutrient Solutions
Powdered nutrients come in the form of dry powders that you mix with water to create a nutrient solution. One advantage of powdered solutions is their long shelf life, as they remain stable for extended periods. They are also more cost-effective in terms of shipping and storage, as the water content is eliminated. However, mixing powdered nutrients requires careful attention to ensure proper dissolution and even distribution of nutrients.
How to Properly Mix and Dissolve Powdered Nutrient Solutions
When using powdered nutrient, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Typically, you’ll need to dissolve the powder in a specific amount of water, ensuring thorough mixing to prevent nutrient imbalances. To ensure proper dissolution, start by adding water to the mixing container, then gradually add the powdered nutrients while stirring continuously. Monitor the solution closely to ensure complete dissolution before using it in your hydroponic system.
Organic Nutrient Solutions
Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources and contain organic compounds rather than synthetic chemicals. These solutions typically utilize plant or animal-based materials, such as compost, seaweed, fish emulsion, or other organic substances, as the primary source of nutrients. Organic nutrients aim to promote sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in hydroponics.
One of the main benefits of organic nutrient solutions is their ability to enhance soil health and fertility over time, which can contribute to better plant growth. They also tend to be gentler on plants, reducing the risk of nutrient burn or imbalances. Additionally, organic nutrients align with the principles of organic gardening, making them an appealing option for environmentally conscious growers.
However, organic nutrients can be more challenging to source and may require more frequent monitoring and adjustment to maintain nutrient levels. They also tend to have a shorter shelf life compared to their synthetic counterparts. It’s important to note that certification standards for organic hydroponic nutrients may vary in different regions, so it’s crucial to ensure the products you choose meet the required organic standards.
When using organic nutrients, it’s essential to consider the specific nutrient requirements of your plants and ensure the organic solution provides adequate levels of essential macro and micro-nutrients. Supplementing with additional organic additives, such as compost teas or natural amendments, can further enhance the nutrient content and microbial activity in the hydroponic system.
Ultimately, the choice between organic and synthetic nutrients comes down to personal preference, environmental considerations, and the specific goals of your hydroponic garden.
Choosing the right type of nutrient is a critical aspect of successful hydroponic gardening. Whether you opt for pre-mixed liquid solutions for convenience, two-part solutions for precise control, powdered solutions for extended shelf life, or organic solutions for sustainable practices, each type offers its unique benefits.
Understanding the pros and cons of different nutrient solutions allows you to make an informed decision based on your gardening preferences, goals, and environmental considerations. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when mixing and using nutrient solutions to ensure proper nutrient balance and optimal plant growth.
In the next section of our ultimate guide, we will know about different elements of hydroponic nutrients and their importance for plants. Get ready to unlock the secrets of nutrient management and take your hydroponic gardening to new heights of success!
Essential Nutrients for Plants
To achieve optimal plant growth and development in hydroponics, it’s crucial to provide plants with the essential nutrients they need. These nutrients can be broadly categorized into macronutrients and micro-nutrients, each playing a vital role in supporting various aspects of plant health.
Macro-nutrients
Nitrogen (N):
Nitrogen is a crucial macronutrient that supports vegetative growth, chlorophyll production, and overall plant vigour. It is an essential component of amino acids, proteins, and enzymes involved in various metabolic processes.
Nitrogen promotes leaf and stem growth, giving plants their lush, green appearance. It is essential for the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids.
Phosphorus (P):
Phosphorus is essential for root development, flower formation, and fruit production. It plays a critical role in energy transfer and is a key component of DNA, RNA, and ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Phosphorus is critical for root development, energy transfer, and the formation of flowers and fruits. It aids in the transfer of genetic information and is involved in various metabolic processes.
Potassium (K):
Potassium is involved in numerous physiological processes, including osmoregulation, enzyme activation, and the synthesis of carbohydrates and proteins. It promotes overall plant health, disease resistance, and fruit quality.
Potassium contributes to overall plant health, disease resistance, and the regulation of water uptake and transpiration. It plays a role in enzyme activation and the synthesis of carbohydrates.
Calcium (Ca):
Calcium is essential for cell wall development, proper root growth, and nutrient uptake. It also helps in preventing disorders like blossom end rot in tomatoes and tip burn in lettuce.
Calcium strengthens cell walls, improves root development, and aids in nutrient uptake and transport within the plant.
Magnesium (Mg):
Magnesium is a central component of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis. It is involved in energy production, enzyme activation, and the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Magnesium is necessary for chlorophyll production and photosynthesis. It also activates enzymes involved in energy metabolism.
Sulfur (S):
Sulfur is necessary for the synthesis of amino acids, vitamins, and enzymes. It contributes to plant growth, root development, and chlorophyll production.
Sulfur is a component of certain amino acids, vitamins, and coenzyme. It is essential for protein synthesis, enzyme activity, and overall plant growth.
Micro-nutrients
Iron (Fe):
Iron is vital for chlorophyll formation and plays a crucial role in electron transport within the photosynthetic process. It is necessary for enzyme activation and overall plant growth.
Iron is crucial for chlorophyll synthesis, enabling plants to carry out photosynthesis and produce energy. It is also involved in the formation of enzymes and plays a role in electron transfer reactions.
Manganese (Mn):
Manganese is involved in various enzyme systems and contributes to photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen metabolism. It also plays a role in the activation of several enzymes.
Manganese participates in photosynthesis, assisting in the breakdown of water molecules and the production of oxygen. It also activates enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and nitrogen.
Zinc (Zn):
Zinc is essential for enzyme activity, hormone regulation, and protein synthesis. It aids in the production of auxins, which are vital for root development and overall growth.
Zinc plays a vital role in enzyme activity, hormone regulation, and the synthesis of proteins and DNA. It is necessary for proper growth and development.
Copper (Cu):
Copper is necessary for enzyme activation and electron transport. It plays a role in various physiological processes, including photosynthesis, lignin synthesis, and carbohydrate metabolism.
Copper is involved in various enzyme systems and plays a role in photosynthesis, respiration, and lignin synthesis. It aids in the utilization of iron and is essential for overall plant growth.
Molybdenum (Mo):
Molybdenum is a cofactor for several enzymes involved in nitrogen metabolism. It facilitates the conversion of nitrate to ammonia, a crucial step in the utilization of nitrogen by plants.
Molybdenum facilitates nitrogen fixation and helps convert nitrate into a usable form for plants. It is involved in enzyme activity and plays a role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds.
Boron (B):
Boron is involved in cell wall formation, pollen germination, and fruit development. It is essential for the transport and utilization of sugars and the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Boron is necessary for cell division, pollen germination, and the movement of sugars within the plant. It also influences calcium uptake and utilization.
By providing the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients, hydroponic gardeners can ensure that plants have all the essential elements they need for healthy growth, optimal yield, and robust resistance to pests and diseases.
In the next section of our ultimate guide, we will discuss how to manage nutrient solutions to provide plants with the precise nutrient ratios they require at different growth stages. Get ready to become a master of nutrient management and unlock the full potential of your hydroponic garden!
Nutrient Solution Management
Proper management of your hydroponic nutrient is crucial for ensuring healthy plant growth and maximizing yields. In this section, we will explore the importance of nutrient solution ratios, the ideal NPK ratio for different growth stages, common nutrient solution problems, and practical tips for preventing and addressing these issues.
Importance of Nutrient Solution Ratios for Different Stages of Plant Growth
As your plants progress through different growth stages, their nutrient requirements change. During the vegetative stage, plants focus on foliage development and require higher levels of nitrogen (N) to promote lush green growth. In contrast, the flowering or fruiting stage demands a shift towards higher phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) levels to support flower formation, fruit development, and overall reproductive growth.
Maintaining the appropriate nutrient ratios is essential to meet your plants’ changing needs as they transition from vegetative to flowering stages. Monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels accordingly ensures that your plants receive the optimal nutrition for each growth phase, leading to healthy and productive crops.
NPK Ratio for Vegetative State and Flowering Stage
The NPK ratio refers to the relative proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in a nutrient solution. During the vegetative stage, a balanced NPK ratio of around 3:1:2 is commonly recommended. This ratio provides sufficient nitrogen for vigorous leaf and stems growth while promoting overall plant health.
As plants transition into the flowering or fruiting stage, shifting towards higher phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) ratio is necessary. A typical NPK ratio for this stage could range from 1:3:4 to 1:4:6, emphasizing phosphorus and potassium to support the development of flowers, fruits, and robust root systems.
Tips for Adjusting Nutrient Solution Ratios
Start with a balanced nutrient solution:
Begin by using a commercially available balanced nutrient that provides a well-rounded mix of macro nutrients and micronutrients. This serves as a baseline for further adjustments.
Monitor plant response:
Observe how your plants respond to the nutrient solution by examining their growth, colour, and overall health. Adjust the nutrient solution ratios if you notice any signs of deficiency or excess.
Adjusting NPK ratios:
Depending on the growth stage, modify the NPK ratio to provide the appropriate nutrients. Increase nitrogen levels for vegetative growth, and adjust phosphorus and potassium levels for flowering and fruiting stages.
Consult plant-specific guidelines:
Different plants have unique nutrient requirements. Refer to plant-specific guidelines or consult reliable sources to determine the ideal nutrient ratios for specific plant species.
Consider water quality:
The quality of your water source can impact nutrient availability and ratios. If your water contains high levels of certain elements, such as calcium or magnesium, you may need to adjust your nutrient solution ratios accordingly to account for these elements. Conduct a water analysis to identify any potential imbalances and make necessary adjustments.
Keep records and track changes:
Maintain a record of the nutrient solution ratios and any adjustments you make. This allows you to track the effects of different ratios on plant growth and make informed decisions for future nutrient management.
Regularly monitor nutrient levels:
Test the nutrient solution regularly using pH and electrical conductivity (EC) meters to ensure that the nutrient ratios remain within the desired range. Adjust nutrient concentrations as needed to maintain optimal levels.
Seek expert advice:
If you’re unsure about adjusting nutrient solution ratios or encounter persistent issues, consult with hydroponic experts or experienced growers. They can provide valuable insights and guidance based on their expertise.
Common Nutrient Issues: Causes and Solutions
Nutrient Toxicities:
Nutrient toxicities can occur when nutrient levels in the solution surpass the plants’ tolerance. Symptoms may include leaf burn, stunted growth, or discolouration. To address this issue, reduce the nutrient concentration by diluting the solution with fresh water and adjusting the nutrient ratios as needed. Regular monitoring of nutrient levels is crucial to prevent toxicities.
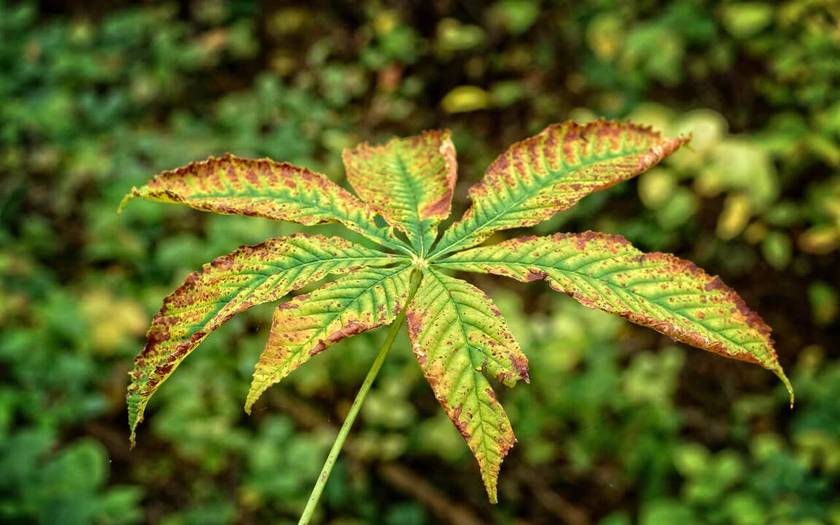

(Image source: Homegrown cannabis.co)
Nutrient Deficiencies:
Nutrient deficiencies manifest as yellowing or chlorosis of leaves, stunted growth, or poor overall plant health. Identifying the specific nutrient lacking can help address the issue. Adjust the nutrient solution by adding the deficient nutrient in the appropriate form and concentration. Regularly monitor nutrient levels and adjust as necessary to prevent deficiencies.
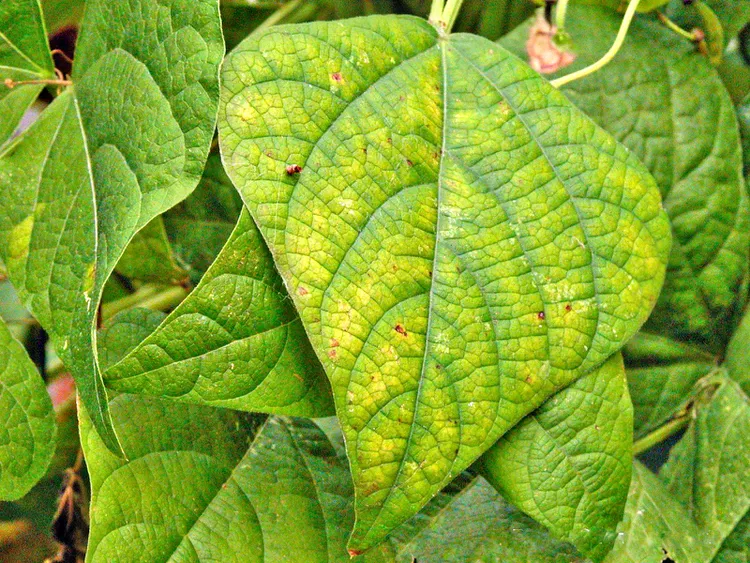

pH Imbalances:
pH imbalances in the nutrient that can affect nutrient availability to plants. Acidic conditions (low pH) can lead to nutrient lockout, while alkaline conditions (high pH) can cause nutrient deficiencies. Regularly monitor the pH level and adjust it using pH-up or pH-down solutions to maintain the desired range for optimal nutrient absorption.
Salt Buildup:
Over time, salts from the nutrient solution can accumulate in the system, leading to salt buildup. This can hinder nutrient absorption and affect plant health. Regularly flush the system with clean, pH-balanced water to remove excess salts and prevent buildup. Periodic maintenance and cleaning of the system are essential for preventing salt accumulation.
| Know more about “How to Troubleshoot Problems in Hydroponic Nutrients Solution“ |
Preventing Nutrient Solution Problems
To maintain a healthy nutrient and prevent problems, consider the following tips:
Regular Monitoring of Nutrient Solutions:
Monitor nutrient levels, pH, and EC regularly using appropriate testing tools. This allows you to catch any imbalances or deviations early on and make timely adjustments.
Tools for Measuring pH and EC Levels:
Invest in reliable pH and EC meters or test kits to accurately measure and monitor the pH and electrical conductivity levels of your nutrient solution. These tools provide valuable insights into the nutrient status and allow for precise adjustments.
Maintaining Proper pH and Nutrient Levels:
Adjust the pH of the nutrient solution as needed to maintain the optimal range for nutrient absorption. Monitor and adjust nutrient levels to match the plant’s specific growth stage requirements. Regularly check and adjust nutrient solution ratios to ensure plants receive the right balance of essential elements.
| Know more about “The Importance of pH in Hydroponic Nutrient Solutions“ |
Maintaining a Clean and Sterile System:
Keep your hydroponic system clean and free from debris, algae, and pathogens. Regularly clean and sanitize the reservoir, pumps, and irrigation components to prevent the growth of harmful organisms. Here are some practices to follow:
- Regularly clean and sanitize all hydroponic equipment, including reservoirs, pumps, and irrigation systems. This helps prevent the growth of algae, bacteria, and fungi that can negatively impact plant health.
- Use sterile growing media, such as rock wool or coco coir, to minimize the risk of introducing pathogens into the system.
- Practice good hygiene by washing your hands thoroughly before handling any hydroponic components or plants. This reduces the chances of introducing contaminants into the system.
- Implement a proper water management strategy to prevent the buildup of impurities and mineral deposits. Use filtered or purified water to avoid introducing unwanted substances into the nutrient.
- Periodically flush the system with clean water to remove any accumulated salts, residues, or excess nutrients.
By maintaining a clean and sterile hydroponic system, you create an environment that promotes healthy plant growth and minimizes the risk of nutrient problems.
Proper Water Quality:
The quality of water used to prepare the nutrient solution can impact plant health. Use filtered or purified water to avoid contaminants and excessive mineral content. If using tap water, test it for pH and mineral composition and make necessary adjustments to create an optimal growing environment.
Consistent Monitoring of Plant Health:
Observe your plants closely for any signs of nutrient deficiencies, toxicities, or other stress symptoms. Early detection allows for prompt action and prevents issues from escalating. Regularly inspect leaves, stems, and roots to identify any potential problems.
Regular monitoring, proper pH adjustment, and nutrient supplementation based on plant requirements are key to maintaining a well-balanced nutrient solution. Additionally, practicing good hygiene and keeping the hydroponic system clean and sterile contribute to the overall health of your plants.
Advanced Techniques for Nutrient Solution Ratio Optimization
In the world of hydroponic farming, there are advanced techniques that can take your nutrient solution management to the next level. These techniques allow you to explore alternative nutrient sources, utilize supplemental nutrient solutions, and customize nutrient solution ratios to meet the specific needs of your plants. Let’s dive into these strategies and discover how they can enhance your hydroponic gardening experience.
Alternative Nutrient Sources
While pre-mixed nutrient solutions are commonly used in hydroponics, there are alternative nutrient sources you can explore to provide a diverse range of essential elements to your plants. Here are a few examples:
Compost Tea:
Compost tea is a nutrient-rich solution made by steeping compost in water. It provides a natural source of micro-nutrients, beneficial microorganisms, and organic matter that can enhance plant growth and soil health.
Fish Emulsion:
Fish emulsion is a liquid fertilizer made from decomposed fish. It contains a balanced mix of macro nutrients and micronutrients, making it an excellent organic alternative to synthetic nutrient solutions.
Seaweed Extract:
Seaweed extract is derived from seaweed and is rich in trace elements, growth hormones, and beneficial compounds that promote plant growth, root development, and overall plant health.
Incorporating alternative nutrient sources into your hydroponic system can introduce additional nutrients and organic matter, promoting a more diverse and balanced nutrient profile for your plants.
Supplemental Nutrient Solutions
Supplemental nutrients can be used alongside your primary nutrients to address specific nutrient deficiencies or boost plant growth during critical stages. Here are a couple of examples:
Cal-Mag Solution:
Calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) are essential nutrients for plant growth. If your primary nutrient solution lacks these elements, you can prepare a separate calcium-magnesium (cal-mag) solution and add it as a supplement to ensure your plants receive adequate levels of these nutrients.
Bloom Boosters:
During the flowering and fruiting stages, plants require higher levels of phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). Bloom boosters are supplemental nutrient solutions specifically formulated to provide elevated levels of these nutrients, enhancing flower formation and fruit development.
Supplemental nutrients can be tailored to address specific plant needs and growth stages, allowing you to fine-tune nutrient ratios and optimize plant performance.
Customizing Nutrient Solution Ratios
Every plant has unique nutritional requirements, and customizing nutrient solution ratios can help meet their specific needs. Here are some considerations when customizing nutrient solution ratios:
Plant Species and Growth Stage:
Different plant species have varying nutrient preferences, so research the specific nutrient requirements of your chosen plants. Additionally, adjust nutrient ratios based on the growth stage.
Plant Health Monitoring:
Regularly monitor the health of your plants to identify any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances. By observing visual cues such as leaf colour, growth patterns, and overall plant vitality, you can make informed adjustments to nutrient solution ratios to address specific nutrient needs.
Experimentation and Observation:
Hydroponic gardening is a dynamic process, and each system may have unique characteristics. Experiment with different nutrient solution ratios and observe how your plants respond. Keep detailed records to track the effects of different ratios on plant growth, yield, and overall health.
Professional Guidance:
If you’re unsure about customizing nutrient solution ratios or encounter persistent nutrient-related issues, seek guidance from hydroponic experts, nutrient providers, or experienced growers. They can offer insights based on their expertise and help you optimize nutrient ratios for your specific plant species and growing conditions.
Customizing nutrient solution ratios is a powerful tool that allows you to fine-tune your hydroponic system and cater to the unique needs of your plants. By exploring alternative nutrient sources, incorporating supplemental nutrient solutions, and customizing ratios based on plant species and growth stages, you can create an optimized environment for maximum plant health and productivity.
Remember, nutrient solution ratio optimization is an ongoing process that requires attention, observation, and adjustments. As you gain experience and understanding of your plants’ nutritional requirements, you can refine and improve your nutrient management strategies.
Thats It!
Congratulations! You have reached the end of our ultimate guide to hydroponic nutrient solutions. We’ve covered a lot of ground, from understanding the components and types of nutrient solutions to optimizing ratios and exploring advanced techniques. Now, let’s recap the key points and leave you with some encouragement and final thoughts.
Throughout this guide, we’ve emphasized the importance of nutrients in hydroponic systems. These solutions provide essential elements that plants need to grow and thrive without soil. By carefully managing nutrient ratios, monitoring pH and EC levels, and addressing common problems, you can create an optimal environment for your plants to flourish.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrient solutions. Every setup and plant type is unique, so don’t be afraid to experiment and find what works best for you. Hydroponic gardening is a journey of discovery, and the joy lies in exploring different nutrient sources, adjusting ratios, and witnessing the incredible growth of your plants.
As you embark on your hydroponic adventure, embrace the inevitable challenges that may come your way. But fear not, for with knowledge and a touch of humour, you can overcome any hurdle. When life gives you nutrient deficiencies, turn it into a nutrient-efficient! And if pH imbalances knock at your garden’s door, show them who’s boss with a pH-adjusting dance-off!
In all seriousness, nutrients are the lifeblood of your hydroponic system. They provide the nourishment your plants need to reach their full potential. So, pay attention to the needs of your plants, stay vigilant with monitoring, and don’t hesitate to seek guidance from fellow growers or experts along the way.
With dedication, curiosity, and a little bit of humour, your hydroponic garden will flourish, providing you with a bountiful harvest and a sense of accomplishment like no other. So, grab your watering can, put on your gardening gloves, and get ready to dive into the exciting world of hydroponics!
Happy growing, and may your plants thrive and bring you joy on this extraordinary journey.











This Post Has 2 Comments
This design is wicked! You most certainly know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Excellent job. I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
There is definately a lot to find out about this topic. I really like all of the points you have made.