Table of Contents
Hydroponic farming is an innovative method of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water solutions. This soil-less cultivation system offers numerous advantages over traditional soil-based farming, such as optimized resource utilization, higher crop yields, and controlled environmental conditions. By eliminating the dependence on soil, it allows for precise control of essential factors like nutrient levels, pH, and water availability, resulting in healthier plants and faster growth rates.
While hydroponic farming offers significant benefits, it is not immune to pest infestations. Pests can damage crops, reduce yields, and compromise the overall health of the system. Therefore, effective pest management is crucial for ensuring the success and sustainability of hydroponic operations.
Integrated Pest Management is a holistic approach to pest management that focuses on sustainable strategies to minimize pest damage while minimizing the use of chemical pesticides. IPM combines various techniques, such as cultural, biological, and chemical controls, to create an integrated and balanced pest management plan. The significance of Pest Management lies in its ability to maintain crop health, reduce environmental impact, and ensure long-term productivity.
The Importance of Integrated Pest Management in Hydroponics
Overview of the challenges of managing pests in hydroponic systems
Hydroponic systems present unique challenges for pest management. The absence of soil as a physical barrier makes plants more susceptible to pests. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponic farming, including temperature and humidity, can create ideal conditions for pest reproduction. These factors necessitate a proactive and strategic approach to pest control.

Benefits of implementing IPM in hydroponics
Implementing Pest Management practices in hydroponic farming offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides, which can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. Secondly, Pest Management improves overall crop health and productivity by focusing on preventative measures and maintaining a balanced ecosystem. Finally, IPM promotes sustainability by minimizing the impact on natural resources and biodiversity.
Understanding Integrated Pest Management
Definition and Core Principles of Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management is an approach that integrates multiple pest control strategies to manage pests effectively and sustainably. The core principles of Pest Management include:
- Pest identification and monitoring
- Setting action thresholds for pest control intervention
- Implementing a combination of preventive measures
- Utilizing biological controls and beneficial organisms
- Applying chemical controls judiciously and as a last resort
- Regularly evaluating and adjusting the Pest Management plan based on effectiveness and changing conditions.

Contrasting IPM with conventional pest management methods
Unlike conventional pest management methods that rely heavily on chemical pesticides, Pest Management emphasizes a more holistic and ecologically friendly approach. It aims to address the root causes of pest problems, such as imbalances in nutrient levels or environmental conditions, rather than simply treating the symptoms. By focusing on long-term solutions and reducing pesticide use,Pest Management promotes sustainable farming practices.
Identifying and Monitoring Pests in Hydroponics
Common pests in hydroponic systems
In hydroponic systems, several pests can pose significant challenges. Some common pests include aphids, thrips, whiteflies, spider mites, fungus gnats, and root-feeding nematodes. It is crucial to identify these pests accurately to implement appropriate control measures effectively.
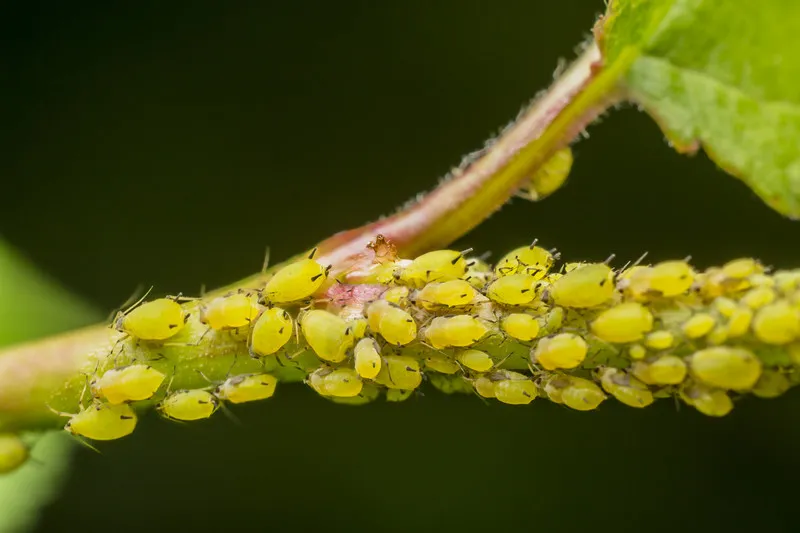
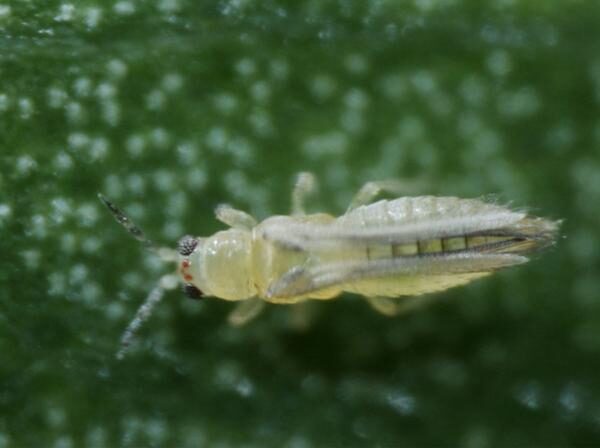
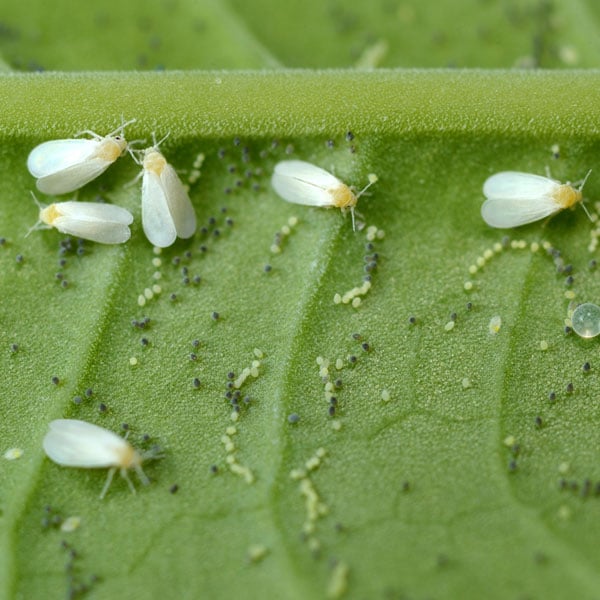
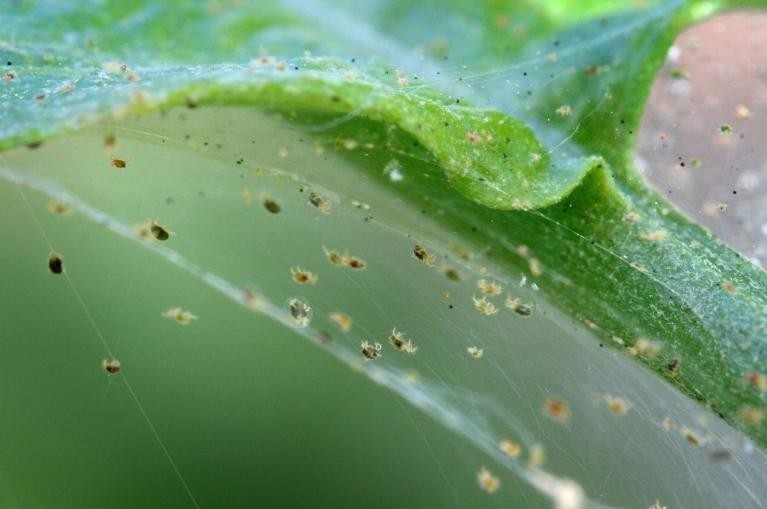
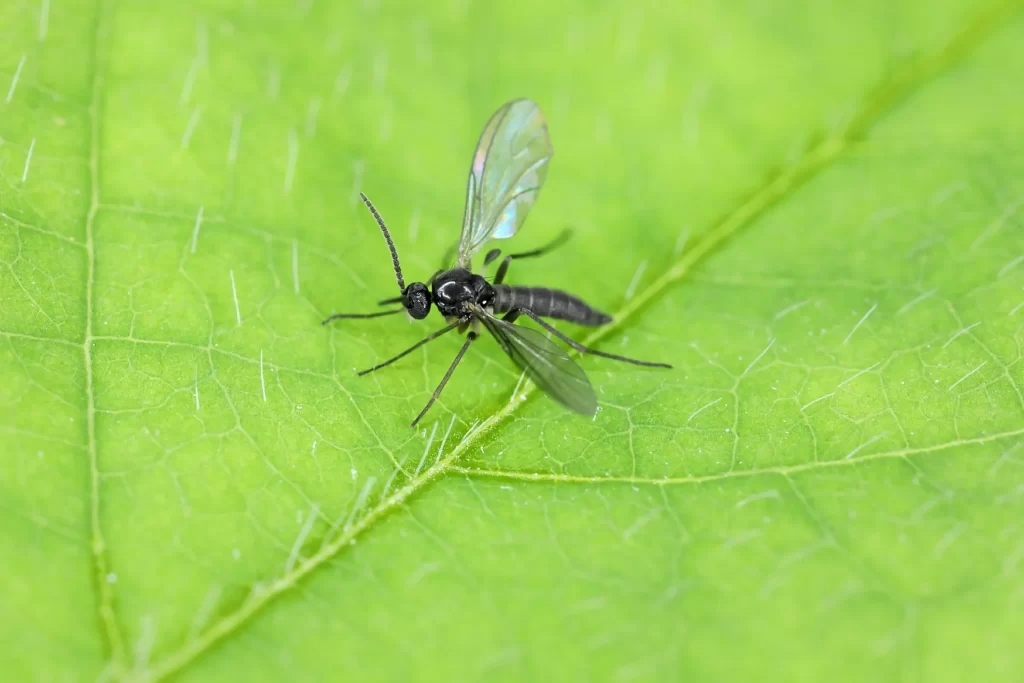
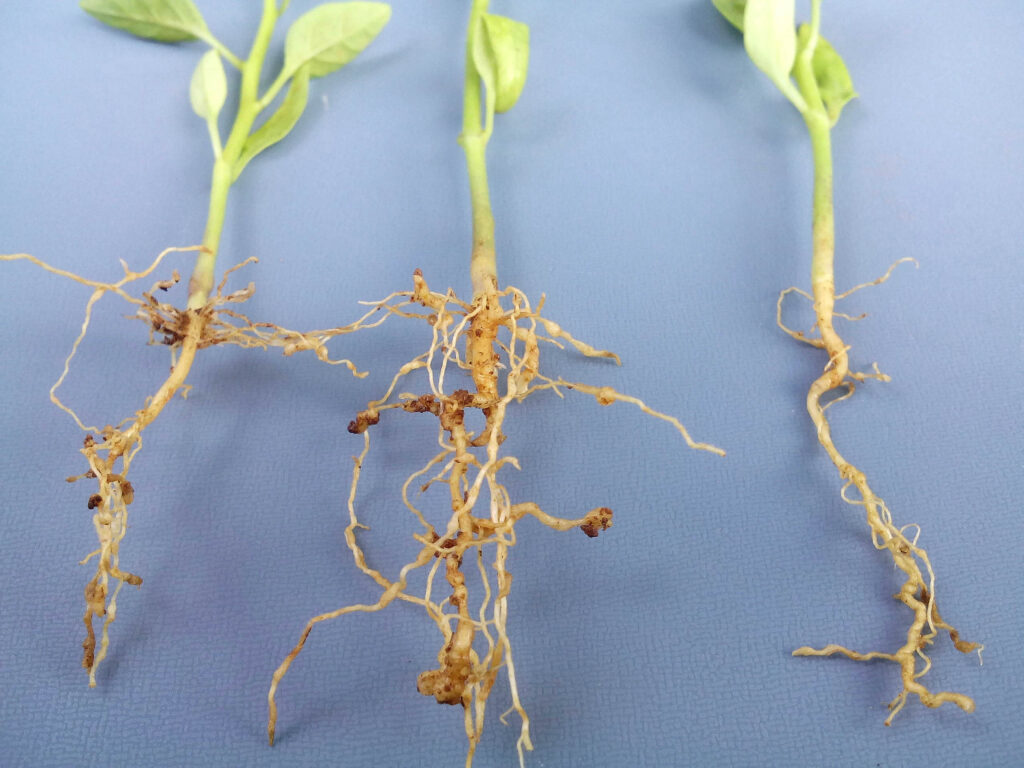






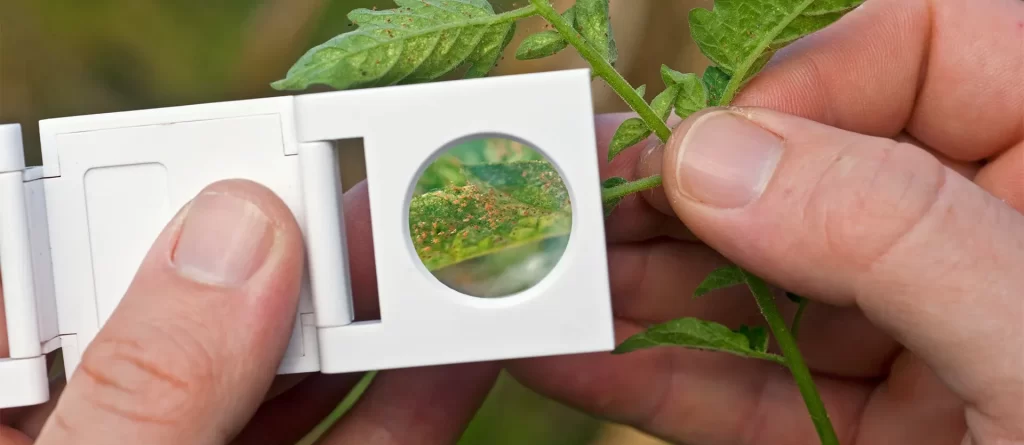
Techniques for early pest detection and monitoring in hydroponic systems
Early detection and monitoring are essential for effective pest management in hydroponics. Techniques such as sticky traps, visual inspections, and scouting can help identify pests at the early stages of infestation. Regular monitoring allows for timely intervention, preventing pest populations from reaching damaging levels.
Prevention Strategies in Hydroponic Pest Management
Implementing proper sanitation practices to minimize pest introduction and spread
Maintaining proper sanitation practices is key to preventing pest infestations. This includes cleaning and disinfecting equipment, removing plant debris, and practising strict hygiene protocols. By reducing potential pest habitats and preventing the spread of pests, growers can minimize the risk of infestation.
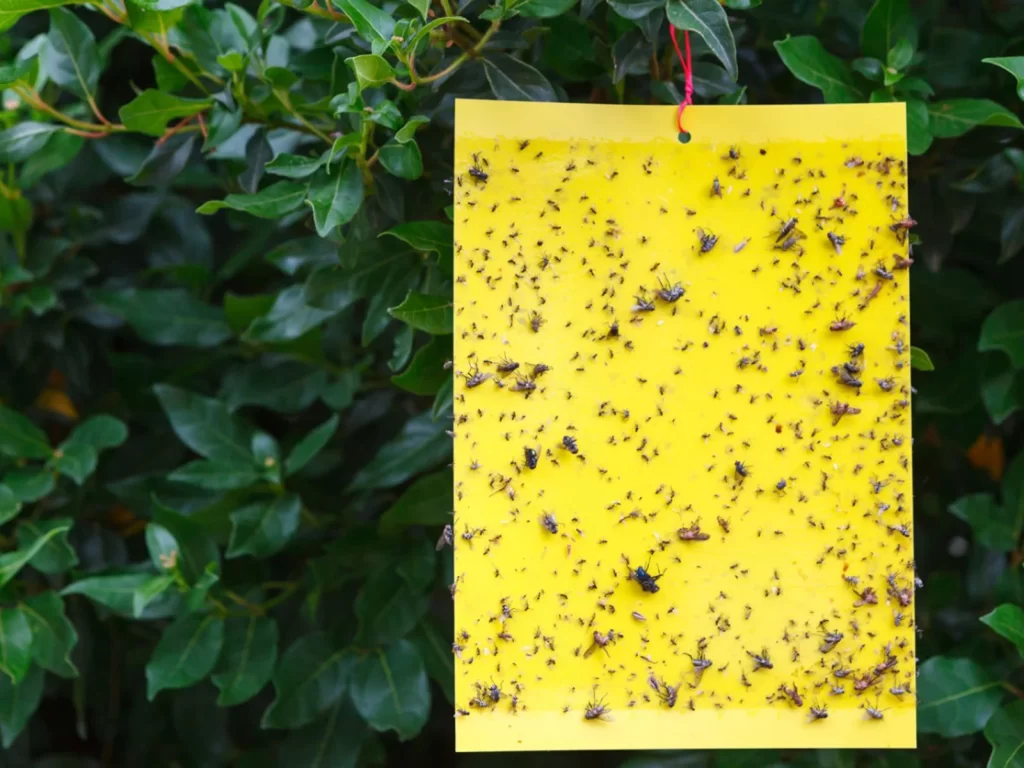

Maintaining a clean and well-ventilated environment
A clean and well-ventilated environment is crucial for preventing pest problems. Good air circulation helps to deter pests and promotes healthier plant growth. Additionally, regularly cleaning and sanitizing the growing area reduces the chances of pests finding suitable breeding grounds.
Utilizing physical barriers and exclusion techniques to prevent pest entry into hydroponic systems
Physical barriers, such as insect screens or nets, can be used to exclude pests from entering the hydroponic system. By preventing pest entry, growers can significantly reduce the risk of infestation and the need for pesticide intervention. Care should be taken to ensure the barriers do not impede air circulation or interfere with plant access to light.
Implementing crop rotation and companion planting strategies in hydroponics
Crop rotation and companion planting strategies are effective in preventing pest build-up in hydroponics. Rotating crops or interspersing susceptible plants with pest-repellent companion plants helps disrupt pest life cycles and reduces pest pressure. This practice also enhances biodiversity, making the system less favourable for pests to establish themselves.
Proper plant nutrition and watering practices to promote plant health and resilience
Maintaining optimal plant nutrition and watering practices is crucial for promoting plant health and resilience against pests. Providing plants with the appropriate balance of nutrients and ensuring adequate hydration helps strengthen their natural defence mechanisms. Healthy plants are less susceptible to pest damage and can better tolerate minor pest infestations.
Biological Controls in Hydroponic Pest Management
Introduction to beneficial insects and mites for pest control in hydroponics
Beneficial insects and mites play a vital role in pest control within hydroponic systems. These natural enemies prey on pests, providing an environmentally friendly and sustainable method of managing infestations. Ladybugs, lacewings, predatory mites, and parasitic wasps are among the most commonly used beneficial organisms.
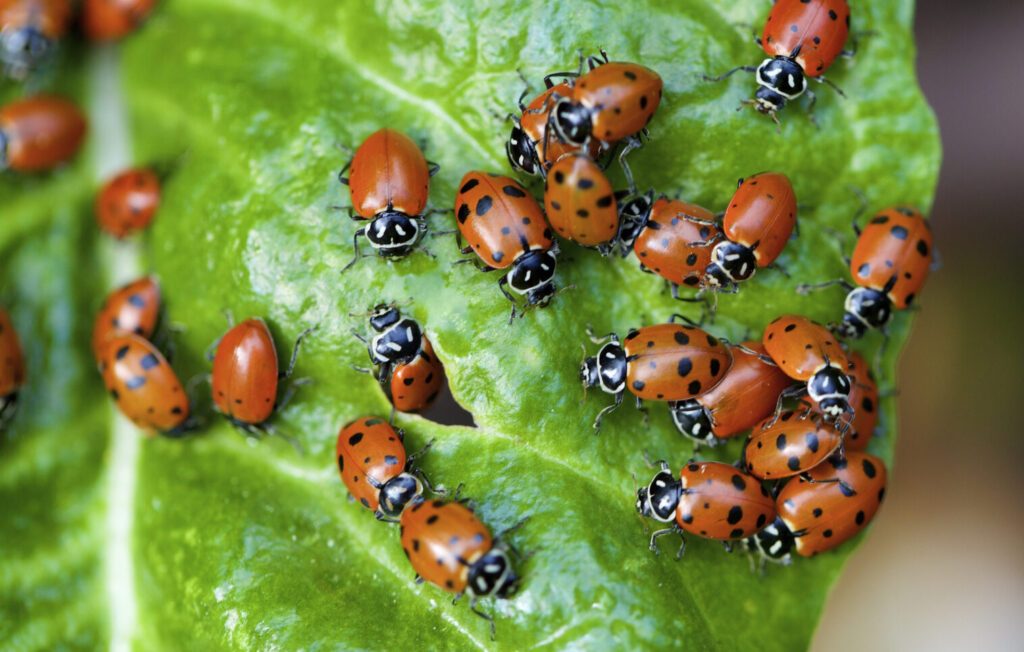
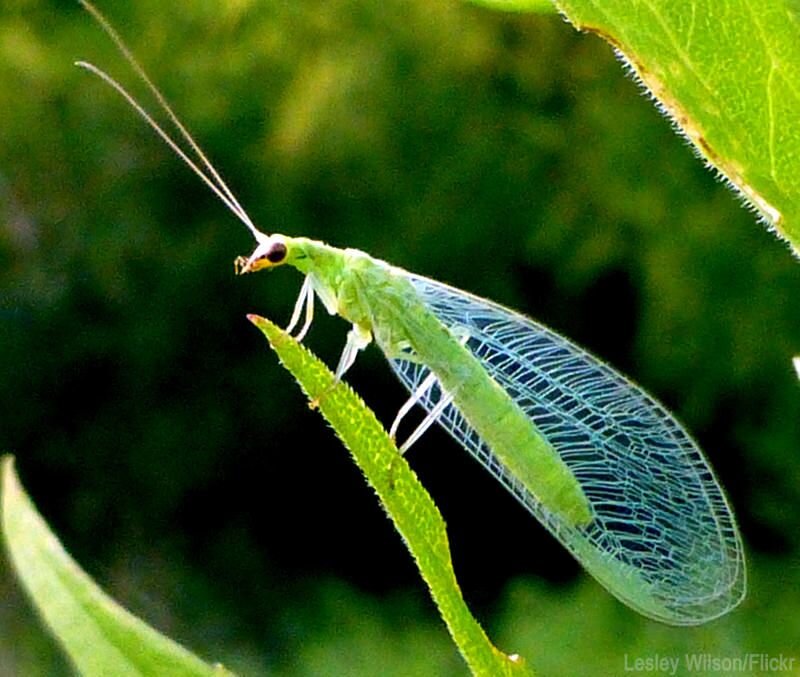
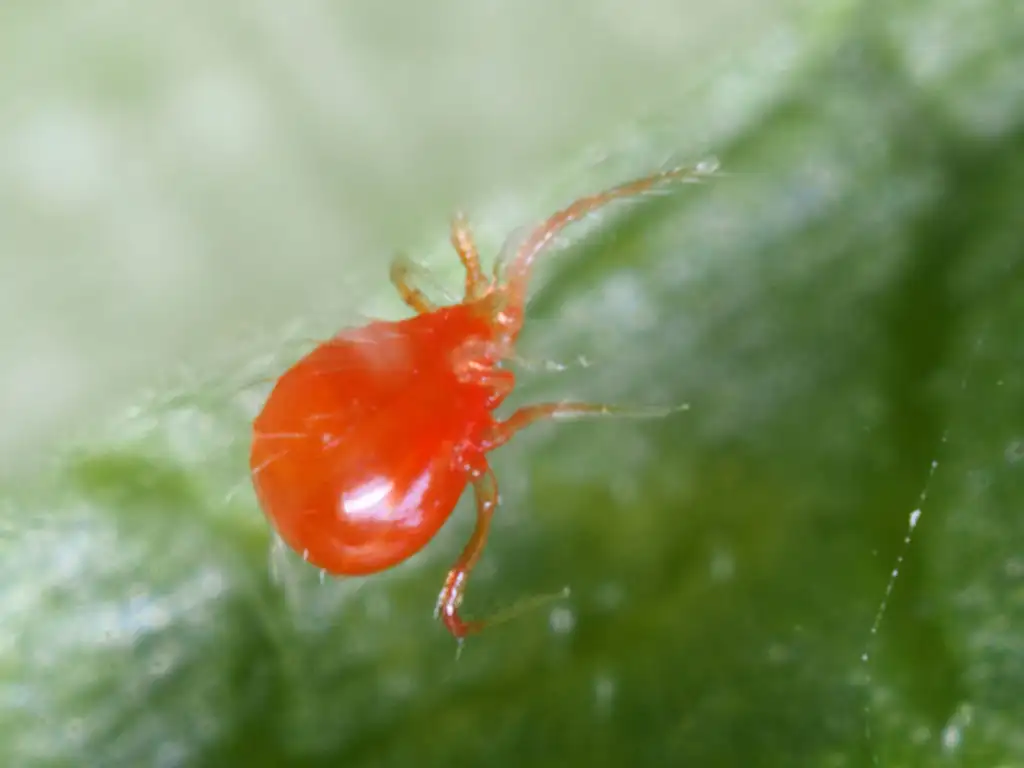



Popular beneficial insects and mites used in hydroponics
Several beneficial insects and mites have proven effective in hydroponic pest control. Ladybugs, for example, are voracious aphid predators. Lacewings feed on aphids, thrips, and whiteflies. Predatory mites target spider mites and other small pests. These beneficial organisms can be introduced into the hydroponic system as a preventive or curative measure to combat pests.
Introduction to nematodes for pest control
Nematodes are microscopic roundworms used for pest control, particularly against root-feeding nematodes and fungus gnats in hydroponic farming. These beneficial nematodes seek out and infect pests, reducing their populations. Applying nematodes to the growing media can effectively control pest infestations and prevent further damage.
Incorporating microbial and fungal controls to suppress pests in hydroponic systems
Microbial and fungal controls offer additional options for pest suppression. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a naturally occurring bacterium that targets specific pests like caterpillars. Entomopathogenic fungi, such as Beauveria bassiana, can infect and kill various insect pests. These biological controls provide targeted and environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical pesticides.
Chemical Controls in Hydroponic IPM
Understanding the judicious use of pesticides in Hydroponics IPM
While chemical pesticides should be used judiciously in Pest Management, they can still play a role in managing severe pest infestations in hydroponic farming. However, it is crucial to consider their potential impacts on human health, beneficial organisms, and the environment. The focus should be on using the least toxic and most targeted pesticides, applying them only when necessary and following label instructions strictly.
Selecting appropriate pesticides for specific pests in hydroponic systems
Selecting the right pesticides for specific pests is essential. Systemic pesticides that can be absorbed by the plants and translocated to pests are often preferred, as they can effectively control pests hiding in concealed areas. Growers should choose pesticides labelled for use in hydroponic farming, targeting the specific pests they need to control, and minimizing non-target effects.
Best practices for pesticide application, safety, and minimizing environmental impact in hydroponics
To minimize the environmental impact of pesticide use in hydroponic farming, several best practices should be followed. These include calibrating and applying pesticides accurately, using appropriate protective equipment, adhering to recommended dosage rates and application timings, and avoiding pesticide drift or runoff. Additionally, proper storage and disposal of pesticides are crucial for maintaining safety and preventing contamination.
Integrated use of pesticides with other Pest Management techniques
Pesticides should be integrated with other Pest Management techniques to maximize their effectiveness and minimize their reliance. By combining chemical controls with preventive measures, biological controls, and cultural practices, growers can achieve synergistic effects, reduce pesticide usage, and maintain a balanced and sustainable pest management approach.
Developing an IPM Plan for Hydroponics
Assessing the pest situation and risks in hydroponic systems
Developing an effective Pest Management plan begins with a thorough assessment of the pest situation and associated risks in the hydroponic system. This includes identifying potential pest threats, understanding their life cycles and vulnerabilities, and evaluating the susceptibility of the crops. Conducting regular pest monitoring and documenting observations helps in making informed decisions.

Establishing action thresholds and monitoring schedules for pest control
Action thresholds, the pest population levels at which intervention is necessary, should be established based on economic or aesthetic considerations. By defining action thresholds, growers can avoid unnecessary treatments while ensuring pest populations do not cause significant damage. Regular monitoring schedules should also be established to detect pests early and intervene promptly.
Choosing appropriate Pest Management strategies for your crops
Based on the pest assessment, growers can select and implement the most appropriate Pest Management strategies for their specific crops and pest challenges. This may include combinations of cultural practices, biological controls, and targeted pesticide applications. The chosen strategies should be compatible with the hydroponic system, crop requirements, and environmental considerations.
Documenting and evaluating the effectiveness of the IPM plan
Documenting the Pest Management plan, including the chosen strategies, application schedules, and outcomes, is crucial for continuous improvement. By evaluating the effectiveness of the Pest Management plan, growers can identify areas for optimization, refine their strategies, and adapt to changing pest dynamics. Regular review and adjustment ensure a dynamic and effective pest management approach.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing IPM
Addressing pesticide resistance and tolerance in hydroponic systems
Pesticide resistance and tolerance can pose challenges in hydroponic systems, as pests can develop resistance to commonly used pesticides. To address this issue, growers should employ a rotation of different pesticide groups, utilize targeted pesticides with different modes of action, and regularly monitor for signs of resistance. Integrated approaches that combine various control methods are also effective in managing resistant pests.
Dealing with pest outbreaks and unforeseen complications in hydroponic farming
Pest outbreaks and unforeseen complications are inevitable in hydroponics, but having a well-planned Pest Management strategy can mitigate their impact. Rapid response and intervention, along with a combination of cultural practices, biological controls, and targeted pesticide applications, can help bring pest populations under control and restore system health.
Acquiring the necessary knowledge, skills, and resources for effective IPM in hydroponic operations
Implementing effective Pest Management in hydroponics requires growers to acquire the necessary knowledge, skills, and resources. Continuous learning through workshops, seminars, and educational resources helps growers stay updated on the latest IPM practices and technologies. Collaborating with experts, sharing experiences with other growers, and investing in appropriate tools and equipment are essential for successful implementation.
Future of IPM in Hydroponics
Emerging Technologies and Innovations in Pest Management
The future of Pest Management in hydroponics holds exciting possibilities with emerging technologies and innovations. Advanced monitoring systems, such as automated pest detection and remote sensing, can enhance pest surveillance and early warning capabilities. Precision application techniques, including drone-based or robotic pesticide delivery, can improve the efficiency and accuracy of treatments. Integrated data analytics and machine learning algorithms can optimize pest management strategies based on real-time environmental and pest data.
Importance of research and development in improving Pest Management practices
Research and development play a critical role in improving Pest Management practices in hydroponic farming. Continued research efforts can lead to the discovery of new beneficial organisms, the development of targeted biopesticides, and the refinement of cultural practices. Collaboration between researchers, growers, and industry stakeholders fosters innovation and enables the adaptation of IPM strategies to evolving pest pressures and sustainable farming practices.
Potential for integration with automation and artificial intelligence
The potential for integrating IPM with automation and artificial intelligence is promising in hydroponic farming. Smart systems equipped with sensors, actuators, and AI algorithms can monitor pest populations, adjust environmental parameters, and automate the delivery of biological controls or targeted pesticides. This integration enhances precision, reduces labour, and optimizes resource utilization, ultimately improving the efficacy and sustainability of pest management in hydroponic operations.
Conclusion
Implementing Integrated Pest Management in hydroponic farming offers numerous benefits. It overcomes the limitations of traditional soil-based farming, improves crop health and productivity, reduces chemical pesticide use, and promotes environmental sustainability. By adopting a holistic and integrated approach to pest management, hydroponic growers can ensure long-term success and optimize their operations.
For hydroponic growers, embracing Pest Management practices is essential for sustainable and efficient production. By implementing preventive strategies, integrating biological controls, utilizing targeted pesticides judiciously, and continuously monitoring and evaluating their IPM plans, growers can effectively manage pests while minimizing environmental impact. The adoption of IPM practices promotes resilience, profitability, and responsible stewardship of resources.
As hydroponics continues to gain popularity, the future of Pest Management holds immense potential. By leveraging emerging technologies, investing in research and development, and integrating automation and artificial intelligence, IPM in hydroponics can become even more effective and sustainable. It is through ongoing collaboration, innovation, and knowledge sharing that the hydroponic industry can shape the future of pest management and pave the way for a resilient and productive agricultural system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can IPM be applied to all types of hydroponic systems?
Yes, IPM principles can be applied to various hydroponic systems, including nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), aeroponics, and others. The specific strategies and techniques may vary based on the system’s design and the crops grown, but the core principles of Pest Management remain applicable.
2. Are chemical pesticides completely eliminated in IPM for hydroponics?
While the goal of Pest Management is to minimize reliance on chemical pesticides, they may still be used when necessary. However, the emphasis is on using the least toxic and most targeted pesticides in a judicious manner. IPM integrates chemical controls with other strategies, such as cultural practices and biological controls, to create a comprehensive and sustainable approach to pest management.
3. Where can I find additional resources on Pest Management for hydroponics?
Additional resources on Pest Management for hydroponics can be found through agricultural extension services, research institutions, and online platforms dedicated to hydroponic farming. These resources may include publications, guides, webinars, and forums where growers can access valuable information, share experiences, and seek advice from experts in the field.
4. Can Pest Management practices be integrated with automation and artificial intelligence in hydroponic farming?
Yes, the integration of Pest Management practices with automation and artificial intelligence holds great potential in hydroponics. Automated pest detection systems, AI algorithms for decision-making, and robotic application of controls can enhance the efficiency, precision, and responsiveness of Pest Management in hydroponic operations. This integration can optimize resource utilization, improve data-driven decision-making, and further reduce human labour requirements.
5. Is IPM suitable for small-scale hydroponic operations?
Absolutely! IPM principles can be applied to hydroponic systems of any scale, including small-scale operations. In fact, Pest Management can be particularly beneficial for small-scale growers, as it promotes sustainable and efficient pest management practices, minimizes costs, and optimizes resource utilization. By implementing Pest Management, small-scale hydroponic operations can achieve improved crop health, increased productivity, and environmental sustainability.
6. Are there any specific pest control methods suitable for organic hydroponic farming?
Yes, organic hydroponic systems can utilize specific pest control methods in line with organic farming principles. These methods include the use of organic-approved pesticides derived from natural sources, such as botanical extracts or microbial agents. Additionally, cultural practices like crop rotation, companion planting, and maintaining a balanced nutrient solution can promote plant health and resilience in organic hydroponic farming.
7. How can I prevent pest introduction in my hydroponic system?
Preventing pest introduction is crucial in maintaining a healthy hydroponic system. To prevent pests, implement proper sanitation practices, including cleaning and disinfecting equipment, using sterile growing media, and practising good hygiene. Additionally, establish a controlled environment by maintaining a clean and well-ventilated growing area, and utilize physical barriers, such as screens or netting, to prevent pest entry into the system.
8. What are some common pests that affect hydroponic systems?
Several pests can affect hydroponic systems. Common examples include aphids, whiteflies, thrips, spider mites, fungus gnats, and root diseases caused by pathogens like Pythium and Fusarium. Regular monitoring and early detection are essential to identify these pests and initiate appropriate control measures.
9. How can beneficial insects be used for pest control in hydroponic systems?
Beneficial insects can be employed as part of biological control strategies in hydroponic systems. Predatory insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites feed on pest insects, helping to control their populations. By introducing these beneficial insects into the hydroponic system, growers can establish a natural balance and reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides.
10. What should I do if I experience a pest outbreak despite implementing IPM practices?
Despite implementing IPM practices, pest outbreaks can still occur. If you experience a pest outbreak, it is important to act promptly. Identify the specific pest causing the outbreak, assess the extent of the infestation, and adjust your Pest Management strategies accordingly. This may involve targeted pesticide applications, enhanced biological control measures, or adjustments to cultural practices. Seek guidance from experts or fellow growers if needed.
11. Is IPM only beneficial for pest control or does it offer other advantages as well?
IPM offers several advantages beyond pest control. By promoting a holistic and balanced approach to plant health, Pest Management enhances overall crop productivity, quality, and resilience. It reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, minimizing risks to human health and the environment. Furthermore, Pest Management encourages sustainable farming practices, conserves beneficial organisms, optimizes resource utilization, and aligns with the principles of environmental stewardship and ecological balance.










