Table of Contents
Hydroponics is a cultivation method that enables plants to grow in a controlled environment, with water serving as the primary medium for delivering essential nutrients. By eliminating the need for soil, hydroponics offers several advantages. First and foremost, it allows for optimal nutrient absorption by plants, leading to accelerated growth rates and increased crop yields. Additionally, hydroponics conserves water by recycling and reusing the nutrient solution, making it a more sustainable alternative to traditional soil-based farming. Moreover, the controlled environment minimizes the risk of pests, diseases, and weeds, reducing the need for pesticides and herbicides. Lastly, hydroponic systems can be implemented in various settings, including urban areas, enabling year-round cultivation and local food production.
The concept of hydroponics traces back to ancient civilizations such as the Hanging Gardens of Babylon and the Aztecs’ floating gardens. However, it wasn’t until the mid-19th century that modern hydroponics emerged as a scientific practice. In 1860, German botanist Julius von Sachs conducted groundbreaking experiments on plant nutrition in water cultures, establishing the foundation for hydroponic research. Over the years, hydroponics has evolved, with notable advancements made by researchers like Dr. William Frederick Gericke in the 1920s, who coined the term “hydroponics” and conducted extensive studies on soilless cultivation. Since then, hydroponics has gained popularity worldwide and continues to evolve with technological advancements.

As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food is increasing at an alarming rate. Hydroponic technology holds immense potential to address this challenge by maximizing crop yields in limited spaces. Unlike traditional agriculture, hydroponics allows plants to grow closer together, utilizing vertical space effectively. This vertical farming approach can significantly increase the production capacity per square meter of land.
Selecting the appropriate hydroponic system is crucial for ensuring the success of your gardening endeavours. Different hydroponic systems have varying requirements and characteristics, making it essential to consider several factors. By choosing the right system, you can optimize plant growth, simplify maintenance, and achieve the desired results.

Different Types of Hydroponic Systems
There are mainly 6 different types of hydroponic systems, which are commercially used. Those 6 hydroponic systems can be broadly categorized into two groups: those without soil (true hydroponics) and those utilizing soilless media(media-based hydroponics). The classification is like-
True Hydroponics:- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Aeroponics, and Deep Water Culture (DWC).
Media-Based Hydroponics:- Drip System, Ebb & Flow, and Wick System.
In this section, we will provide an overview of the various hydroponic systems and explore their working principles, pros and cons, suitable plant types, and factors to consider when choosing each system.
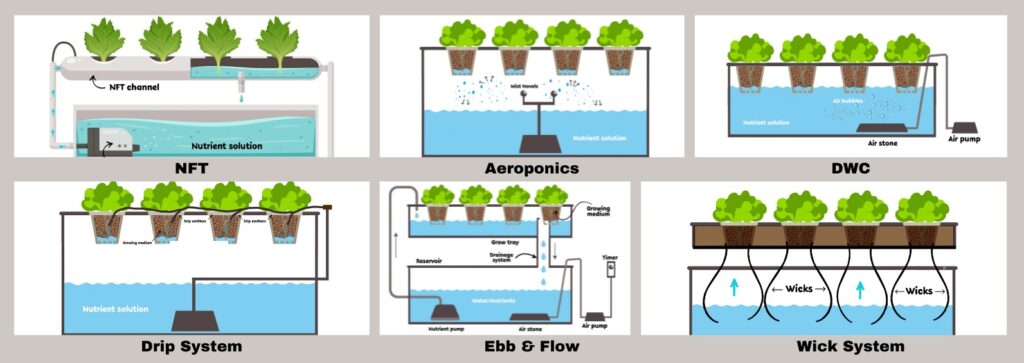
1. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
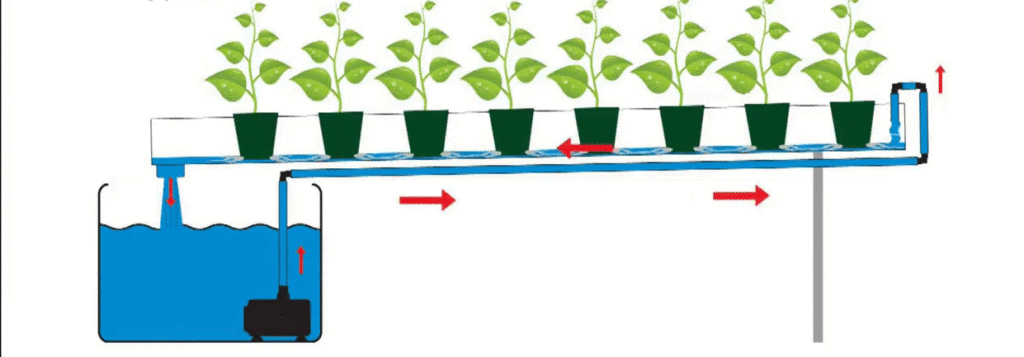
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is a popular hydroponic system that involves a continuous flow of a thin film of nutrient solution over plant roots.
Description and Working Principle
NFT relies on gravity to deliver the nutrient solution, which is pumped to the highest end of the sloping channel or tray. The nutrient solution then flows over the roots, gradually reaching the lower end of the system. The roots absorb the required nutrients and oxygen from the thin film of the solution, while the excess solution is collected and returned to the reservoir for recirculation.
Pros and Cons
NFT offers several advantages, including efficient nutrient delivery, water conservation, and effective use of space. The continuous flow of nutrient solution ensures that plants receive a consistent supply of nutrients, promoting healthy growth. NFT also minimizes water usage since the thin film of the solution is continuously recycled. However, one drawback of NFT is its susceptibility to power outages or pump failures, which can disrupt the flow of nutrients and harm plant health.
Suitable Plant Types for NFT Systems
NFT systems are particularly well-suited for cultivating leafy greens, herbs, and small-statured plants with shallow root systems. Plants like lettuce, spinach, basil, and other similar varieties thrive in NFT setups.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an NFT System/ How to choose an NFT system
When selecting an NFT system, consider factors such as the size of the channel or tray, the slope of the system, and the availability of a reliable power source. It is important to ensure that the system is properly designed to prevent any interruptions in the nutrient flow.

2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC), also known as the reservoir method, is a hydroponic system where plant roots are immersed in a nutrient solution. The plants are supported by floating platforms or net pots, allowing their roots to absorb nutrients directly from the oxygenated solution.
Description and Working Principle
In a DWC system, plants are placed in containers filled with the nutrient solution. Air stones or diffusers are used to oxygenate the solution, providing a constant supply of oxygen to the roots. The plant roots grow and spread in the nutrient-rich solution, taking up the necessary nutrients for growth.
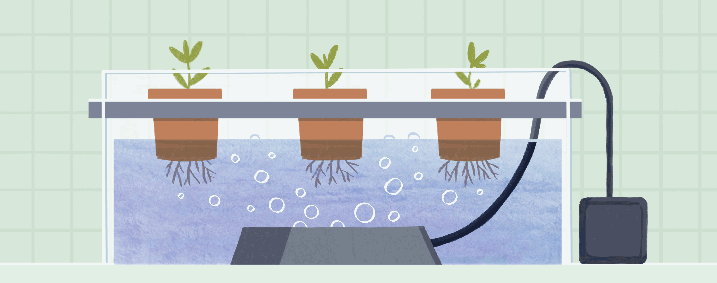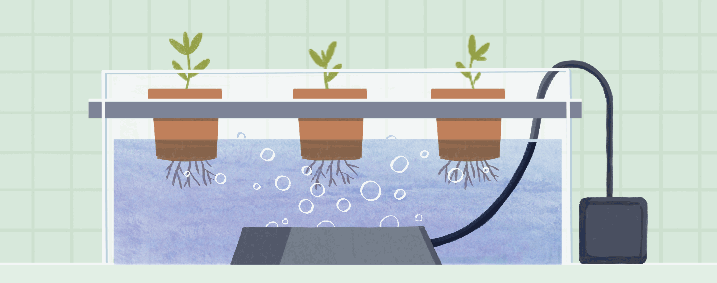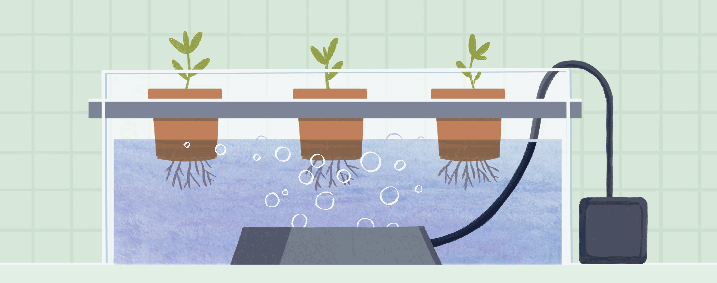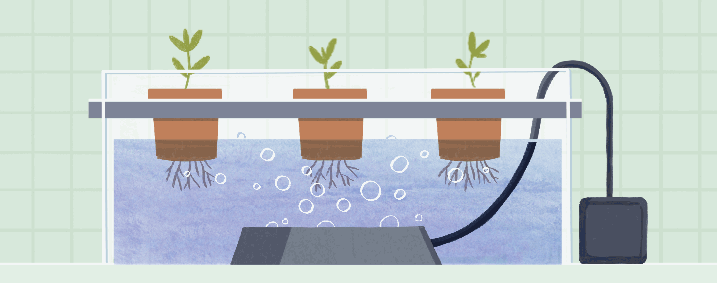
Pros and Cons
DWC offers simplicity and ease of use, making it an ideal system for beginners. The direct exposure of roots to the nutrient solution facilitates efficient nutrient uptake and promotes rapid plant growth. Additionally, DWC systems require minimal equipment and are relatively low-cost compared to other hydroponic setups. However, maintaining proper oxygenation of the nutrient solution is critical in DWC systems, as inadequate oxygen levels can lead to root rot and plant health issues.
Suitable Plant Types for DWC Systems
DWC systems are well-suited for cultivating a wide range of plants, including leafy greens, herbs, and larger fruiting plants such as tomatoes and peppers. Plants with extensive root systems can benefit from the ample space provided by DWC setups.
Factors to Consider When Choosing DWC System/ How to choose DWC system
When considering a DWC system, factors to consider include the size of the reservoir, the quality and reliability of the air stones or diffusers, and the availability of a backup oxygenation system. Adequate oxygenation is crucial to ensure healthy root development and prevent oxygen deficiencies.
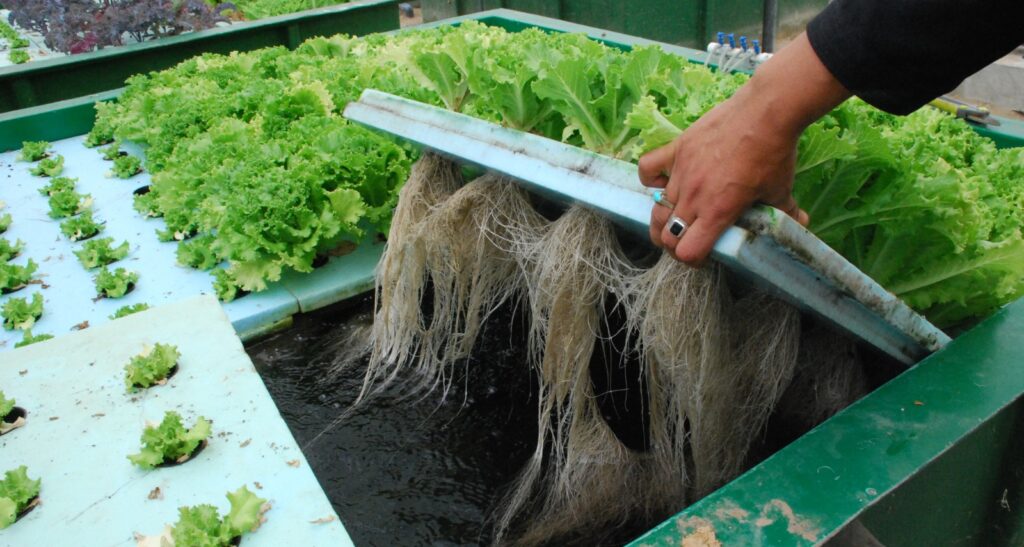

3. Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
The Ebb and Flow system, also known as Flood and Drain, is a hydroponic system that periodically floods the plant roots with a nutrient solution, which is then drained away. This cyclic flooding and draining action provide plants with the necessary nutrients while allowing for oxygenation and root respiration during the drainage phase.
Description and Working Principle
In an Ebb and Flow system, plants are placed in containers or trays filled with a soilless medium such as perlite or coconut coir. At regular intervals, the nutrient solution is pumped into the containers, flooding the medium and saturating the roots. After a specific duration, the excess solution is drained away, allowing the roots to access oxygen.
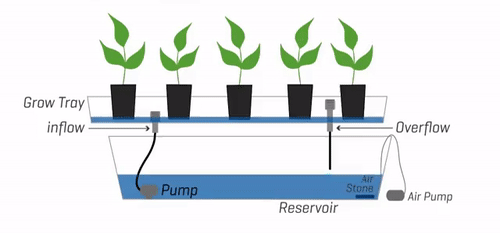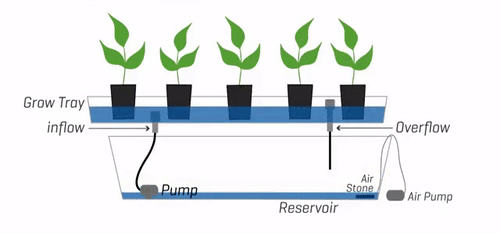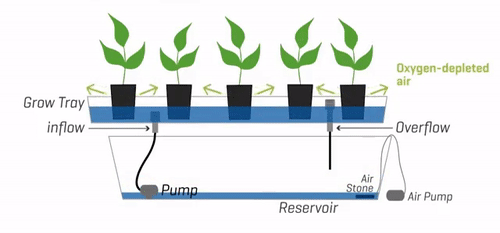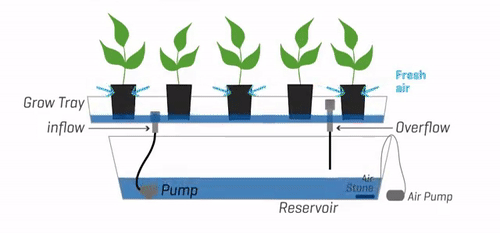
Pros and Cons
The Ebb and Flow system offers flexibility and simplicity in nutrient delivery. The periodic flooding and draining cycles promote healthy root growth and oxygenation, preventing issues like root rot. This system also allows for the use of various growing mediums and accommodates a wide range of plant types. However, the reliance on timers and pumps makes the system vulnerable to potential malfunctions, which can disrupt the flood-drain cycles.
Suitable Plant Types for Ebb and Flow Systems
Ebb and Flow systems are suitable for a variety of plants, including vegetables, herbs, and flowering plants. The flexibility in growing mediums makes it adaptable to different plant types and growth requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Ebb and Flow System/ How to choose Ebb and Flow system
Considerations when selecting an Ebb and Flow system include the size and design of the containers or trays, the frequency and duration of the flood-drain cycles, and the reliability of the timers and pumps. Proper timing and drainage are essential to ensure the roots receive adequate nutrients and oxygen.

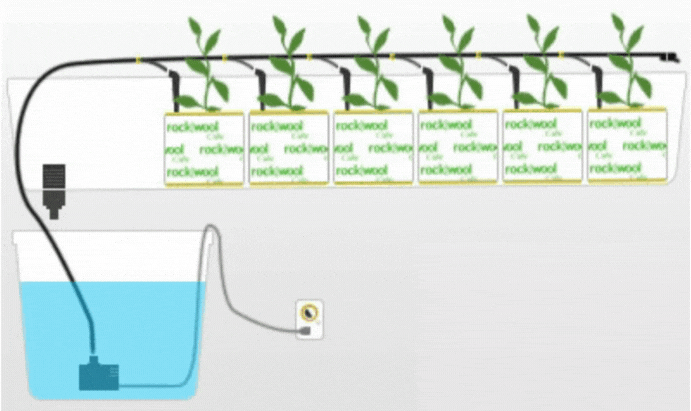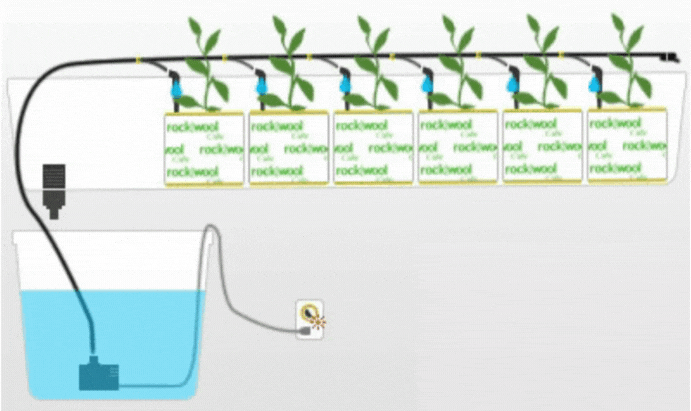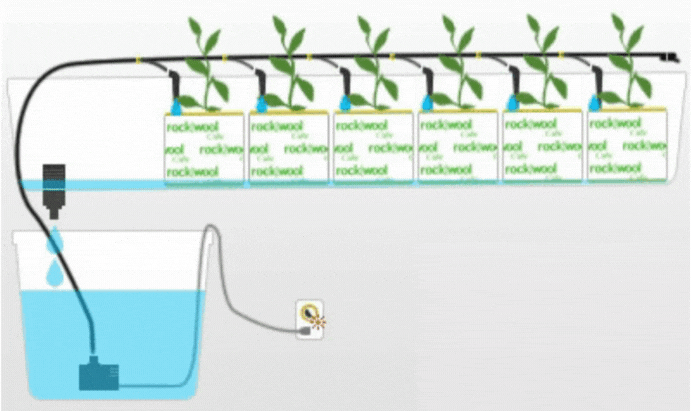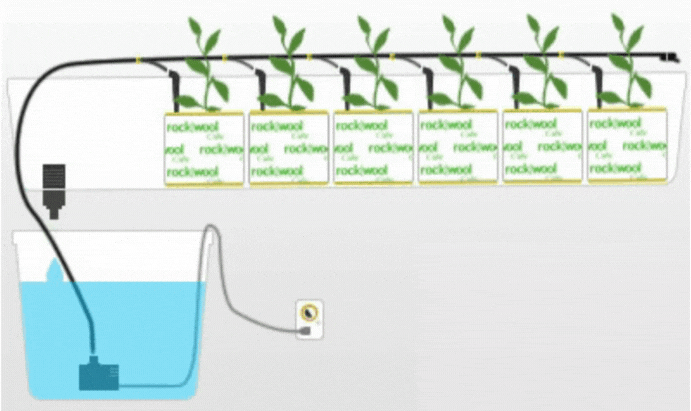
4. Drip System
The Drip system is a widely used hydroponic technique where a nutrient solution is delivered to the plants through a network of tubes and emitters. The nutrient solution is dripped directly onto the growing medium or root zone, ensuring a slow and controlled supply of nutrients.
Description and Working Principle
In a Drip system, a pump delivers the nutrient solution to the main supply line, which is then distributed to individual plants through drip emitters. The emitters release droplets of the nutrient solution onto the growing medium, allowing it to percolate through and reach the roots. The excess solution is collected and recirculated or disposed of.
Pros and Cons
Drip systems offer precise control over nutrient delivery and allow for individual customization of nutrient concentrations for each plant. The slow and controlled dripping action ensures efficient nutrient uptake and minimizes water wastage. Drip systems are versatile and can be adapted to various scales of cultivation. However, the use of emitters and tubes requires regular maintenance to prevent clogging and ensure consistent nutrient flow.
Suitable Plant Types for Drip Systems
Drip systems are suitable for a wide range of plants, including both small and large-scale crops. It is particularly useful for plants with moderate water and nutrient requirements, such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and strawberries.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Drip System/ How to choose Drip system
When considering a Drip system, factors to consider include the type and quality of emitters, the spacing between plants, and the filtration system to prevent clogging. Adequate filtration and regular maintenance of the system are essential for uninterrupted nutrient delivery.

5. Aeroponics
Aeroponics is an advanced hydroponic system that suspends plant roots in the air and mists them with a nutrient-rich solution. This system provides an oxygen-rich environment, promoting rapid and efficient nutrient absorption by the roots.
Description and Working Principle
In an Aeroponics system, plants are typically supported by a platform or structure, and their roots hang freely in the air. A fine mist or aerosolized nutrient solution is periodically sprayed onto the roots, ensuring they remain moist and well-nourished. The mist droplets are small enough to allow efficient nutrient absorption and oxygenation of the roots.

Pros and Cons
Aeroponics offers several advantages, including accelerated plant growth, efficient nutrient uptake, and water conservation. The oxygen-rich environment facilitates optimal root development and nutrient absorption, leading to faster growth rates and increased yields. Additionally, since the roots are exposed to air, there is no need for a growing medium, reducing the risk of disease and simplifying maintenance. However, Aeroponics requires precise control of misting intervals and nutrient concentration, making it a more complex system to manage.
Suitable Plant Types for Aeroponic Systems
Aeroponic systems are suitable for a wide range of plants, including leafy greens, herbs, and larger fruiting plants like tomatoes and cucumbers. It is particularly beneficial for plants that require efficient nutrient absorption and have a short harvest cycle.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Aeroponic System/ How to choose Aeroponic system
Considerations when selecting an Aeroponic system include the misting interval and duration, the quality and reliability of the misting mechanism, and the availability of backup systems in case of power outages or malfunctions. Proper monitoring and control are essential to ensure consistent misting and nutrient delivery.
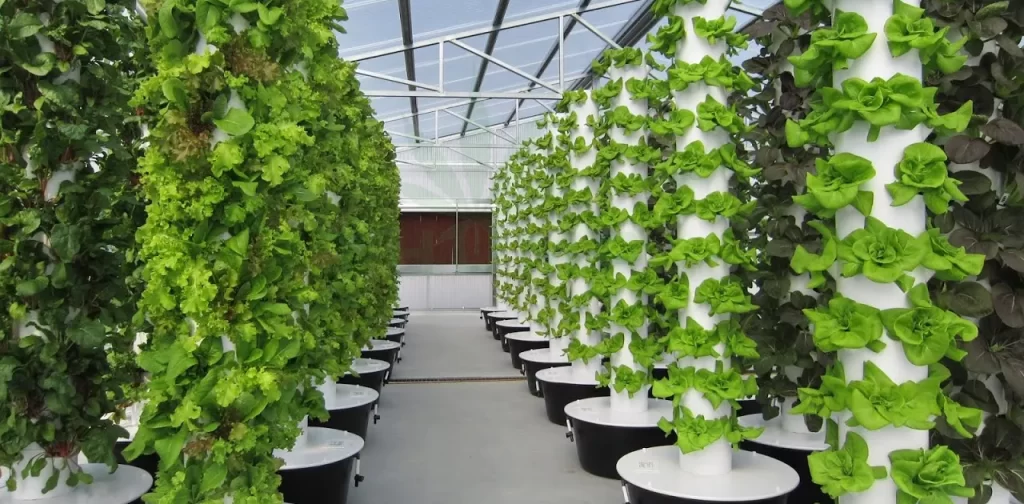

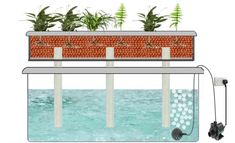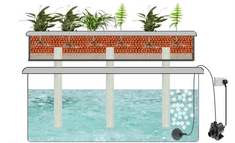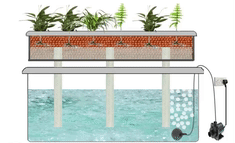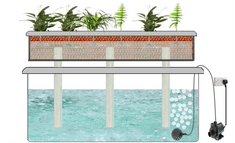
6. Wick System
The Wick system is a passive hydroponic technique that utilizes a wick to deliver the nutrient solution from a reservoir to the plant roots. This system relies on capillary action, allowing the roots to absorb the necessary nutrients without the need for pumps or electricity.
Description and Working Principle
In a Wick system, a wick made of a porous material, such as cotton or felt, is placed in both the nutrient solution reservoir and the growing medium. The wick acts as a conduit, drawing the nutrient solution from the reservoir and delivering it to the roots through capillary action. The roots absorb the nutrients as needed, ensuring proper nourishment.
Pros and Cons
The Wick system is straightforward and low-maintenance, making it an ideal choice for beginners or those with limited resources. It requires no electricity or pumps, relying solely on the natural capillary action. The simplicity of the system also means fewer potential points of failure. However, the Wick system may not be suitable for larger plants or those with higher nutrient demands, as the capillary action may not provide an adequate nutrient supply.
Suitable Plant Types for Wick Systems
The Wick system is best suited for smaller plants with lower nutrient requirements, such as herbs, lettuce, and other leafy greens. These plants can thrive in the Wick system due to their relatively lower nutrient demands.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Wick System/ How to choose Wick system
When considering a Wick system, factors to consider include the choice of wick material, the size and capacity of the nutrient reservoir, and the compatibility of the system with the chosen plant types. It is important to ensure that the wick provides consistent and sufficient nutrient delivery to support healthy plant growth.
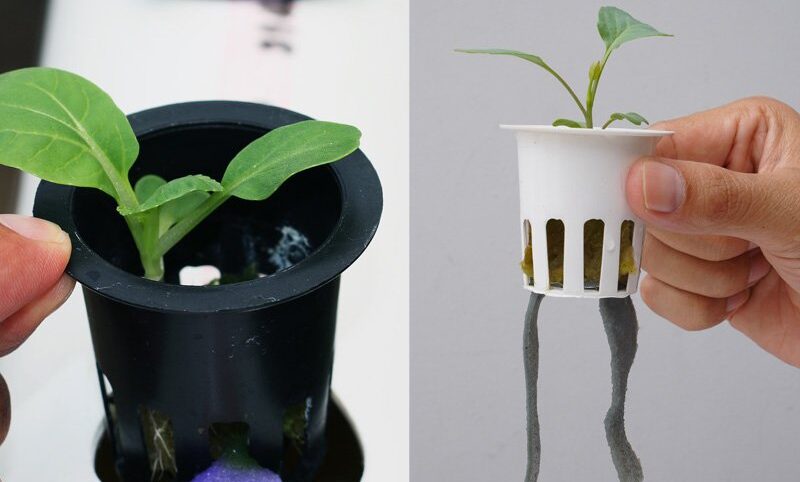

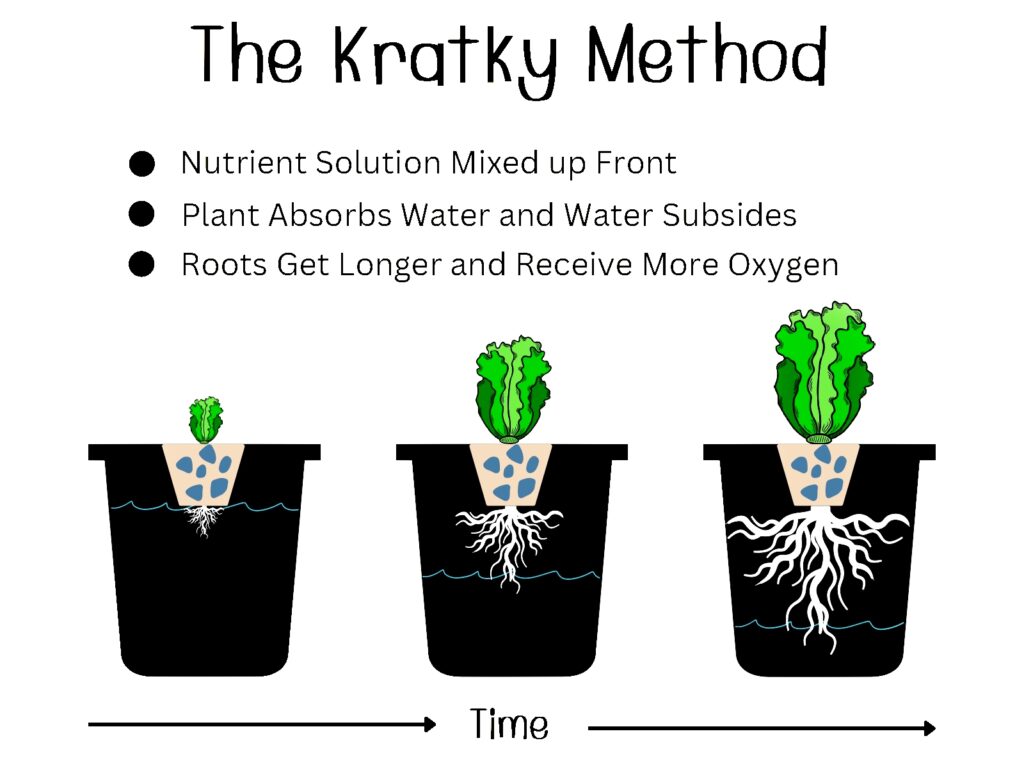
7. Kratky Method (Passive Hydroponics)
The Kratky method, also known as passive hydroponics, is a simple and low-cost hydroponic technique that requires no electricity or pumps. It involves growing plants in a stationary container with a nutrient solution that gradually depletes as the plants consume the nutrients.
Description and Working Principle
In the Kratky method, plants are grown in containers filled with a growing medium, such as perlite or vermiculite, which supports the plant roots. The container is then filled with a nutrient solution, providing initial nourishment. As the plants consume the nutrients and the solution level decreases, air is introduced into the container, allowing the roots to access oxygen.

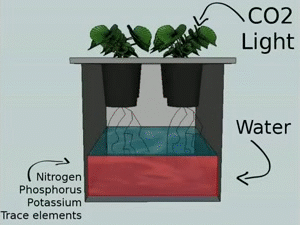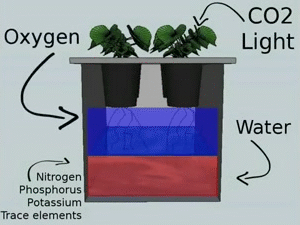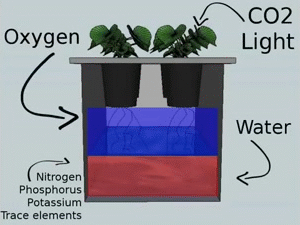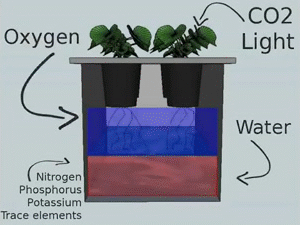
Pros and Cons
The Kratky method offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness, as it requires minimal equipment and maintenance. It is suitable for small-scale gardening and is an excellent option for beginners or those with limited resources. However, this method is best suited for plants with shorter growth cycles, as the nutrient solution may become depleted before longer-term crops reach maturity.
Suitable Plant Types for the Kratky Method
The Kratky method is ideal for growing smaller plants and herbs, including lettuce, basil, and other leafy greens. These plants can thrive in the self-contained system, utilizing the available nutrients until harvest.
Factors to Consider When Choosing the Kratky Method/ How to choose Kratky system
When considering the Kratky method, factors to consider include the container size, the choice of growing medium, and the nutrient solution’s initial concentration. It is crucial to select plants with shorter growth cycles and ensure that the nutrient solution provides sufficient nourishment until harvest.

Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Hydroponic System
When choosing a hydroponic system, several factors should be taken into account to ensure successful and efficient cultivation.
Available Space and Setup Requirements
Evaluate the available space for your hydroponic setup, whether it’s indoors, outdoors, or in a greenhouse. Different systems have varying space requirements, and you need to choose one that fits your available area. Consider the layout, including vertical space, and select a system that optimizes the use of your available space.
Budget and Cost Considerations
Consider your budget for setting up and maintaining a hydroponic system. Some systems may require more initial investment or ongoing costs than others. Assess the cost of equipment, growing mediums, nutrient solutions, and any additional components required for each system.
Desired Plant Types and Growth Characteristics
Identify the specific plants you intend to grow and their growth requirements. Some plants have different nutrient and lighting needs, while others may require more space for root development. Choose a hydroponic system that can accommodate the growth characteristics of your desired plant types.
Required Maintenance and Monitoring
Consider the level of maintenance and monitoring each system demands. Some systems may require regular adjustments, monitoring of pH and nutrient levels, and potential troubleshooting. Assess your availability and commitment to regular maintenance tasks to choose a system that aligns with your capabilities.
Personal Experience and Expertise Level
Evaluate your level of experience and expertise in hydroponics. Some systems may be more suitable for beginners, while others require more advanced knowledge and skills. Consider your familiarity with hydroponic techniques and choose a system that matches your expertise level.
Environmental Factors: Temperature, Humidity, and Light Requirements
Take into account the environmental conditions of your growing space. Different plants have specific temperature, humidity, and light requirements. Ensure the selected system can provide adequate environmental control or can be adapted to suit the needs of your plants.
Comparison of Different Systems’ Pros and Cons
Refer back to the earlier sections outlining the pros and cons of each hydroponic system. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of each system based on your specific needs, preferences, and constraints.
Tips for Making an Informed Decision
- Research and gather information about each hydroponic system to understand their workings and requirements.
- Seek advice from experienced hydroponic gardeners or experts who can provide insights based on their practical knowledge.
- Consider visiting local hydroponic farms or attending workshops to see different systems in action and gain firsthand experience.
How to Choose the Right Hydroponic System
Choosing the right hydroponic system involves a step-by-step decision-making process to ensure the best fit for your needs. Here is a guide to help you make an informed decision:
Step-by-Step Guide for Decision-Making Process
- Assess your available space and determine the location for your hydroponic setup.
- Set a budget for your hydroponic venture, considering both initial setup costs and ongoing expenses.
- Identify the specific plant types you want to grow and their growth characteristics.
- Evaluate your maintenance capabilities and determine the level of time and effort you can commit to your hydroponic system.
- Consider your personal experience and expertise level in hydroponics.
- Take into account the environmental factors of your growing space, such as temperature, humidity, and lighting conditions.
- Compare the pros and cons of different hydroponic systems based on the factors mentioned above.
- Seek advice from experts or experienced hydroponic gardeners to gain valuable insights and recommendations.
- Consider visiting hydroponic farms or attending workshops to see different systems in action and learn from practical demonstrations.
- Make a final decision based on a comprehensive evaluation of all the factors and considerations.
Considering Specific Needs and Preferences
While considering the objective factors, also consider your specific needs and preferences. Think about the aesthetics, scalability, and long-term goals of your hydroponic endeavor. Some systems may align better with your vision and aspirations.
Consulting Experts and Experienced Hydroponic Gardeners
Consulting experts and experienced hydroponic gardeners can provide valuable guidance and advice. They can share their experiences, offer insights into specific systems, and help you make an informed decision. Engaging in online communities or local gardening groups can also provide opportunities to connect with knowledgeable individuals.
Conclusion
Hydroponics is a versatile and innovative approach to modern agriculture, offering numerous benefits such as water efficiency, higher yields, and the ability to grow crops in diverse environments. Choosing the right hydroponic system is crucial for successful and sustainable cultivation. By considering factors such as available space, budget, plant types, maintenance requirements, personal expertise, and environmental conditions, you can make an informed decision.
Each hydroponic system has its advantages and disadvantages, catering to different needs and preferences. Whether you opt for the simplicity of the Wick system, the precision of the Drip system, or the advanced technology of Aeroponics, remember to evaluate the pros and cons and align them with your goals.
Embrace the future of hydroponics and explore the endless possibilities it offers. Experiment with different systems, adapt techniques to suit your requirements and enjoy the rewards of growing fresh, healthy, and sustainable crops throughout the year.

As you embark on your hydroponic journey, remember to continuously learn and stay updated with the latest developments in hydroponic technology and practices. By staying informed and sharing knowledge with fellow enthusiasts, we can collectively contribute to the growth and advancement of hydroponics in agriculture.
Together, let’s cultivate a greener, more sustainable future through the power of hydroponics.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can any plant be grown using hydroponics?
While hydroponics can accommodate a wide variety of plants, some are better suited for specific systems. Leafy greens, herbs, and smaller fruiting plants are generally well-suited for most hydroponic systems. Larger fruiting plants like tomatoes and cucumbers thrive in systems that provide adequate support and nutrient delivery. It is essential to choose plant types that align with the capabilities and requirements of the selected hydroponic system.
2. Is hydroponics suitable for beginners?
Yes, hydroponics can be suitable for beginners, especially with simpler systems like the Wick method or Kratky method. These systems are relatively low-maintenance and require minimal equipment. They provide an excellent entry point for beginners to learn the basics of hydroponics. However, it is important to start with proper research, gain knowledge, and seek guidance from experienced gardeners to ensure successful cultivation.
3. Do hydroponic systems require a lot of maintenance?
The level of maintenance required depends on the type of hydroponic system chosen. Some systems, like the Wick method or Kratky method, have minimal maintenance requirements. However, more complex systems like NFT or Aeroponics may require regular monitoring of nutrient levels, pH adjustments, and equipment maintenance. It is essential to choose a system that matches your availability and commitment to maintenance tasks.
4. Can hydroponics be used for large-scale commercial farming?
Yes, hydroponics can be used for large-scale commercial farming. Many commercial farms have successfully implemented hydroponic systems to produce a variety of crops efficiently. However, setting up and managing large-scale hydroponic operations requires thorough planning, significant investment, and specialized expertise. It is advisable to start with smaller-scale hydroponics and gain experience before scaling up to larger operations.
5. Are hydroponically grown crops organic?
Hydroponically grown crops can be organic if the appropriate organic practices and inputs are followed. Organic hydroponics focuses on using organic nutrients, pest control methods, and substrates that comply with organic certification standards. It is important to source organic-certified inputs and follow organic practices to ensure the organic integrity of hydroponically grown crops.
6. Can hydroponics be used in home gardens?
Absolutely! Hydroponics can be an excellent option for home gardens. With compact and scalable systems available, hydroponics allows individuals to grow fresh produce in limited spaces, such as balconies or small yards. Home hydroponics kits are available that simplify the setup process and make it accessible for gardening enthusiasts. It provides the opportunity to grow a variety of herbs, greens, and even small fruiting plants for personal consumption.
7. Do hydroponic plants require pollination?
Some hydroponic plants, particularly fruiting plants like tomatoes and cucumbers, require pollination for fruit set. In natural environments, pollination is typically achieved through wind or insect activity. In hydroponics, manual pollination is often necessary. This can be done by gently shaking the plants or using a small brush to transfer pollen between flowers. Alternatively, some hydroponic growers introduce bumblebees or use specialized techniques to aid in pollination.
8. What lighting is best for hydroponic systems?
In hydroponic systems, artificial lighting is commonly used to provide the necessary light energy for plant growth. LED (Light Emitting Diode) lights are a popular choice for hydroponics due to their energy efficiency and customizable spectrum options. Full-spectrum LED lights that mimic natural sunlight are ideal for supporting all stages of plant growth. The intensity and duration of lighting can vary depending on the specific plants and their light requirements.









This Post Has 3 Comments
I would like to know more about hydroponic farming Iin depth and would like to discuss. This was really insightful information
To gain more knowledge about Hydroponics you can checkout our blog page, where u can find more topics about hydroponic farming. And
i think you need to start from “The history of hydroponics” this article.
Thanks for connecting us. Have a good day.
Very ѕhortly this web page will be famous among all blogging people, due to it’s pleasant articles
or reviews