Table of Contents
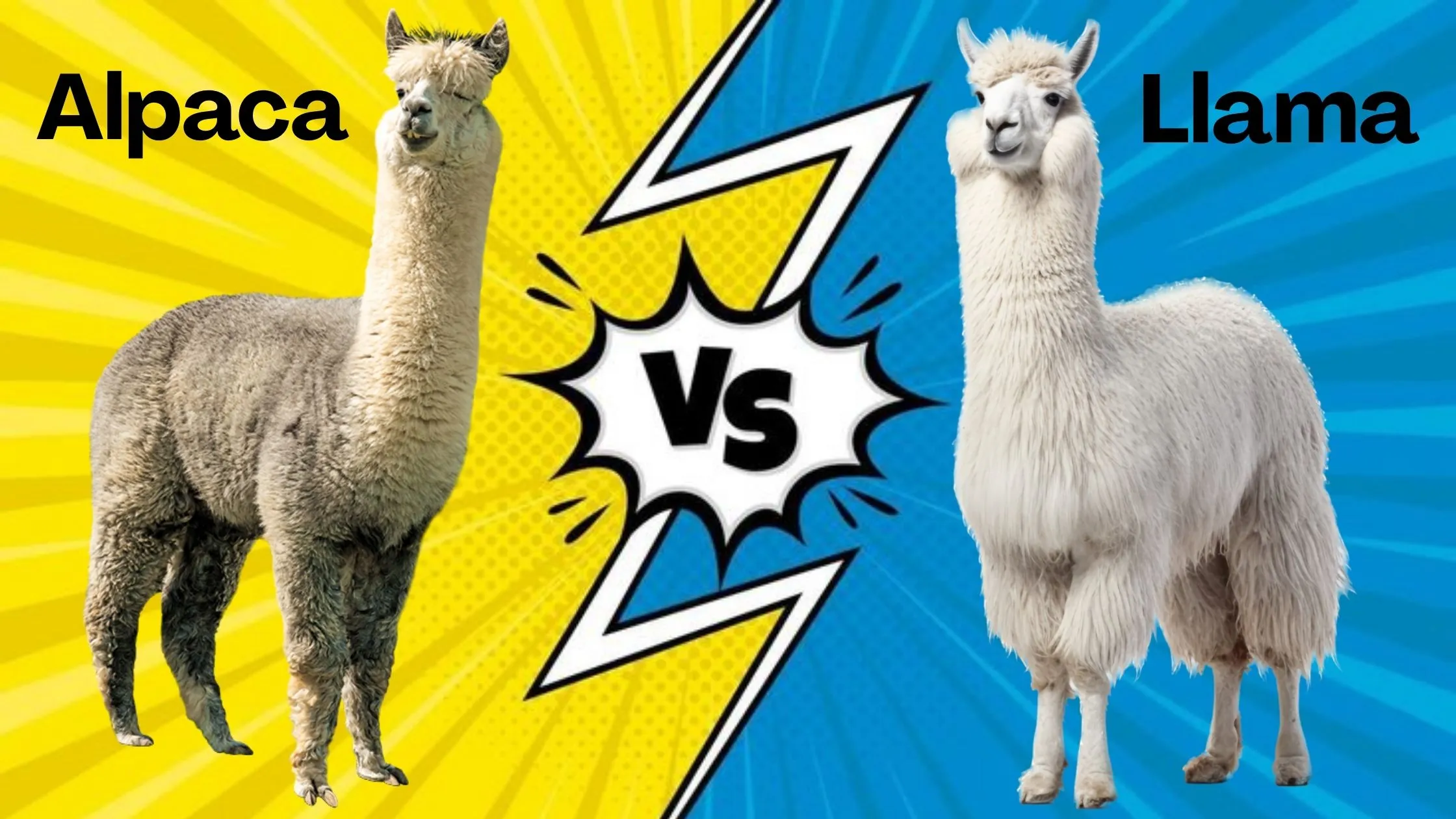
Alpacas and llamas are often mistaken for one another, but despite their similarities, they have distinct differences that set them apart. Both species belong to the camelid family and have been domesticated in South America for thousands of years. While alpacas are primarily raised for their luxurious fleece, llamas are known for their strength and ability to carry heavy loads.
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between alpacas and llamas, covering everything from their physical traits to their behavior and uses. If you’ve ever wondered which one is the best fit for your farm or fiber production needs, this guide will help you make an informed decision.
Background Information
Historical Context and Cultural Significance
Alpacas and llamas have been essential to Andean cultures for centuries. The Inca civilization valued them for transportation, fiber production, and religious ceremonies. Llamas were the preferred pack animals, carrying goods across mountainous terrain, while alpacas were prized for their soft and warm fleece.
Economic and Modern-Day Importance
Today, alpacas are farmed worldwide for their fleece, which is used in luxury textiles. Llamas, on the other hand, still serve as pack animals and livestock guardians. In the U.S., they are commonly seen on farms, fiber festivals, and even as therapy animals.
Taxonomy and Evolution
Both animals belong to the Camelidae family, which includes camels, guanacos, and vicuñas. Alpacas (Vicugna pacos) are descended from vicuñas, while llamas (Lama glama) originated from guanacos. Selective breeding has further emphasized their distinct traits over time.
Alpaca vs Llama: 10 Key Differences Between Alpacas and Llamas
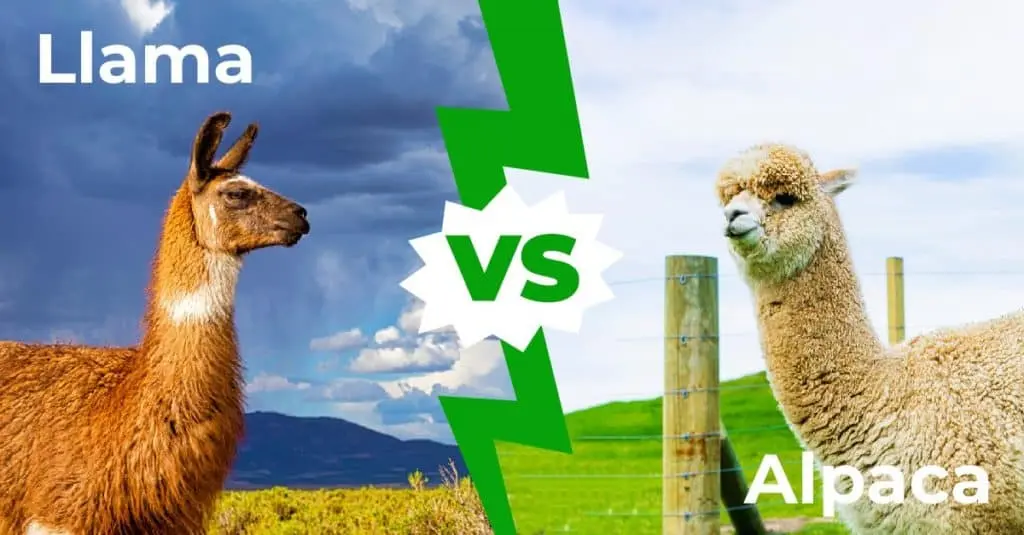

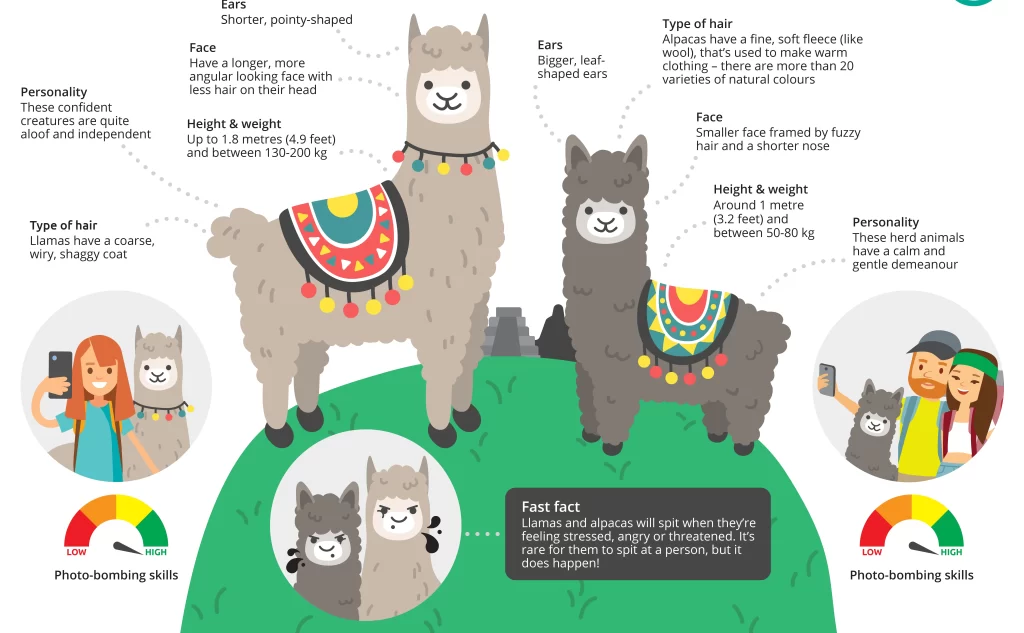
1. Size and Build Difference Between Alpacas And Llamas
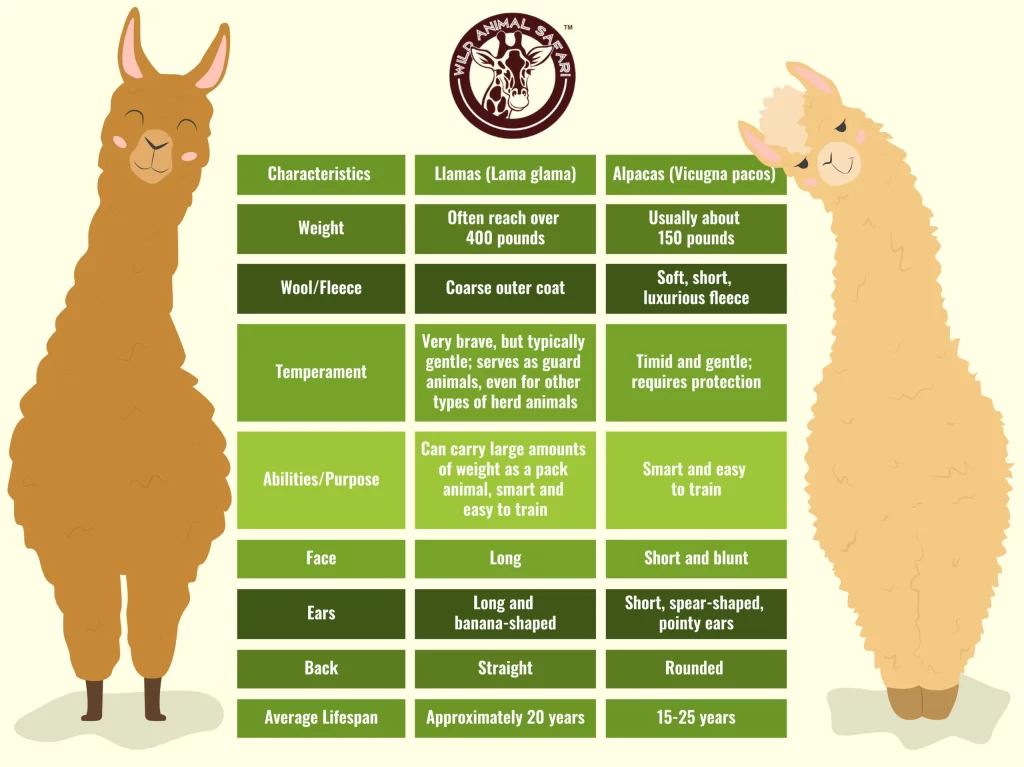
- Alpacas are smaller, standing around 3 feet at the shoulder and weighing between 100–175 pounds. Their compact and stocky build makes them efficient for fiber production, as they do not require extensive feed compared to larger animals.
- Llamas are much larger, reaching up to 4 feet at the shoulder and weighing 250–450 pounds. Their taller, more muscular frame is built for endurance, allowing them to carry heavy loads of up to 25–30% of their body weight. This size difference is one of the most noticeable ways to distinguish between the two species.
2. Facial Features and Ears Between Alpacas And Llamas
- Alpacas have short, blunt faces with a soft, endearing expression. Their muzzles are covered in dense fleece, giving them a rounder and more teddy-bear-like appearance.
- Llamas have elongated faces with a more pronounced snout and a distinctively noble expression. Their most recognizable feature is their large, banana-shaped ears, which stand tall and curve slightly inward. These ears are a reliable way to tell the two species apart at a glance.
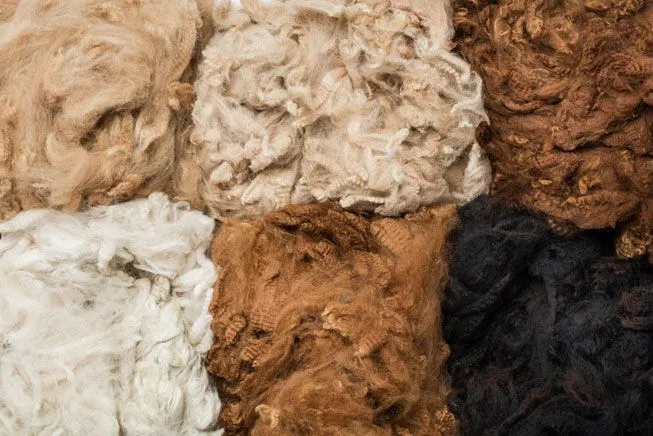
3. Wool and Fiber Quality
- Alpacas produce one of the finest and softest natural fibers in the world. Their fleece is hypoallergenic, moisture-resistant, and comes in over 22 natural colors. Alpaca fiber is used in high-end clothing and textiles due to its lightweight yet warm nature. There are two main types:
- Huacaya Alpaca: Fluffy, crimpy fleece with a soft, woolly appearance.
- Suri Alpaca: Silky, lustrous fleece that grows in long, wavy locks. Alpaca wool, or alpaca fiber or fleece, has been revered for thousands of years, even being called “The fiber of the Gods” by the Incan civilization.
- Llamas, in contrast, have a dual coat with a coarse outer layer and a finer undercoat. While their fiber is used in textiles, it is not as fine or soft as alpaca fleece, making it more suitable for rugs, ropes, and blankets rather than luxury garments.

4. Temperament and Behavior
- Alpacas are shy, docile, and herd-oriented animals. They tend to be more nervous around humans and prefer the safety of their group. While they can be socialized with regular interaction, they generally do not enjoy being handled as much as llamas.
- Llamas are more confident, independent, and sometimes even assertive. They are often used as livestock guardians because of their protective nature, especially against predators like coyotes. Llamas can also form strong bonds with humans and can be trained more easily for tasks like packing and leading.
5. Diet and Grazing Habits
Both alpacas and llamas are efficient grazers, consuming grasses, hay, and occasional grain supplements. However, there are notable differences in how they forage:
- Alpacas primarily graze on soft pasture grass and require a more controlled diet to maintain their fiber quality.
- Llamas are more adaptable and can browse on a wider variety of vegetation, including shrubs and coarse plants. Their ability to thrive on lower-quality forage makes them more resilient in harsher environments.
6. Native Habitat and Environmental Adaptability
- Alpacas originate from the high-altitude regions of the Andes, where their thick fleece protects them from cold temperatures. They are best suited to cooler climates and require shade and proper care in hot environments.
- Llamas are highly adaptable and can thrive in diverse environments, from mountains to lowland pastures. Their less dense coat makes them more tolerant of heat compared to alpacas.
7. Domestication and Usage
- Alpacas are bred primarily for their fiber and are commonly found in fiber farms. They are also popular in agritourism and petting zoos due to their charming appearance.
- Llamas have historically been used as pack animals in South America and are still employed in trekking expeditions. Additionally, they serve as effective livestock guardians, warding off potential predators.
8. Reproductive and Breeding Characteristics
- Both species have a similar gestation period of about 11.5 months, but llamas typically give birth to larger crias (baby llamas) compared to alpacas.
- Alpacas and llamas do not have a heat cycle and instead are induced ovulators, meaning that mating stimulates ovulation.
9. Llama Lifespan vs Alpaca Lifespan and Health Considerations
- Alpacas typically live 15–20 years with proper care, while llamas can live 20–25 years.
- Both require routine veterinary checkups, vaccinations, deworming, and hoof trimming. Shearing is essential for alpacas, while llamas can sometimes go longer without shearing due to their coarser coat.
10. Vocalization and Communication Styles
- Alpacas hum softly and use ear and tail movements to communicate within their herd. Their vocalizations are usually subtle and indicate contentment or mild distress.
- Llamas have a broader range of vocalizations, including humming, snorting, and alarm calls when they sense danger. They are more expressive and can even communicate displeasure through spitting.
Additional Comparisons and Fun Facts
- Llamas can spit! While alpacas occasionally spit, llamas are known for their accurate aim when annoyed.
- Alpacas and llamas can crossbreed, resulting in a hybrid known as a Huarizo, which has an intermediate size and fiber quality.
- Both animals can be trained to walk on a lead, making them great for parades and petting zoos.
10 Things Alpacas and Llamas Have in Common
- Both are domesticated members of the camelid family.
- Both originate from South America and have been essential to Andean cultures for thousands of years.
- They have padded feet, which make them gentle on pastures and prevent soil erosion.
- Both have a communal dung pile, helping maintain a clean living environment.
- They communicate using body language and vocalizations, such as humming.
- Both are social herd animals and thrive in groups.
- They have a similar gestation period of approximately 11.5 months.
- Neither species has upper front teeth; instead, they have a hard dental pad.
- They are both excellent guard animals for livestock, deterring predators.
- Both require regular shearing and routine health care to maintain their well-being.
That’s It!
Alpacas and llamas may look similar at first glance, but they serve different roles in agriculture, fiber production, and companionship. Alpacas, with their soft and luxurious fleece, are perfect for fiber enthusiasts and textile industries. Llamas, being larger and stronger, excel as pack animals and livestock guardians. Understanding these differences helps farmers, breeders, and pet owners make informed decisions based on their needs. Whether you prefer the cuddly charm of an alpaca or the bold presence of a llama, both species have unique qualities that make them valuable and fascinating animals.