Table of Contents
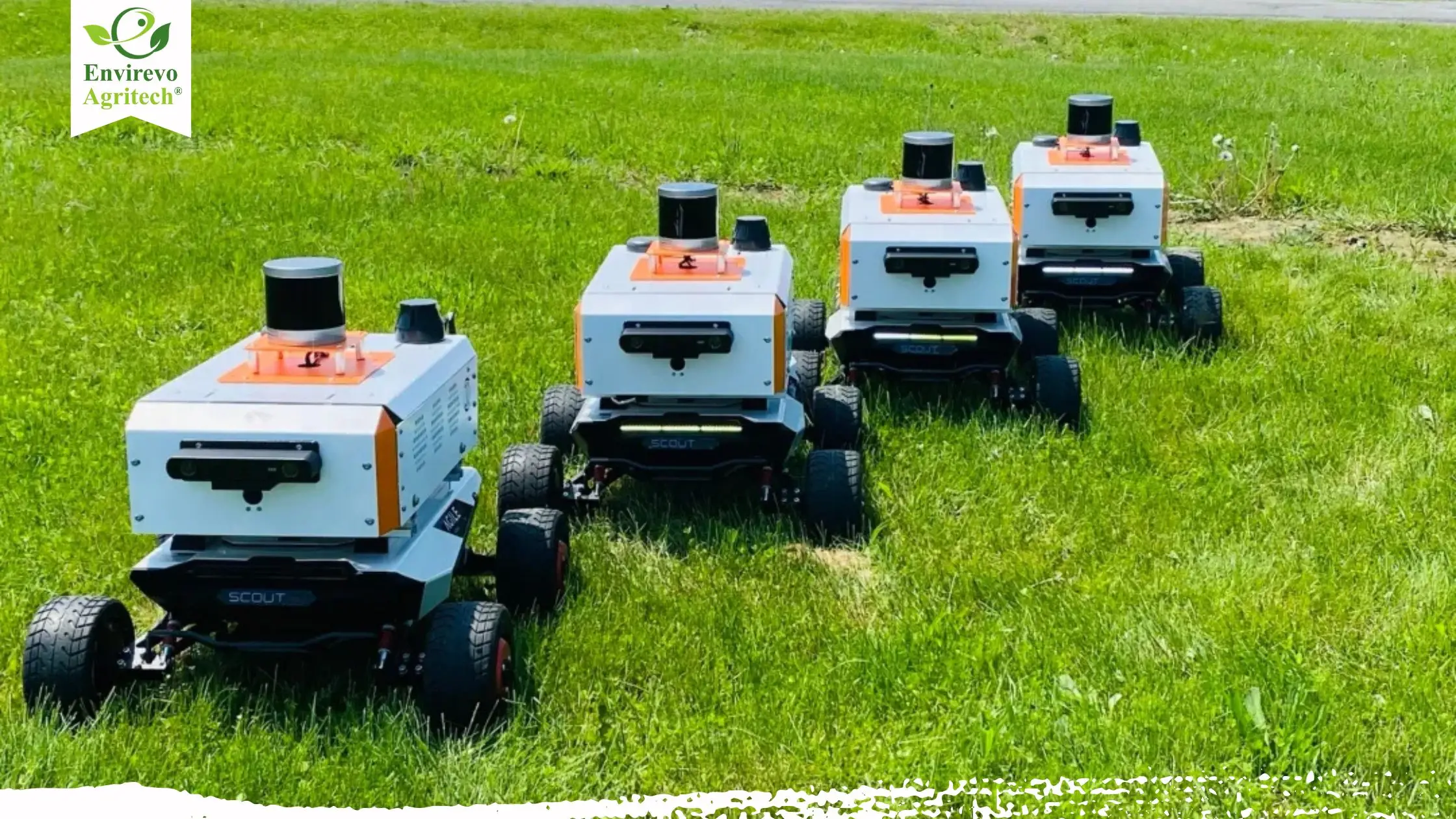
Imagine a fleet of autonomous robots working harmoniously across vast farmlands—planting seeds with precision, monitoring crop health in real-time, and harvesting produce efficiently, all without human intervention. This isn’t a scene from a science fiction movie; it’s the emerging reality of modern agriculture, powered by swarm robotics.
As the agricultural industry grapples with challenges like labor shortages, climate change, and the need for sustainable practices, swarm robotics in agriculture offers a transformative solution. By mimicking the collective behavior of social insects such as ants and bees, these intelligent machines operate collaboratively to perform complex tasks, enhancing productivity and resilience on the farm.
In this article, we’ll delve into how swarm robotics is revolutionizing farming practices, exploring its applications, benefits, and the promising future it holds for agriculture in the United States and beyond.
Understanding Swarm Robotics in Agriculture
What is Swarm Robotics?
Swarm robotics involves the coordination of numerous autonomous robots that operate based on local interactions and simple rules, without centralised control. This decentralised approach allows the swarm to adapt to dynamic environments, ensuring robustness and flexibility in operations.
Biological Inspiration
The concept draws inspiration from nature, where social insects exhibit collective intelligence through simple individual behaviours. In agriculture, this translates to a fleet of robots working collaboratively to perform tasks such as planting, monitoring, and harvesting, enhancing efficiency and resilience.

Core Applications of Swarm Robotics in Farming
1. Precision Planting and Seeding
Swarm robotics revolutionises the planting process by enabling precise seed placement. Each autonomous robot in the swarm can be programmed to plant seeds at optimal depths and intervals, ensuring uniform germination and growth. This level of precision reduces seed wastage and enhances crop yields.
Moreover, these robots can adapt to varying soil conditions in real-time, adjusting planting strategies accordingly. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in large-scale farming operations where soil composition can vary significantly across different field sections.
2. Targeted Fertilization and Pest Control
Traditional methods of fertilization and pest control often involve blanket applications, leading to resource wastage and environmental concerns. Swarm robotics addresses this by enabling targeted interventions. Equipped with advanced sensors and AI algorithms, these robots can detect specific areas requiring fertilization or pest control.
By applying treatments only where necessary, swarm robots minimise chemical usage, reduce costs, and mitigate environmental impact. This precision approach not only conserves resources but also promotes healthier crop growth by preventing over-application of chemicals.
3. Real-Time Crop Monitoring and Data Collection
Continuous monitoring is crucial for timely decision-making in agriculture. Swarm robots facilitate real-time crop monitoring by traversing fields and collecting data on various parameters such as soil moisture, nutrient levels, and plant health indicators.
The data collected is transmitted to centralised systems where it is analysed to provide actionable insights. This enables farmers to make informed decisions regarding irrigation schedules, fertilization, and pest control measures, thereby optimising crop management practices.
4. Automated Harvesting
Harvesting is a labour-intensive process that can benefit significantly from automation. Swarm robotics offers a solution by deploying multiple robots that work collaboratively to harvest crops efficiently. These robots can be programmed to identify ripe produce and pick them with precision, reducing damage and ensuring quality.
The use of swarm robots in harvesting not only addresses labor shortages but also allows for timely harvesting, which is critical for maintaining crop quality and market value.
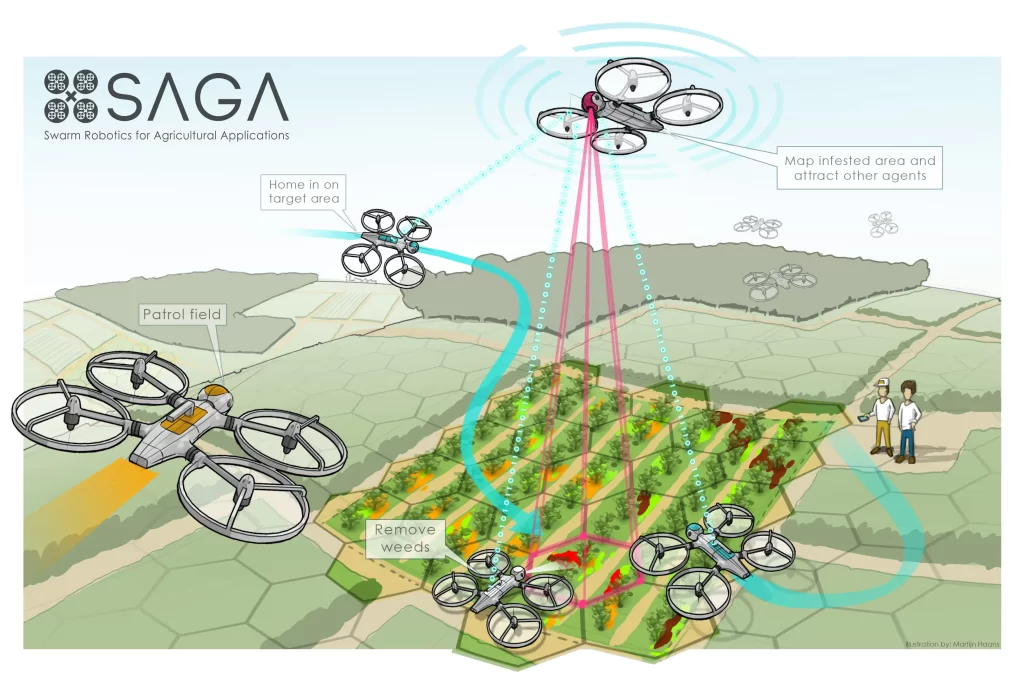
5. Weed Detection and Management
Weed management is a persistent challenge in agriculture. Swarm robots equipped with vision systems and AI can identify and target weeds with high accuracy. By distinguishing between crops and weeds, these robots can apply herbicides selectively or employ mechanical means to eliminate weeds.
This targeted approach reduces herbicide usage, lowers costs, and minimizes environmental impact. Additionally, it helps in preventing the development of herbicide-resistant weed species.
6. Soil Analysis and Health Monitoring
Understanding soil health is fundamental to successful farming. Swarm robots can conduct soil analysis by collecting samples and measuring parameters such as pH, moisture content, and nutrient levels.
The insights gained from soil analysis enable farmers to implement site-specific management practices, optimizing input usage and enhancing crop productivity. Regular soil monitoring also aids in early detection of issues, allowing for prompt remedial actions.
7. Irrigation Management
Efficient water usage is critical in agriculture, especially in regions facing water scarcity. Swarm robots contribute to irrigation management by monitoring soil moisture levels across different field zones.
Based on the data collected, these robots can control irrigation systems to deliver water precisely where and when needed. This precision irrigation conserves water, reduces costs, and ensures that crops receive adequate moisture for optimal growth.
8. Pollination Assistance
Pollination is essential for the reproduction of many crops. Swarm robots can assist in pollination, especially in scenarios where natural pollinators are scarce.
By mimicking the behaviour of pollinators, these robots can transfer pollen between flowers, ensuring successful fertilization. This application is particularly valuable in controlled environments like greenhouses, where natural pollination may be limited.
Advantages of Implementing Swarm Robotics in Agriculture
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Swarm robotics enables continuous, 24/7 operations, allowing tasks such as planting, monitoring, and harvesting to be performed with minimal human intervention. The decentralized nature of these systems ensures that if one robot encounters an issue, others can seamlessly continue the task, reducing downtime and increasing overall productivity.
- Precision Agriculture and Resource Optimization: By utilizing real-time data and advanced sensors, swarm robots can apply inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides precisely where needed. This targeted approach minimizes waste, reduces costs, and lessens environmental impact.
- Reduction in Soil Compaction: Traditional heavy machinery can lead to soil compaction, adversely affecting soil health and crop yields. Swarm robots, being smaller and lighter, exert less pressure on the soil, preserving its structure and promoting better root growth and water infiltration.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Swarm robotics systems are inherently scalable. Farmers can adjust the number of robots deployed based on the size of the field or the complexity of the task. Moreover, these robots can be reprogrammed or equipped with different tools to perform various functions, from seeding to weed control, offering unparalleled flexibility.
- Improved Crop Monitoring and Disease Management: Equipped with advanced imaging and sensing technologies, swarm robots can monitor crop health in real-time, detecting signs of disease, pest infestations, or nutrient deficiencies early.
- Cost-Effective Operations: While the initial investment in swarm robotics technology can be significant, the long-term operational savings are substantial. Reduced labor costs, optimized resource usage, and decreased crop losses contribute to a favorable return on investment over time.
- Enhanced Pollination and Livestock Management: Swarm robotics isn’t limited to crop management. Robotic swarms can assist in pollination, especially in areas facing a decline in natural pollinators. Additionally, they can monitor livestock health and behavior, ensuring timely interventions and improving animal welfare.
- Environmental Sustainability: By reducing the overuse of chemicals and minimizing soil disturbance, swarm robotics promotes environmentally friendly farming practices.
Challenges and Considerations
- Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs: The adoption of swarm robotics requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance, which may be a barrier for small-scale farmers.
- Technical Limitations: Challenges such as battery life, sensor accuracy, and reliable communication networks among robots need to be addressed to ensure seamless operations.
- Regulatory and Ethical Concerns: The deployment of autonomous machines raises questions about data privacy, job displacement, and the need for clear policies governing their use in agriculture.
The Future Landscape: Swarm Robotics in the USA
- Current Research and Development: In the USA, research institutions and tech companies are actively exploring swarm robotics applications in agriculture. For instance, Texas A&M University is investigating adaptive swarm robotics to enhance smart agriculture practices.
- Market Adoption Trends: Companies like SwarmFarm Robotics are expanding their technologies into North America, indicating a growing interest and investment in agricultural robotics.
- Potential Impact on Food Security: By increasing efficiency and sustainability, swarm robotics can play a crucial role in meeting the food demands of a growing population, contributing to enhanced food security.

Conclusion: Embracing the Next Generation of Farming
As agriculture faces mounting challenges—from labor shortages and climate change to the pressing need for sustainable practices—swarm robotics in agriculture emerges as a transformative solution. By harnessing the collective intelligence of autonomous machines, farmers can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, precision, and environmental stewardship.
Innovations like SwarmFarm Robotics’ autonomous platforms are already making significant strides, enabling site-specific crop management and reducing chemical usage . Similarly, adaptive swarm robotics research is paving the way for smarter, more responsive farming systems.
The integration of swarm robotics into farming practices not only addresses current agricultural challenges but also sets the stage for a more resilient and sustainable future. By embracing these technologies, the agricultural sector can ensure food security, protect natural resources, and foster innovation for generations to come.








